We aimed to test a new telerehabilitation device for stress urinary incontinence (SUI) in order to make an initial assessment of its effectiveness.
Patients and methodRandomized, controlled pilot study. Intervention: experimental group (10 patients): pelvic floor muscle training, device training and home treatment with it; control group (9 patients): conventional rehabilitation treatment. Outcome measures (baseline and 3 months) overall and specific quality of life: International Consultation Incontinence Questionnaire and King's Health Questionnaire, bladder diary, perineometry, satisfaction with the program and degree of compliance.
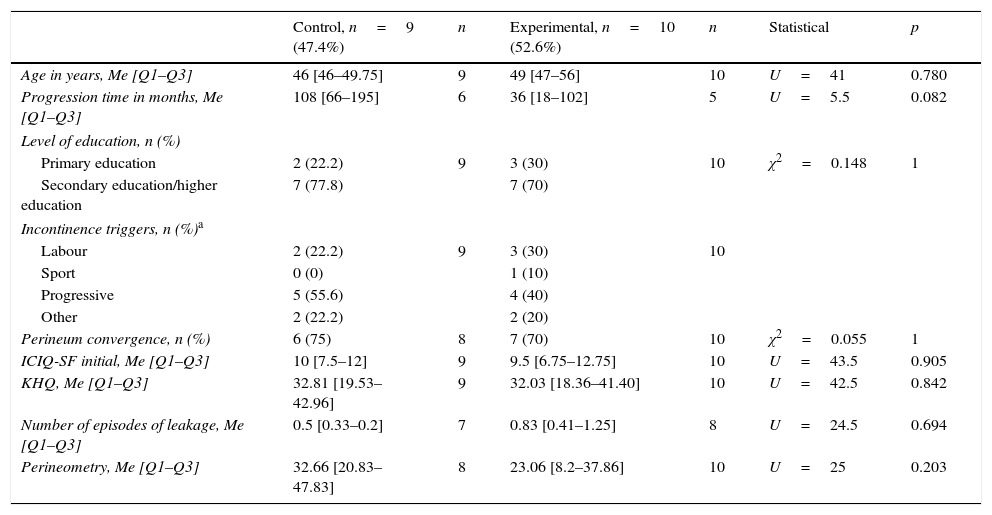
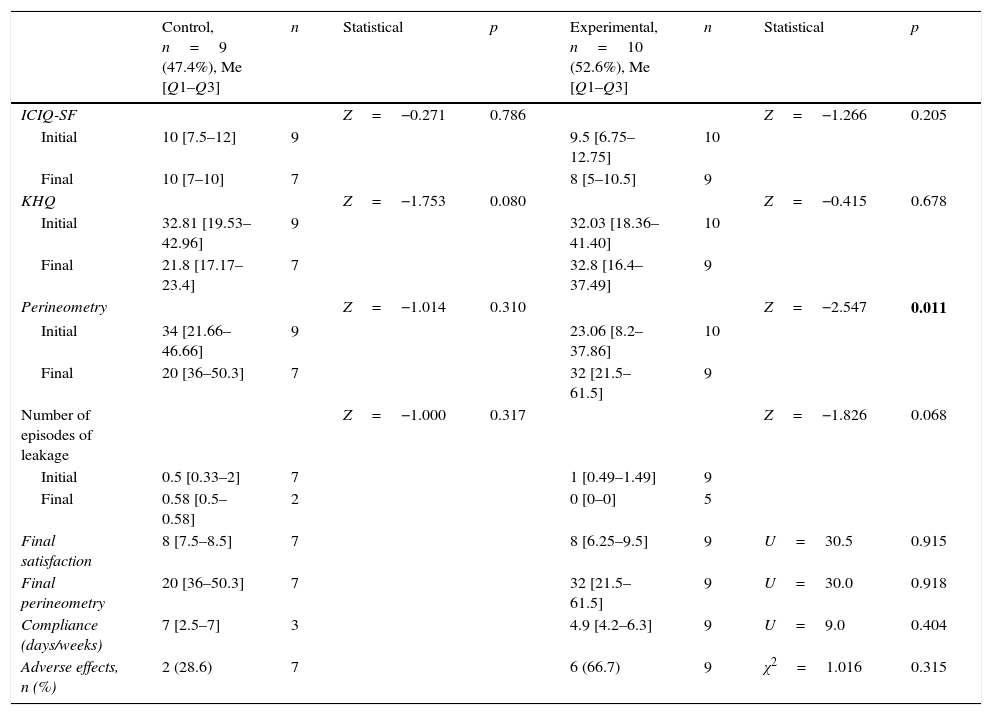
ResultsBaseline characteristics were similar in both groups. There was no statistically significant difference for any outcome measures between groups at the end of the follow-up. The change in perineometry values at baseline and after the intervention was significant in the experimental group (23.06–32.00, p=.011). No group in this study had any serious adverse effects.
ConclusionsThe tested device is safe and well accepted. Although there is some evidence of its efficacy in the rehabilitation treatment of SUI, larger trials are needed to appropriately evaluate the potential advantages.
Testar un nuevo dispositivo de telerrehabilitación para la incontinencia urinaria de esfuerzo (IUE) y hacer una valoración inicial de su eficacia.
Pacientes y métodoEstudio piloto controlado y aleatorizado en pacientes con IUE. En el grupo experimental (n=10) la intervención consistió en entrenamiento de la musculatura del suelo pé lvico, adiestramiento y tratamiento domiciliario con el dispositivo. En el grupo control (n=9) se realizó tratamiento rehabilitador convencional. Las medidas de resultados (iniciales y a los 3 meses) fueron la calidad de vida específica y gené rica determinada mediante: International Consultation Incontinence Questionnaire y King's Health Questionnaire, diario miccional, perineometría, satisfacción con el programa y grado de cumplimiento.
ResultadosAmbos grupos presentaban características basales similares. No hubo diferencias estadísticamente significativas en ninguna medida de resultados entre ambos grupos al final del período de seguimiento. Los valores iniciales y finales de la perineometría del grupo experimental mostraron diferencias con significación estadística (23,06 frente a 32, p=0,011). No se presentaron efectos adversos graves en ningún grupo.
ConclusionesEl dispositivo testado es seguro y bien aceptado. Aunque hay indicios de su eficacia en el tratamiento rehabilitador de la IUE, son necesarios estudios má s amplios para valorar adecuadamente sus ventajas.