Our objective was to evaluate the cortical metabolic changes and clinical outcome in patients affected by idiopathic normal pressure hydrocephalus (iNPH) after a placement of ventriculoperitoneal (VP) shunt.
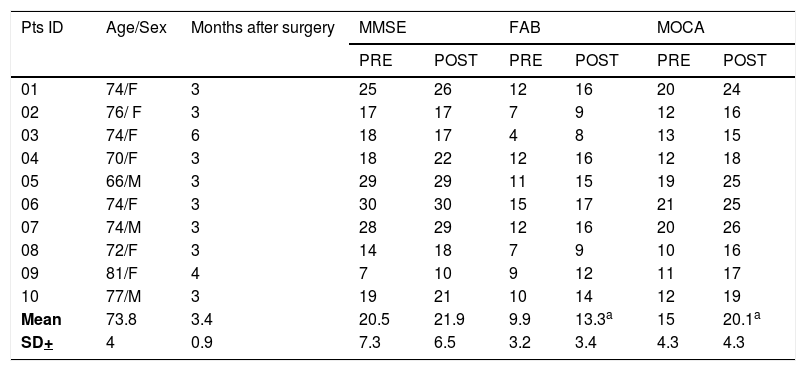
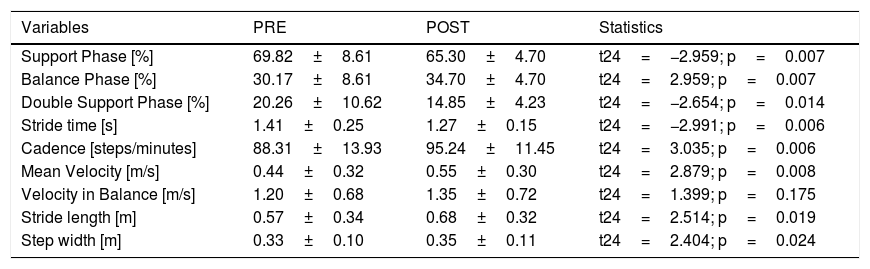
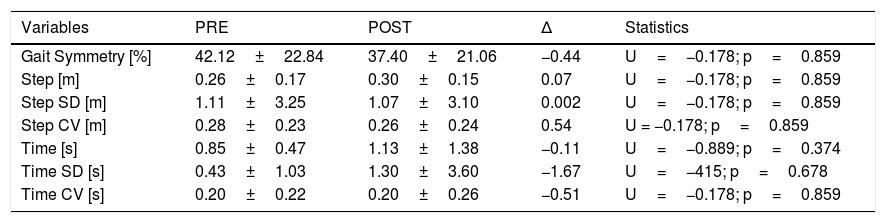
Materials and methods10 patients affected by suspected iNPH underwent a CSF hydrodynamics evaluation based on a lumbar infusion test (LIT). The main selection criterion for surgery was based on intracranial elasticity (IE)>0.30. All subjects with an IE>0.30 underwent a PET scan with18fluorodeoxoglucose (18F-FDG) at baseline (PET1) and 1 month after surgery (PET2). Furthermore, the same patients were submitted to clinical evaluation before and 1 month after surgery through neuropsychological tests and gait analysis.
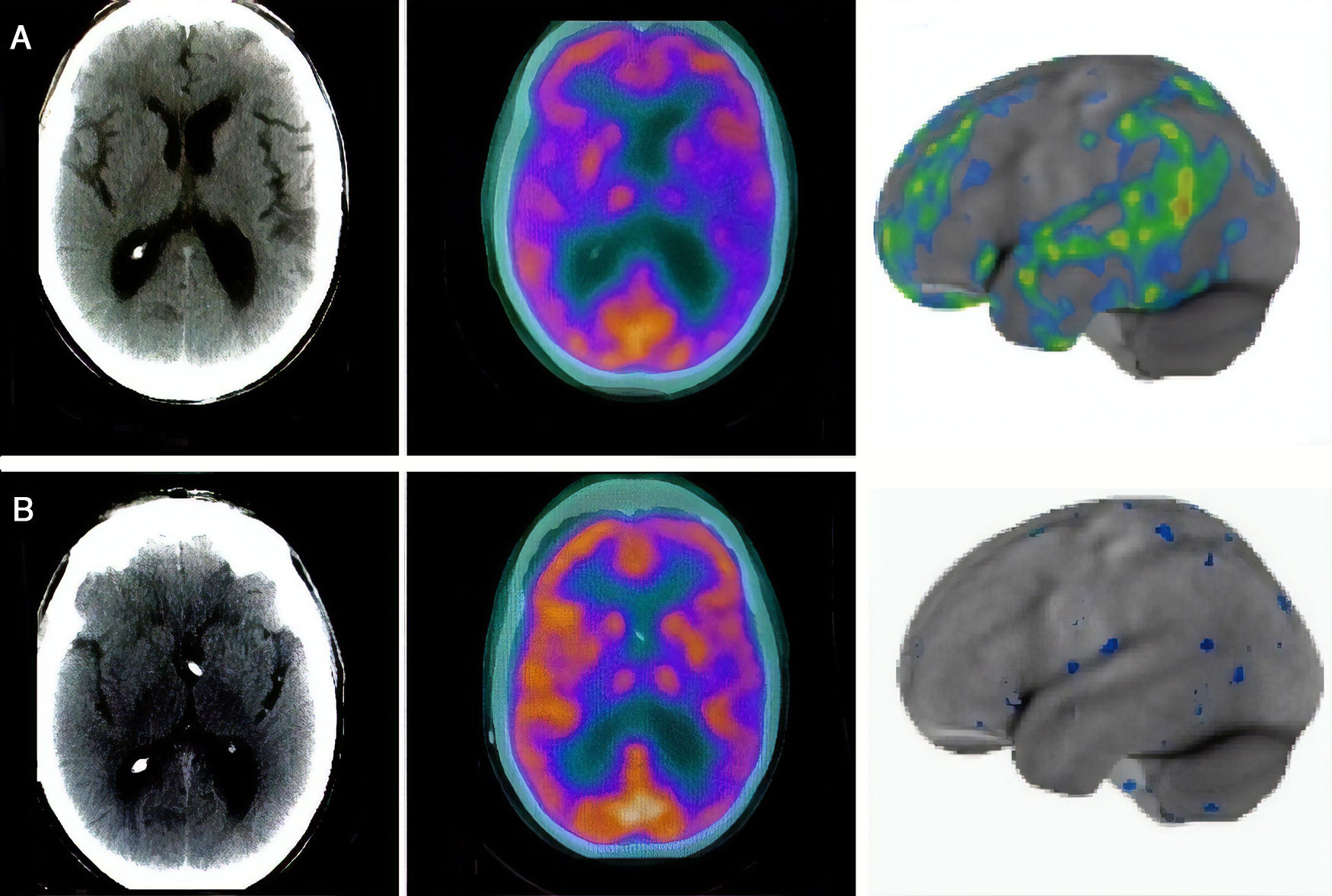
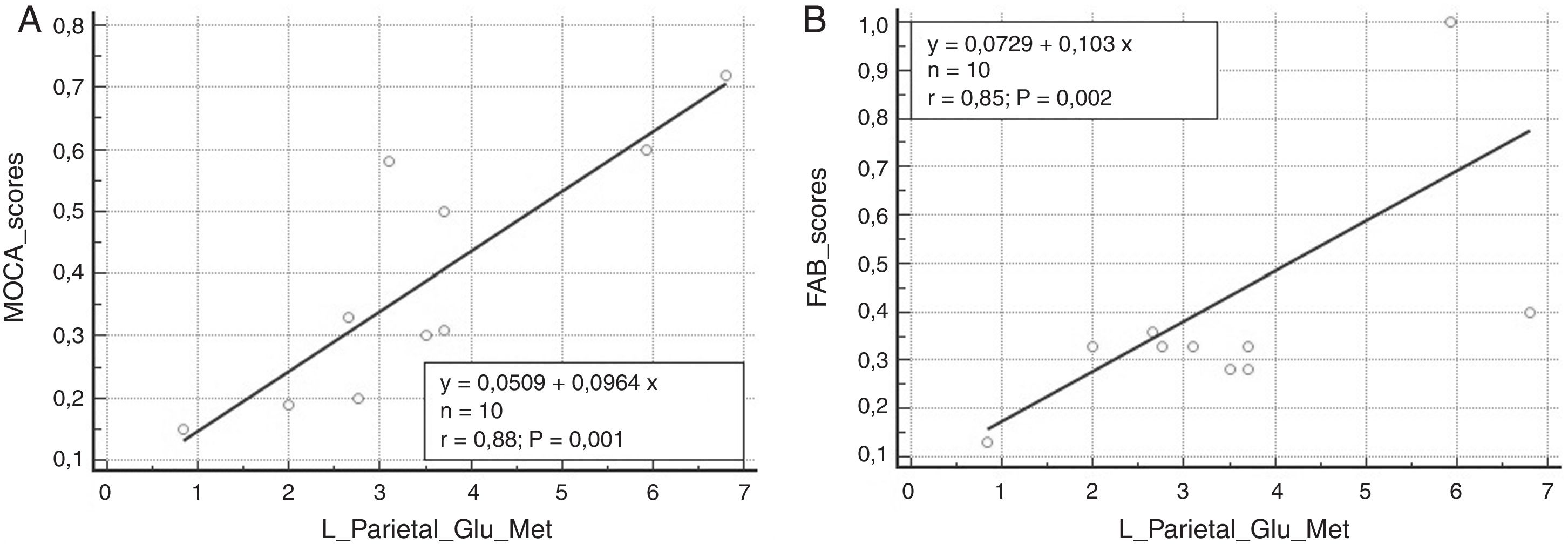
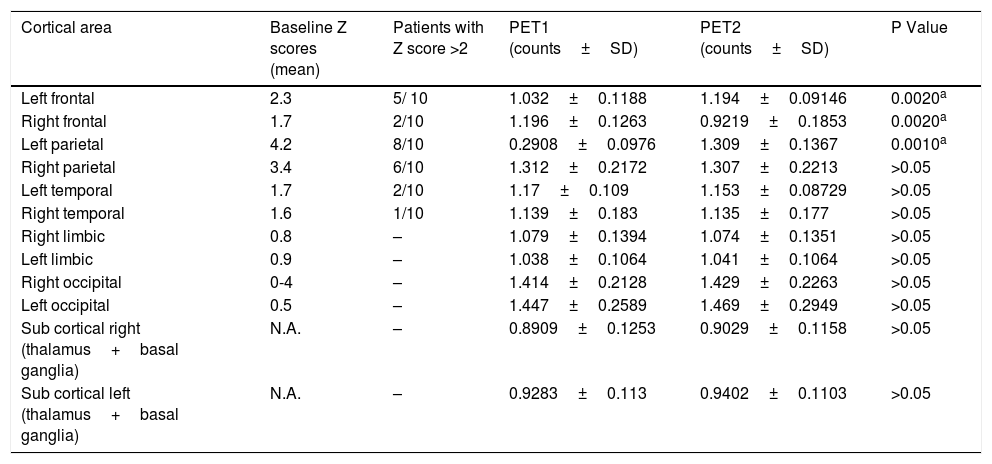
ResultsAn overall number of 20 18F-FDG PET scans were performed in all the enrolled patients. As compared to PET1, PET2 showed an increase in glucose consumption in the left frontal and left parietal lobe in PET2 as compared to PET1 (p<0.001). All the enrolled patients presented a significant increase in neuropsychological scores (i.e Frontal Assessment Battery and Montreal Cognitive Assessment) and have clinically improved at gait analysis. A significant correlation was found between the increase of cortical glucose consumption in the left parietal area and the cognitive improvement as detectable by neuropsychological assessment.
ConclusionsImprovement in 18F FDG PET glucose metabolism could be considered a useful imaging marker for the assessment of iNPH response to VP shunting.
Nuestro objetivo fue evaluar los cambios metabólicos corticales y el resultado clínico en los pacientes afectados por la hidrocefalia idiopática de presión normal (iNPH) después de la colocación de una derivación ventriculoperitoneal (VP).
Materiales y métodos10 pacientes afectados por la sospecha de iNPH se sometieron a una evaluación de la hidrodinámica del LCR basada en una prueba de infusión lumbar (LIT). El principal criterio de selección para la cirugía se basó en la elasticidad intracraneal (EI) > 0,30. Todos los sujetos con una EI>0,30 se sometieron a una exploración TEP con 18 fluorodeoxoglucosa (18F-FDG) en la línea de base (TEP1) y un mes después de la cirugía (TEP2). Además, los mismos pacientes fueron sometidos a una evaluación clínica antes y 1 mes después de la cirugía mediante pruebas neuropsicológicas y análisis de la marcha.
Los resultadosSe realizó un número total de 20 exploraciones de PET 18F-FDG en todos los pacientes reclutados. En comparación con el PET1, el PET2 mostró un aumento en el consumo de glucosa en el lóbulo frontal izquierdo y el lóbulo parietal izquierdo en el PET2 en comparación con el PET1 p<0,001. Todos los pacientes reclutados presentaron un aumento significativo en las puntuaciones neuropsicológicas i.e. Batería de Evaluación Frontal y Evaluación Cognitiva de Montreal y han mejorado clínicamente en el análisis de la marcha. Se encontró una correlación significativa entre el aumento del consumo de glucosa cortical en el área parietal izquierda y la mejoría cognitiva detectable por la evaluación neuropsicológica.
ConclusionesMejora en. 18F FDG PET metabolismo de la glucosa podría considerarse un marcador de imagen útil para la evaluación de la respuesta de la iNPH a la derivación de la VP.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)