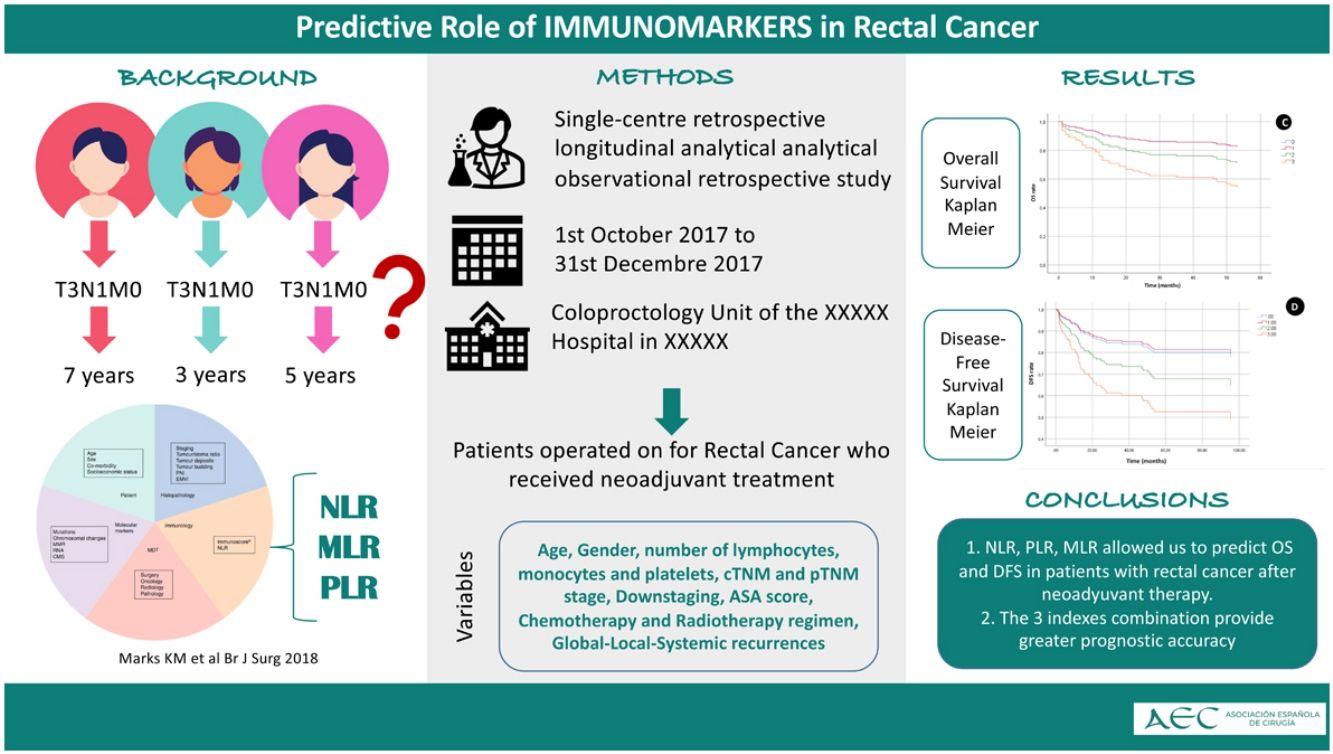
In daily clinical practice, patients with similar risk profiles often show varied oncologic outcomes, including differing responses to neoadjuvant therapy and surgery. In this study, we seek to analyze the relationship of neutrophil-to-lymphocyte (NLR), platelet-to-lymphocyte (PLR), and monocyte-to-lymphocyte (MLR) ratios with survival and recurrence in patients treated for locally advanced rectal cancer.
Material and methodsWe have conducted a retrospective analysis of patients operated on due to rectal cancer with neoadjuvant long-course radiotherapy and sensitizing chemotherapy. After neoadjuvant therapy and before surgery, these immunomarker indices were analyzed. Each index was assigned a cut-off point to assess their association with overall survival (OS) and disease-free survival (DFS).
ResultsA total of 156 patients were analyzed with a median follow-up of 71.5 months (51–89). The NLR index was identified as an independent predictor of 5-year OS and DFS. Values above the 6.3 cut-off point showed an OS of 58.9% (P = .019); in patients with values above 4.72, DFS was 57.4% (P = .034). Patients whose 3 indices (NLR, PLR, MLR) were elevated had a 5-year OS of 25% (HR 3.16, 95% CI [1.45−6.87], P = .004); and a 5-year DFS of 39.4% (HR 2.88, 95% CI [1.35–6.17], P = .006).
ConclusionsElevated preoperative immunomarker values are related to worse outcomes in terms of OS and DFS in those patients with locally advanced rectal cancer after neoadjuvant therapy. The combination of the three indices is more accurate in predicting OS and DFS. These immunomarkers may be useful in choosing an individualized therapeutic strategy.
En la práctica clínica diaria, pacientes con perfiles de riesgo similares a menudo muestran resultados oncológicos variados, incluyendo respuestas diferentes a la terapia neoadyuvante y a la cirugía. En este estudio, pretendemos analizar la relación de los índices neutrófilos-linfocitos (NLR), plaquetas-linfocitos (PLR) y monocitos-linfocitos (MLR) con la supervivencia y la recurrencia en pacientes tratados por cáncer de recto localmente avanzado.
Material y métodosSe realizó un análisis retrospectivo de pacientes operados por cáncer de recto con radioterapia neoadyuvante de larga duración y quimioterapia sensibilizadora. Tras la terapia neoadyuvante y antes de la cirugía se analizaron estos índices como inmunomarcadores. A cada índice se le asignó un punto de corte para evaluar su asociación con la supervivencia global (SG) y la supervivencia libre de enfermedad (SLE).
ResultadosSe analizaron 156 pacientes con una mediana de seguimiento de 71,5 meses (51–89). El índice NLR se identificó como predictor independiente de la SG y la SLE a 5 años. Los valores superiores al punto de corte 6,3, mostraron una SG del 58,9% (p = 0,019); en los pacientes con valores superiores a 4,72, la SLE fue del 57,4% (p = 0,034). Los pacientes con los 3 índices (NLR, PLR y MLR) elevados obtuvieron una SG a 5 años del 25% (HR 3,16, IC 95% (1,45−6,87), p = 0,004); y una SLE a 5 años del 39,4% (HR 2,88, IC 95% (1,35−6,17), p = 0,006).
ConclusionesValores elevados de los inmunomarcadores preoperatorios se relacionan con peores resultados en términos de SG y SLE en aquellos pacientes con cáncer de recto localmente avanzado tras terapia neoadyuvante. La combinación de los tres índices es más precisa para predecir la SG y la SLE. Estos inmunomarcadores pueden ser útiles en la elección de una estrategia terapéutica individualizada.