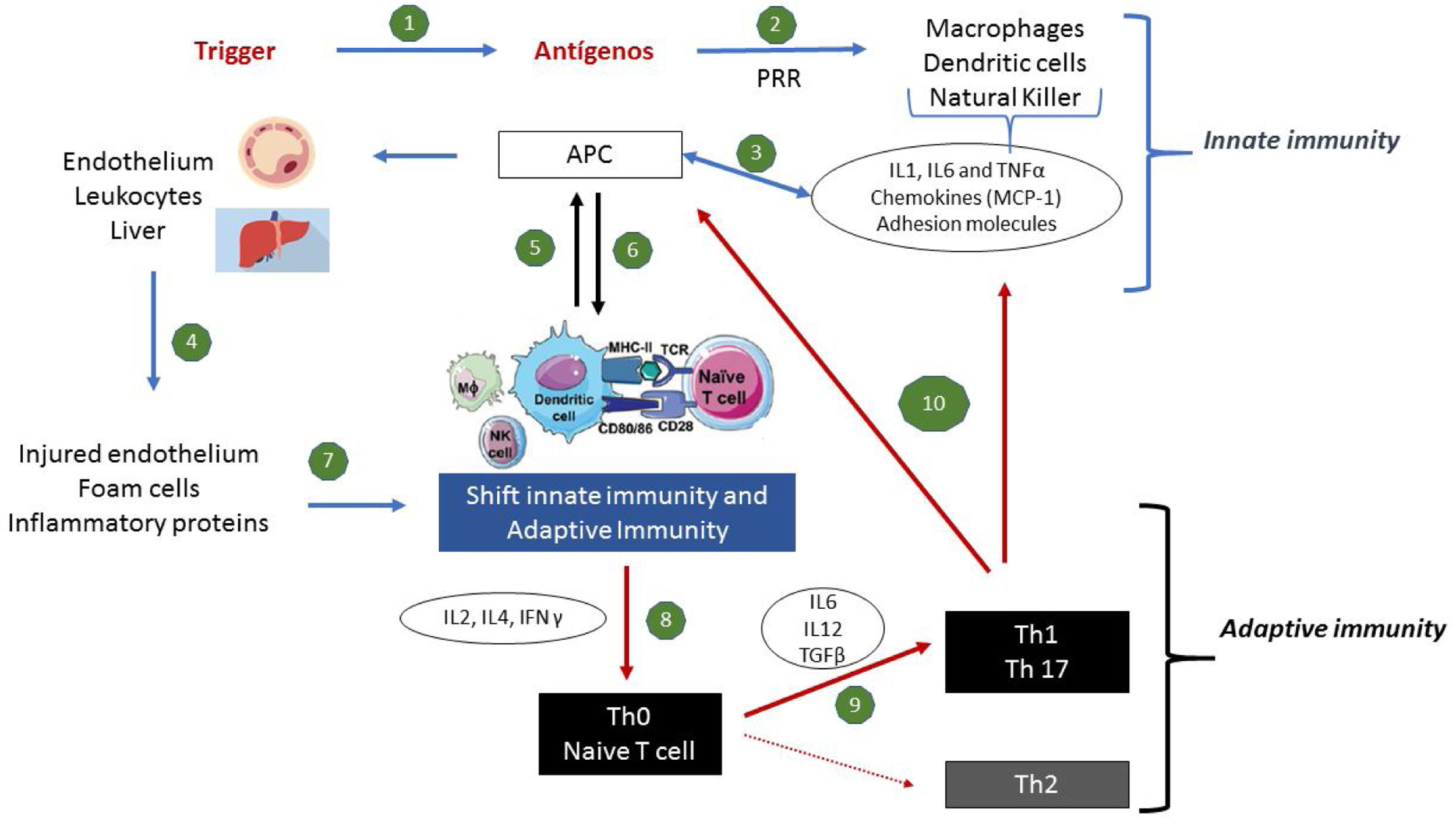
The association between hypertension and cardiovascular disease (CVD) has been increasingly studied through early inflammatory biomarkers. The monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 (MCP-1) is the main chemokine implicated in the inflammatory endothelial process, attracting monocytes and macrophages to the atherosclerotic plaque.
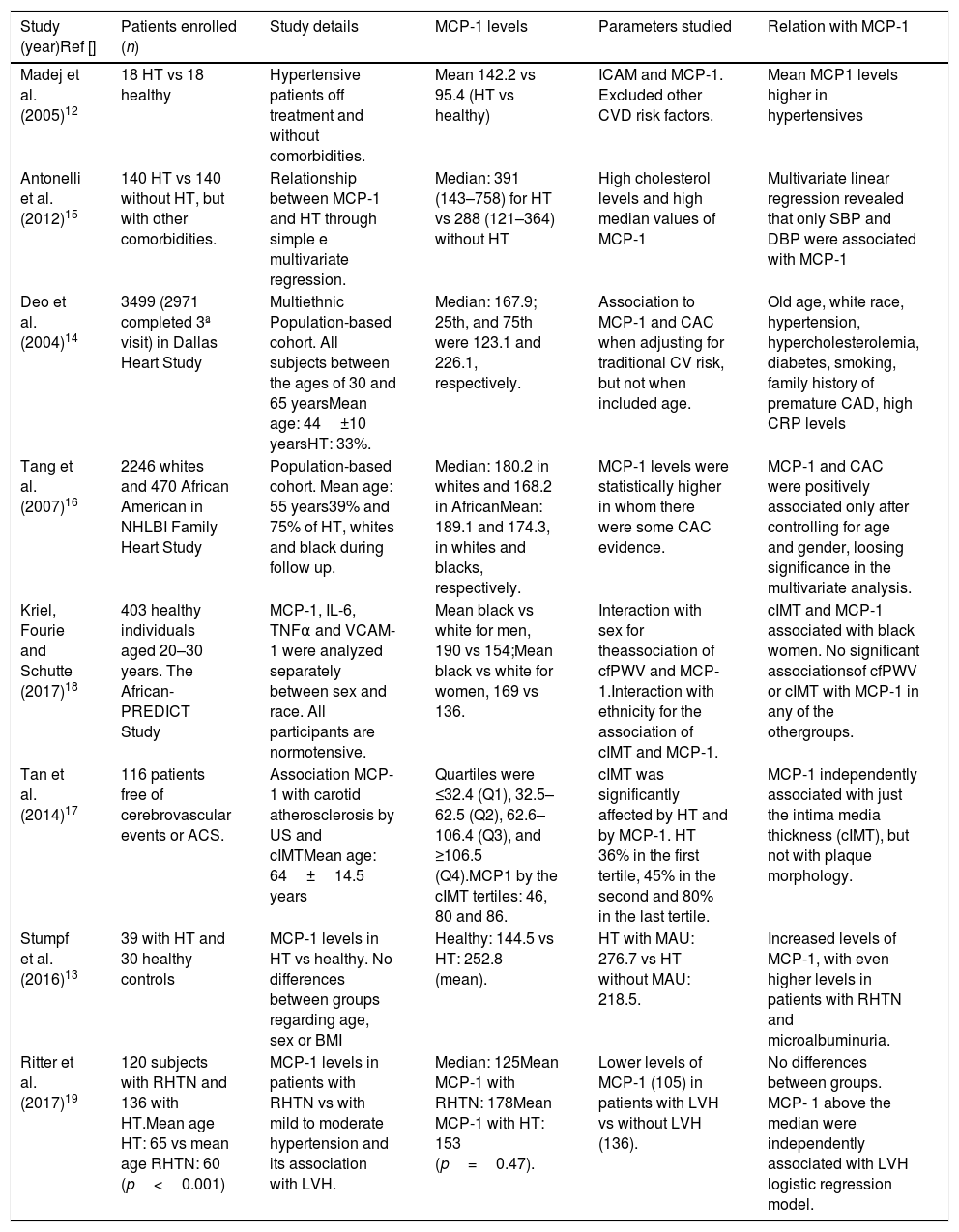
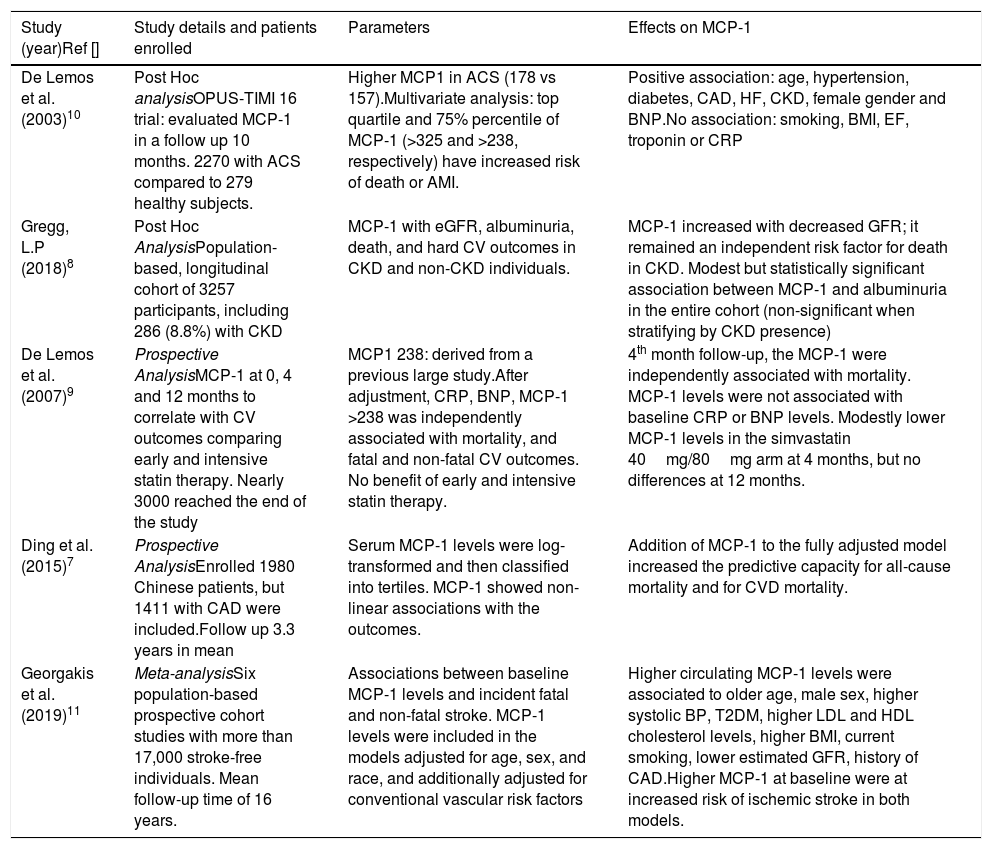
MethodsWe reviewed the main observational studies that have analyzed serum MCP-1 in patients with hypertension regardless of CVD, relating them to target organ damage (TOD).
ResultsAs endothelial dysfunction continues and TOD accumulates, MCP-1 has been perpetuated at higher levels. The relationship between this chemokine and the increase in comorbidities, such as chronic kidney disease, dyslipidaemia, diabetes, and coronary artery disease, became clearer from the observational studies. However, patients with such morbidities use medications with potential anti-inflammatory effects.
ConclusionThere is no normal threshold of MCP-1 for the healthy population, nor a uniform curve pattern, due to a balance between genetic factors, age, gender, comorbidities, TOD, and anti-inflammatory effects of drugs. In fact, MCP-1 seems to have a promising role as a tool for further improvement in cardiovascular risk stratification, as prognostic studies have demonstrated an association with fatal and non-fatal cardiovascular outcomes, regardless of other clinical and laboratory predictors.
Se ha venido estudiando con mayor frecuencia la asociación entre hipertensión y enfermedad cardiovascular a través de los biomarcadores inflamatorios tempranos. La proteína 1 quimioatrayente de monocitos (MCP-1) es la principal quimioquina implicada en el proceso inflamatorio endotelial, que atrae monocitos y macrófagos a la placa aterosclerótica.
MétodosRevisamos los principales estudios observacionales que han analizado la MCP-1 sérica en pacientes hipotensos independientemente de enfermedad cardiovascular, relacionándolos con el daño del órgano diana.
ResultadosA medida que prosigue la disfunción endotelial, y se acumula daño en el órgano diana, MCP-1 se perpetúa a niveles mayores. La relación entre esta quimioquina y el incremento de las comorbilidades, tales como la enfermedad renal crónica, la dislipidemia, la diabetes y la enfermedad arterial coronaria se hizo más evidente a partir de los estudios observacionales. Sin embargo, los pacientes con dichas morbilidades utilizan medicaciones con efectos antiinflamatorios potenciales.
ConclusiónNo existe un umbral normal de MCP-1 para la población sana, ni un patrón de curva uniforme, debido al equilibrio entre factores genéticos, edad, sexo, comorbilidades, TOD y efectos antiinflamatorios de los fármacos. De hecho, MCP-1 parece tener un rol prometedor como herramienta de mejora futura de la estratificación del riesgo cardiovascular, ya que los estudios pronósticos han demostrado una asociación con los resultados cardiovasculares fatales y no fatales, independientemente de otros factores predictivos clínicos y de laboratorio.