The objective of this research is to assess the accuracy and reliability of metagenomic next-generation sequencing (mNGS) in identifying pathogens in spontaneous bacterial peritonitis (SBP) patients and its impact on antibiotic treatment decisions.
MethodsElectronic databases were searched up to July 31, 2023. Studies reporting mNGS diagnostic sensitivity and specificity in SBP were included. Random or fixed-effects models were used. Heterogeneity was assessed using Chi-squared test and I2 statistics.
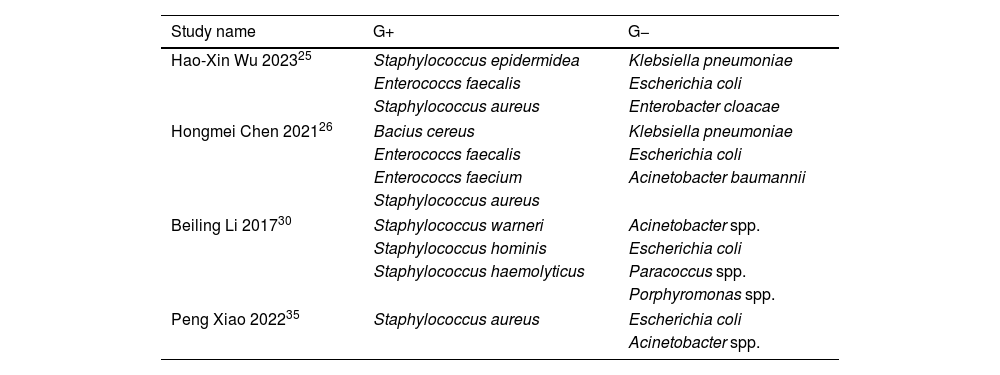
ResultsOut of 75 identified studies, four studies with a total of 420 SBP patients were included. The pooled sensitivity for mNGS in ascites was 94% (95% CI: 86–97%), and specificity was 81% (95% CI: 71–89%). The AUC was calculated to be 0.95 (95% CI: 0.92–0.96), indicating high diagnostic accuracy. The most common pathogens identified by mNGS were Gram-positive bacteria (36%), followed by Gram-negative bacteria (29%), viruses (22%), and fungi (11%).
ConclusionmNGS shows high diagnostic accuracy in detecting pathogens in SBP patients, offering significant value in optimizing antimicrobial therapy. Its ability to identify a broad spectrum of pathogens makes it a promising tool in clinical management of SBP.
El objetivo de esta investigación es evaluar la precisión y confiabilidad de la secuenciación metagenómica de próxima generación (mNGS) en la identificación de patógenos en pacientes con peritonitis bacteriana espontánea (PBE) y su impacto en las decisiones de tratamiento con antibióticos.
MétodosSe realizaron búsquedas en bases de datos electrónicas hasta el 31 de julio del 2023. Se incluyeron estudios que informaban la sensibilidad y la especificidad diagnósticas de la mNGS en la PBE. Se utilizaron modelos aleatorios o de efectos fijos. La heterogeneidad se evaluó mediante la prueba de la chi al cuadrado y las estadísticas I2.
ResultadosDe los 75 estudios identificados, se incluyeron 4 estudios con un total de 420 pacientes con PBE. La sensibilidad combinada de la mNGS en la ascitis fue del 94% (IC del 95%: 86-97%) y la especificidad fue del 81% (IC del 95%: 71-89%). Se calculó que el AUC era de 0,95 (IC del 95%: 0,92-0,96), lo que indica una alta precisión diagnóstica. Los patógenos más comunes identificados mediante mNGS fueron bacterias grampositivas (36%), seguidas de bacterias gramnegativas (29%), virus (22%) y hongos (11%).
ConclusiónLa mNGS muestra una alta precisión diagnóstica en la detección de patógenos en pacientes con PBE, lo que ofrece un valor significativo para optimizar la terapia antimicrobiana. Su capacidad para identificar un amplio espectro de patógenos la convierte en una herramienta prometedora en el manejo clínico de la PBE.