To evaluate the results of the implementation of an enhanced recovery programme (ERAS) for open approach radical cystectomy compared to the historical cohort of the same hospital.
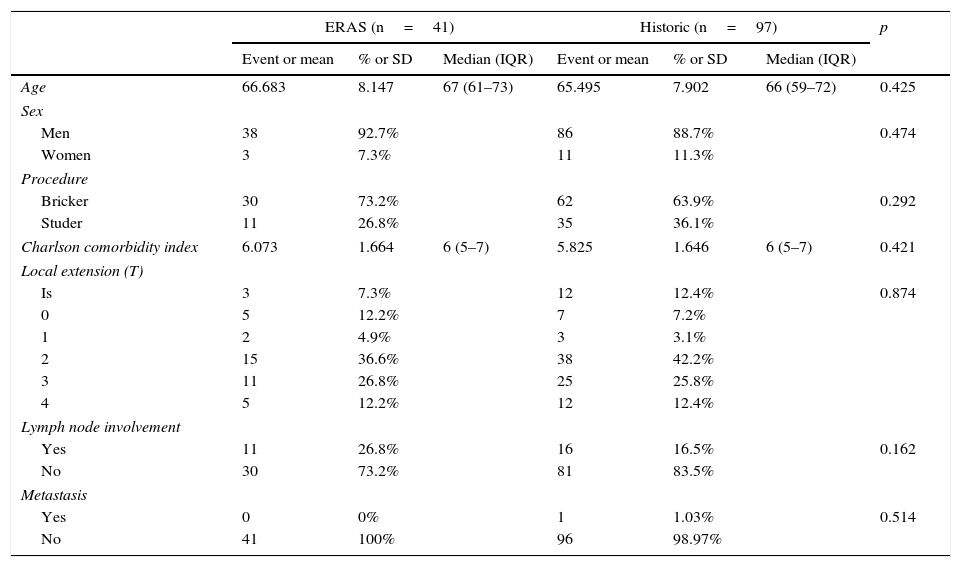
Material and methodsA retrospective analysis of 138 consecutive patients who underwent radical cystectomy with Bricker or Studer ileal derivation (97 historical vs. 41 ERAS). Overall complication rate, Clavien–Dindo stage >2 complications, mortality, hospital and critical care length of stay and readmission rates, as well as need for reoperation, nasogastric intubation, transfusion or parenteral nutrition were compared.
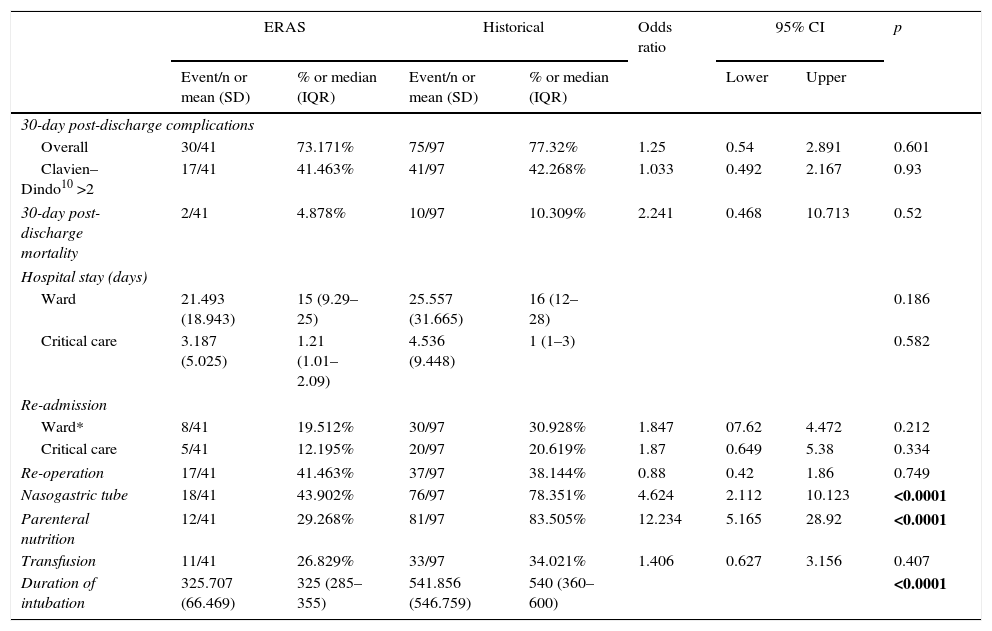
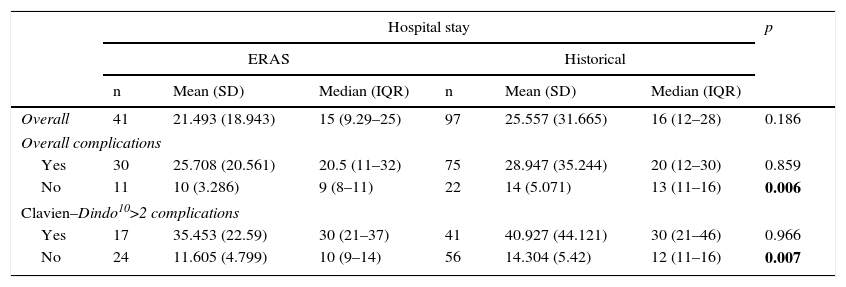
ResultsNo statistically significant differences in overall complication rate were found (73.171 vs. 77.32%; OR 1.25, 95% CI 0.54–2.981; p=0.601) nor in Clavien–Dindo >2 complications (41.463 vs. 42.268%; OR 1.033, 95% CI 0.492–2.167; p=0.93), mortality, lengths of stays readmission and reoperation rates. The need for nasogastric tube insertion was lower in the ERAS group (43.902 vs. 78.351%; OR 4.624, 95% CI 2.112–10.123; p<0.0001), as well as the need for total parenteral nutrition (26.829 vs. 34.021%; OR 12.234, 95% CI 5.165–28.92; p<0.0001), and time under endotracheal intubation since anaesthesia induction (median [IRQ]=325 (285–355) vs. 540 (360–600) min; p<0.0001).
ConclusionEnhanced recovery programmes in radical cystectomy decrease interventionism on the patient without increasing morbidity and mortality.
Evaluar los resultados de la instauración de un programa de recuperación intensificada (ERAS) para cistectomía radical en abordaje abierto con respecto a la cohorte histórica de un mismo hospital.
Material y métodosEstudio de análisis retrospectivo de 138 pacientes sometidos a cistectomía radical con derivación ileal tipo Bricker o Studer de forma consecutiva (97 históricos vs. 41 ERAS). Se compararon tasa de complicaciones a 30 días, complicaciones estadio Clavien-Dindo>2, mortalidad, estancia y tasa de readmisión en el hospital y en cuidados críticos, reintervención y necesidad de sondaje nasogástrico, trasfusión o nutrición parenteral.
ResultadosNo se hallaron diferencias estadísticamente significativas en cuanto a la tasa de complicaciones globales tras 30 días de alta (73,171 vs. 77.32%; OR 1,25, IC 95% 0,54-2,981; p=0,601) ni en Clavien-Dindo>2 (41,463 vs. 42.268%; OR 1.033, IC 95% 0,492-2,167; p=0,93), así como en mortalidad, estancias o tasas de readmisión y reintervención. La necesidad de sondaje nasogástrico fue menor en el grupo ERAS (43,902 vs. 78,351%; OR 4,624, IC 95% 2,112-10,123; p<0,0001), así como la necesidad de nutrición parenteral total (26,829 vs. 34,021%; OR 12,234, IC 95% 5,165-28,92; p<0,0001) y el tiempo bajo intubación orotraqueal desde la inducción anestésica (mediana [RIC]=325 (285-355) vs. 540 (360-600) min; p<0,0001).
ConclusiónLos programas de recuperación intensificada en cistectomía radical disminuyen el intervencionismo sobre el paciente sin aumentar la morbimortalidad.