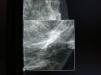
To determine whether the introduction of digital mammography in breast cancer screening has resulted in changes in the detection and management of microcalcifications.
Material and methodsWe retrospectively studied the performance indicators of our breast cancer screening program that are related to the diagnosis of microcalcifications (rates of recall and recommendation of intermediate follow-up after screening, rate of indication of invasive procedures for microcalcifications and their positive predictive value, detection rate for microcalcifications, and number of ductal carcinomas in situ (DCIS) diagnosed). We compared the results obtained using direct digital mammography (September 2008–August 2009) with those obtained using analog mammography (September 2006–August 2007).
Statistical analysisChi-square test and measures of association.
ResultsWe found that using digital mammography led to significant increases in the recall rate (from 50.8 to 64‰), in the rate of intermediate follow-up after screening (from 9.41 to 18.7‰), in the rate of indication for invasive procedures (from 1.88 to 3.01‰), in the cancers detected through microcalcifications (from 0.86 to 1.36‰), and in the number of DCIS diagnosed.
ConclusionDirect digital mammography has improved the detection of microcalcifications, increasing the number of DCIS diagnosed without decreasing the positive predictive value of the invasive procedures indicated for microcalcifications. However, direct digital mammography has had a negative effect by increasing the recall rate and indication for short-term follow-up, possibly due to the difficulty of comparing the findings with those of earlier analog mammograms.
Valorar si la introducción de la mamografía digital (MD) en el cribado del cáncer de mama ha supuesto cambios en cuanto a la detección y manejo de las microcalcificaciones.
Material y métodosSe ha realizado un estudio retrospectivo de los indicadores de rendimiento de un programa de cribado del cáncer de mama que se relacionan con el diagnóstico de microcalcificaciones (tasas de recitación y de recomendación de controles intermedios después del cribado, tasa de indicación de procedimientos invasivos por microcalcificaciones, y su valor predictivo positivo, tasa de detección por microcalcificaciones y número de carcinomas ductales in situ [CDIS] diagnosticados). Se han comparado los resultados obtenidos con la mamografía digital directa (septiembre 2008-agosto 2009) frente a la mamografía analógica (septiembre 2006-agosto 2007). Para el análisis estadístico se utilizaron la Prueba de χ2 y medidas de asociación.
ResultadosCon MD se ha observado un aumento significativo de las tasas de recitación (de 50,8 a 64‰), de realización de controles intermedios (de 9,41 a 18,7‰), de indicación de pruebas invasivas (de 1,88 a 3,01‰), de cánceres detectados por microcalcificaciones (de 0,86 a 1,36‰) y del número de CDIS.
ConclusiónLa MD directa ha mejorado la detección de microcalcificaciones incrementando el número de CDIS diagnosticados, sin disminuir el valor predictivo positivo de los procedimientos invasivos indicados por microcalcificaciones. Sin embargo, ha tenido un efecto negativo por el aumento en la tasa de recitación y de indicación de seguimiento a corto plazo, posiblemente debido a la dificultad de comparación con estudios analógicos anteriores.