To analyse articles retracted due to authors’ misbehaviors contributes to know the scientific integrity situation of a discipline or a country. The largest worldwide database on retracted articles is Retraction Watch (RW). The objective was to know the reasons and features of the biomedical articles retracted of Spanish authors.
Material and methodsA search was conducted in the RW database of 7 types of scientific articles from 9 biomedicine disciplines –biology, genetics, medicine, microbiology, neurosciences, nutrition, dentistry, public health and toxicology–, with at least one author working in a Spanish center, and published between 1970 and 2018. The features of the articles and the reasons for their retraction were recorded.
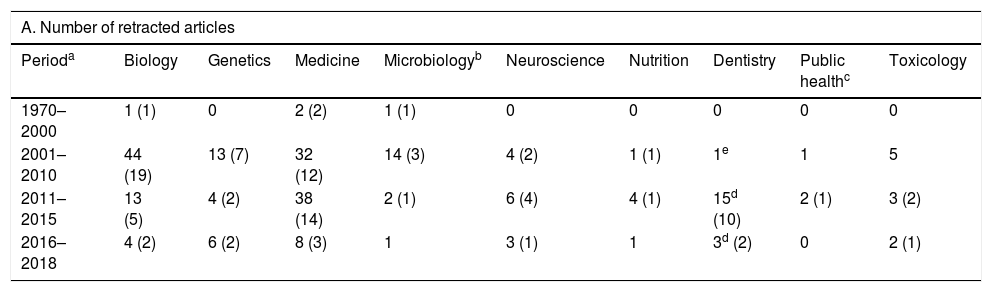
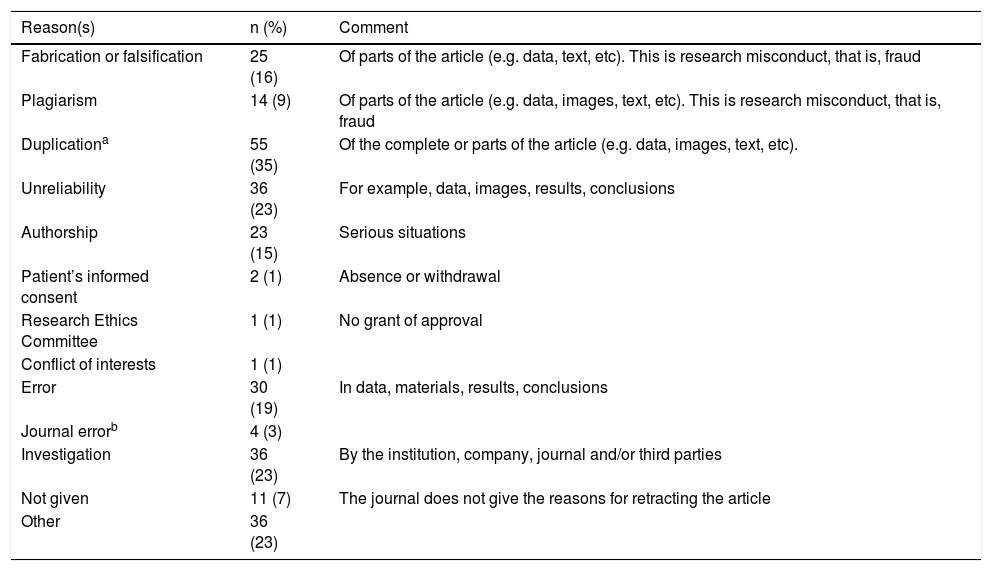
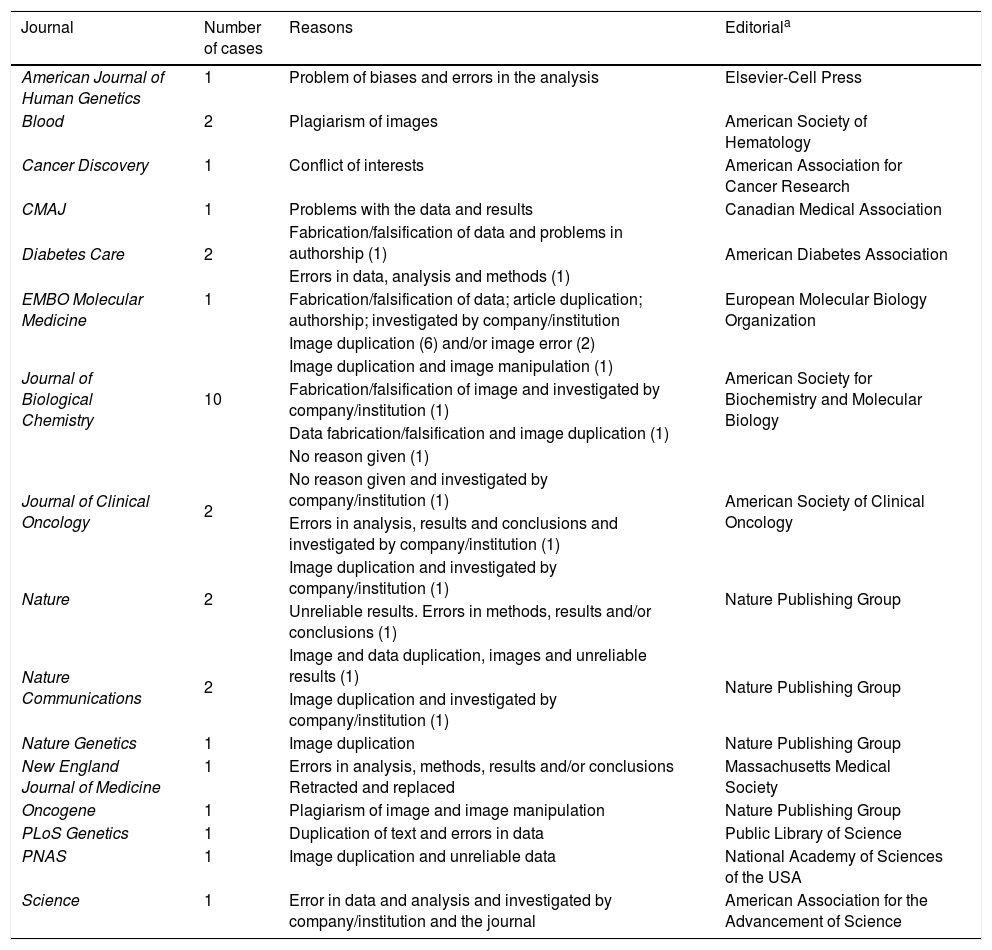
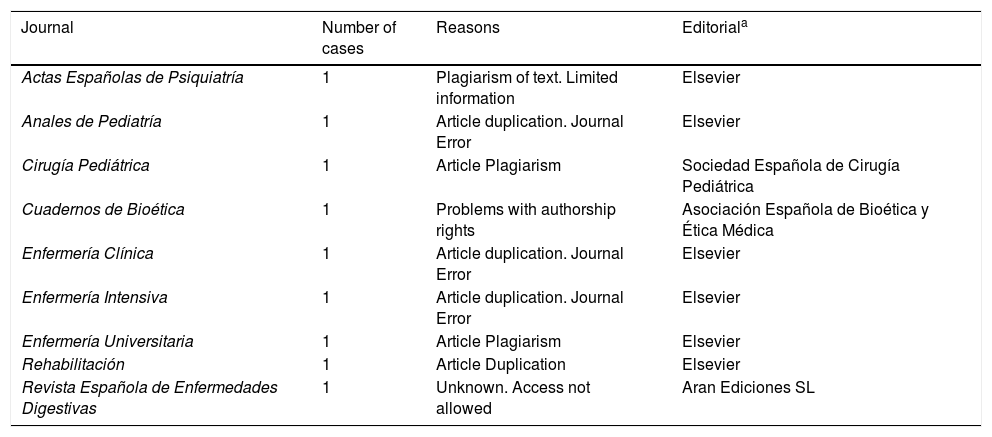
ResultsOf the 18,621 retracted articles, 217 (1%) were from Spanish authors; 155 (74%) were of biomedicine and the types of article of interest. In a majority of cases, there were several reasons to retract an article. Scientific misconduct (fabrication, falsification, plagiarism) and duplication were involved in 23% and 35% of the cases, respectively. Only 8% of the articles were retracted due to errors of the authors or the journals. A dentist retracted 18 articles –all from the same journal and in the same year, 2018–, which accounts for 12% of all biomedicine retracted articles.
ConclusionThe number of biomedicine retracted articles by Spanish authors is low. Scientific misconduct was a reason frequently involved, with few articles retracted by honest errors.
Analizar los artículos retractados por irregularidades de los autores contribuye a conocer el estado de la integridad científica de una disciplina o un país. La base de datos Retraction Watch (RW) es la que contiene más artículos retractados a nivel mundial. El objetivo fue conocer las razones y características de los artículos retractados de biomedicina de autores españoles.
Material y MétodosSe realizó una búsqueda en la base de datos RW de 7 tipos de artículos científicos de 9 disciplinas de biomedicine −biología, genética, medicina, microbiología, neurociencias, nutrición, odontología, salud pública y toxicología−, con al menos un autor que trabajase en un centro español, publicados en 1970–2018. Se registraron las características de los artículos y las razones de su retractación.
ResultadosDe los 18.621 artículos retractados 217 (1%) lo eran de españoles; 155 (74%) eran de biomedicina y de los tipos de artículos de interés. En la mayoría, hubo varias razones para retractar el artículo. La mala práctica científica (fabricación, falsificación, plagio) y la duplicación estaban involucradas en 23% y el 35% de los casos, respectivamente. Sólo el 8% de los artículos se retractaron por errores de los autores o de las revistas. Un odontólogo retractó 18 artículos –todos de la misma revista y en el mismo año, 2018−, lo que supone el 12% de todos los artículos retractados de biomedicina.
ConclusiónEl número de artículos retractados de autores españoles en biomedicina es bajo. La mala práctica científica es una razón frecuentemente involucrada, con pocos artículos retractados por errores involuntarios.