We aim to establish the prognostic value of metabolic parameters of the primary tumor in patients diagnosed with vulvar squamous cell carcinoma (VSCC) who underwent a pretreatment F-18 FDG PET/CT scan.
Materials and MethodsThis retrospective study included 47 patients with a histopathologically confirmed diagnosis of VSCC, and who underwent a F-18 FDG PET/CT scan prior to treatment. The disease stage and age at diagnosis, and the maximum standardized uptake value (SUVmax), SUVmean, metabolic tumor volume (MTV) and total lesion glycolysis (TLG) values of the primary tumor, based on a baseline PET scan, were recorded. The relationship between these factors, and progression-free survival (PFS) and overall survival (OS) was evaluated.
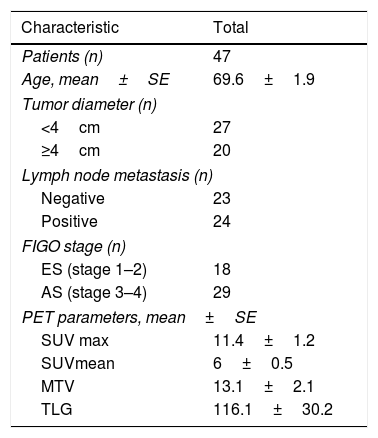
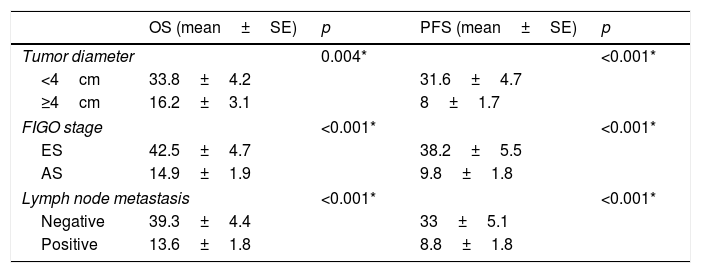
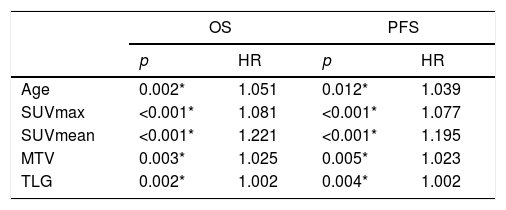
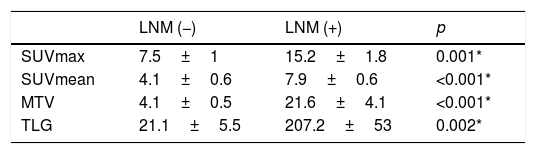
ResultsThe mean age of the 47 study patients was 69.6±1.9 years. Among the patients, 18 were in early stage of the disease and 29 were in the advanced stage. The age, and SUVmax, SUVmean, MTV and TLG values were statistically significantly associated with OS and PFS. Furthermore, it was noted that OS and PFS were significantly longer in the early stage patients than in the advanced stage patients, in patients with a tumor size <4cm than those with a tumor size ≥4cm, and in patients with a negative lymph node metastasis than those with a positive lymph node metastasis.
ConclusionOur findings suggest that PET parameters are prognostic factors for VSCC. To the best of our knowledge, this study is the first to investigate the prognostic value of the PET parameters of primary tumors in patients with VSCC, and as such, we believe it contributes to literature.
Nuestro propósito es establecer el valor prognóstico de los parámetros metabólicos del tumor primario en pacientes diagnosticadas de carcinoma vulvar de células escamosas (VSCC) en las que se realizó un 18F- FDG PET/TC pretratamiento.
Materiales y métodosestudio retrospectivo que incluyó 47 pacientes con un diagnóstico histopatológico confirmado de VSCC en las que se realizó un 18F- FDG PET/TC antes del tratamiento. Se registraron la fase de la enfermedad, la edad de diagnóstico y el valor estandarizado de captación máximo (SUVmax), los valore de SUVmean, del volumen de tumor metabólico (MTV) y de la glicólisis total de la lesión (TLG) del tumor primario, según una PET basal. Se evaluó la relación entre estos factores, la supervivencia libre de progresión (PFS) y la supervivencia global (OS).
ResultadosLa edad media de las 47 pacientes del estudio era de 69,6±1,9 años. Entre las pacientes, 18 estaban en la fase inicial de la enfermedad y 29 estaban en fase avanzada. La edad y los valores de SUVmax, SUVmean, MTV y TLG estaban asociados de forma estadísticamente significativa con la OS y PFS. Además, se observó que OS y PFS era significativamente mayor en los pacientes en fases iniciales que en las pacientes en fase avanzada; en pacientes con un tamaño del tumor <4cm que en aquellas con un tamaño del tumor de ≥4cm y en pacientes con metástasis de ganglios linfáticos negativa respecto a aquellos con metástasis ganglionar positiva.
ConclusiónNuestros resultados sugieren que los parámetros del PET son factores pronósticos del VSCC. Hasta donde sabemos, este estudio es el primero en investigar el valor pronóstico de los parámetros PET de los tumores primarios en pacientes con VSCC, y por esta razón, creemos que contribuye a la literatura especializada.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)