Primary tumors of the inferior vena cava are rare tumors of mesenchymal origin. They arise from the smooth muscles of the vena cava wall. Due to its low prevalence, there are few definitive data on its treatment and prognosis. Its treatment is based on general oncological principles.
MethodsA series of 6 cases operated from 2010 to 2020 were analyzed. Different parameters related to the demographic characteristics, the tumor, the treatment received, and the results obtained in survival and morbidity were analyzed. In addition, a bibliographical review of the currently available evidence was carried out.
ResultsOptimal surgical resection was accomplished in all patients with R0 in 4/6 and R1 in 2/6. The greatest morbidity occurred in a patient who died in the intraoperative period. Cavorraphy was performed in one patient and cavoplasty in 5/6 using cryopreserved graft in 3/6 and prothesis in 2/6. The 50% were still alive at the end of the follow-up (with a mean follow-up of 10.7 months). The mean survival was 11.3 ± 9.07 months. 3/6 patients presented hematogenous recurrences with a disease-free interval of 9 ± 2 months.
ConclusionThe diagnosis and treatment of inferior vena cava leiomyosarcoma is still a challenge. Due to its low prevalence, it will be difficult to establish a totally standardized treatment and its approach is recommended in specialized centers. On the other hand, a multicentric study should be made to collect the most cases as possible in order to advance in the understanding of the approach to this disease.
Los tumores primarios de vena cava inferior son tumores raros de origen mesenquimal que surgen de la musculatura lisa de la pared. Debido a su escasa prevalencia, existen pocos datos definitivos sobre su tratamiento y pronóstico. Su tratamiento se basa en principios oncológicos generales.
MétodosSe ha analizado una serie de 6 casos intervenidos desde 2010 a 2020, evaluando distintos parámetros relacionados con las características demográficas, del tumor, del tratamiento recibido y los resultados obtenidos en supervivencia y morbilidad. Además, se ha llevado a cabo una revisión bibliográfica de la evidencia disponible actualmente.
ResultadosEn todos los pacientes se llevo a cabo resección quirúrgica óptima con R0 en 4/6 y R1 en 2/6. La mayor morbilidad sucedió en un paciente fallecido en periodo intraoperatorio. Se realizó cavorrafia en un paciente y cavoplastia en 5/6 utilizando injerto criopreservado en 3/6 y prótesis en 2/6. Al final del seguimiento de nuestra serie (con una media de seguimiento de 10,7 meses), el 50% de los pacientes continúan vivos. La media de supervivencia fue de 11,3 ± 9,07 meses. De los 6 pacientes, tres presentaron recidivas hematógenas con un intervalo libre de enfermedad de 9 ± 2 meses.
ConclusiónEl diagnóstico y tratamiento del leiomiosarcoma de vena cava inferior continúa siendo un reto. Debido a su baja prevalencia, resultará difícil establecer un tratamiento totalmente estandarizado y se recomienda su abordaje en centros especializados. Por otra parte, se deberían intentar aunar los casos intervenidos de cara a avanzar en el conocimiento del abordaje de esta enfermedad.
Primary tumours of the inferior vena cava are rare tumours of mesenchymal origin arising from the smooth musculature of the inferior vena cava wall, with intra- or extraluminal growth1,2. Their management is based on general oncological considerations due to their low prevalence, and therefore there is little definitive data on their treatment and prognosis.
The main and accepted treatment is surgical removal, which is a surgical challenge due to their unique location, neighbouring organs, and the haemodynamic management they require.
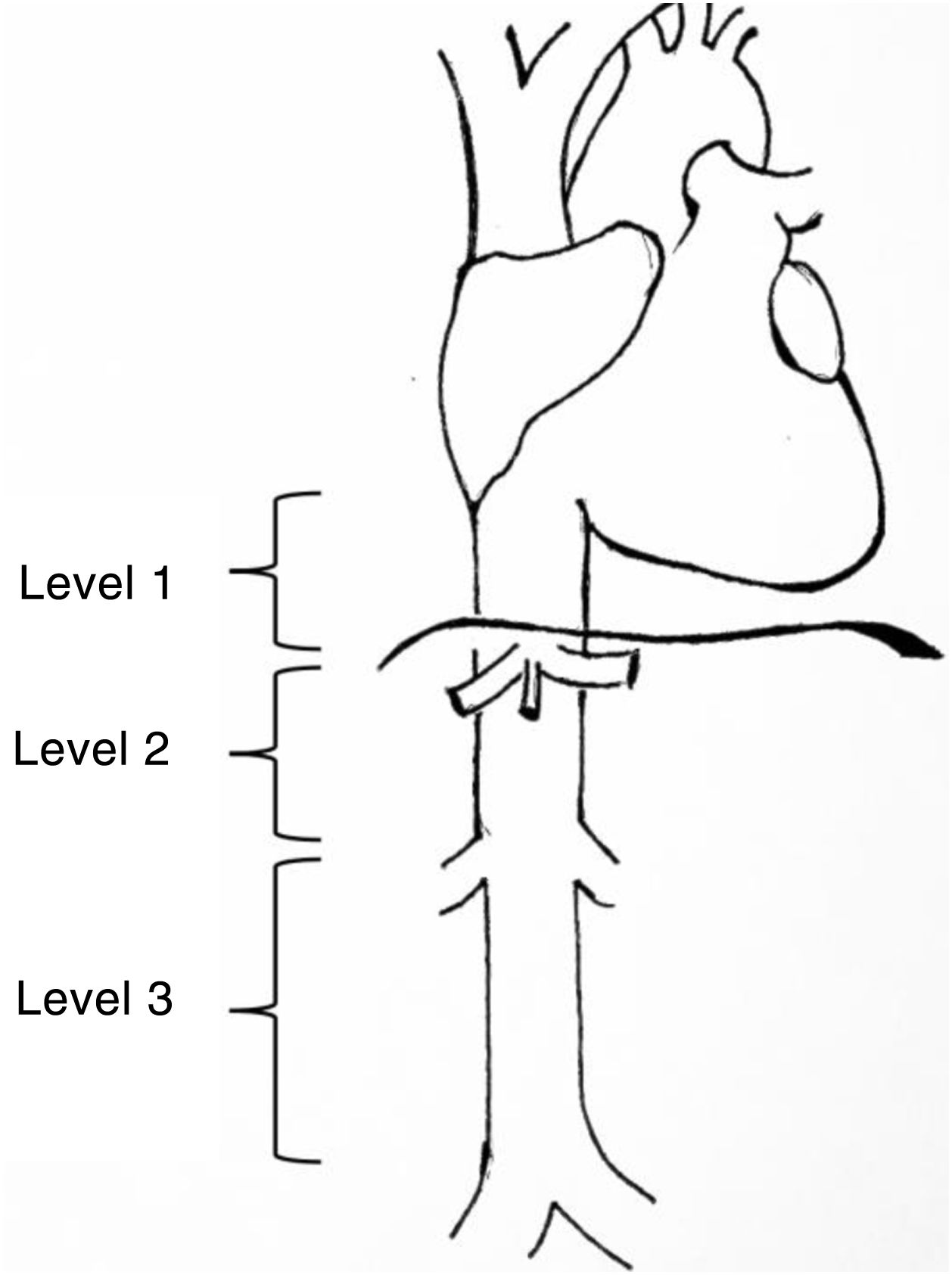
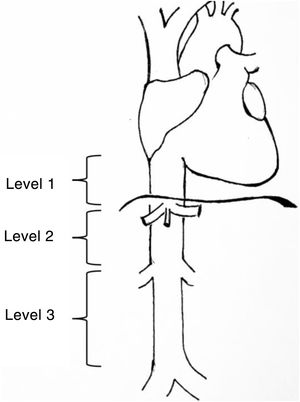
Leiomyosarcomas of the vena cava are described and classified according to various aspects such as patient age, size, tumour characteristics, tumour approach, and location3. One of the most widely used classifications is that proposed by Kulaylat et al.4, which divides these tumours according to their location into 3 different levels (Fig. 1). There are 3 surgical approaches: resection and ligation of the cava, resection and primary suture or resection accompanied by reconstruction with prosthesis. The main approach in most series is resection with reconstruction. For venous reconstruction there are several options in the literature, and none have been shown to be superior because there are so few cases described. Biological materials can be used, such as grafts from the patient's own vein (saphenous vein, left renal vein, jugular vein, etc.), grafts from bovine pericardium, or preserved vascular grafts from cadaveric donor. And synthetic materials can be used (PTFE, Dacron®).
Levels of involvement according to the classification by Kulaylat et al.4.
The purpose of our study is to analyse the series of cases operated on in our unit, evaluating morbidity and mortality, reconstruction techniques and overall and disease-free survival.
MethodsThe patients were analysed from a retrospective database, collected between 2010 and 2020. Patients signed their informed consent, and the descriptive study was approved by our centre’s ethics committee.
The classification by Kulaylat et al.4 for leiomyosarcomas according to location was used, in which the inferior vena cava is divided into 3 segments. Level 1: from the entry point of the suprahepatic veins into the inferior vena cava to the entry point to the right ventricle; level 2: from the outflow of the renal veins to the suprahepatic veins and level 3: from the iliac venous confluence to the outflow of the renal veins (Fig. 1).
Resectability was classified as R0 (free margins in the pathology specimen); R1 (macroscopically free margins, but with suspicion of microscopic disease) and R2 (visible to the naked eye that the margins are not free). Postoperative morbidity was assessed using the Dindo-Clavien5 scale that categorises postoperative complications from level 1, small deviations in the postoperative period, to level 5, corresponding to the patient's death in this period. The cut-off point for major morbidity was level 3, as this is the cut-off point where patients require radiological, endoscopic, or surgical interventions; clearly indicating higher severity of the underlying complication. The Charlson Comorbidity Index was used to assess the comorbidity of the patients at the time of surgery6.
Adjuvant therapy was divided into chemotherapy, radiotherapy or chemoradiotherapy. The most used chemotherapy regimens were based on adriamycin, ifosfamide, or trabectedin. Neoadjuvant therapy, when provided, consisted of external radiotherapy.
Quantitative variables were analysed as mean and standard deviation and qualitative variables as percentages. IBM SPSS® v.18.0 software was used.
ResultsFrom 2010 to 2020, 6 patients underwent surgery at our centre for vena cava leiomyosarcoma. We excluded cases of leiomyosarcoma in other locations from our analysis, and patients with metastatic disease not candidates for surgery. No patient was intraoperatively unresectable.
The demographic data are shown in Table 1. The mean age was 63 ± 14.6 years. Women predominated (83%). The most frequent symptoms at diagnosis were abdominal discomfort and pain in 66.6%. The most frequent location was level 2 (83.3%). The maximum diameter was 10.38 ± 5.16 cm. Adjacent organs had to be resected in 2/6 patients. All but one patient underwent preoperative biopsy.
Demographic and perioperative characteristics.
| Variable | Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 70 | 58 | 38 | 79 | 73 | 60 |
| Sex | Female | Female | Female | Female | Female | Male |
| Symptoms on diagnosis | Elevated ferritin | Abdominal pain | Right flank tumour | Abdominal pain | Abdominal pain | Abdominal pain |
| Pre-op. biopsy | Yes | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Size | 6 × 5 × 7.5 cm | 12cm | 8 × 9.3 × 7.5 cm | 20×14cm | 7.8×6.5×5.5cm | 5.7×5.5×5.4cm |
| Predominant growth | Extraluminal | Extraluminal | Extraluminal | Extraluminal | Extraluminal | Extraluminal |
| Thrombus | No | Yes | No | No | No | No |
| IVC segments included | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 1 | 2 |
| Location (level) | 2 | 1 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 1 + 2 |
| Incision | Subcostal bilateral | Rio Branco | Río Branco | Mercedes Benz | Mercedes Benz | SIML |
| IVC resection and repair | Cavoplasty with PTFE | Cavoplasty with | Cavorraphy | Cavoplasty with cryopreserved pulmonary artery | Cavoplasty with cryopreserved pulmonary artery | Cavoplasty with cryopreserved pulmonary artery |
| Dacron® | ||||||
| Complete resection | R0 | R1 | R0 | R1 | R0 | R0 |
| Resection of adjacent organs | No | No | Yes (gall bladder) | Yes Kidney and right suprarenal gland | No | Yes Kidney and right suprarenal gland |
| Postoperative time to discharge (days) | 4 | 21 | 6 | — | 8 | 8 |
| Dindo-Clavien≥3 at 30 days | No | No | No | V | No | No |
| Charlson Index | 5 | 4 | 2 | 9 | 5 | 5 |
| Antithrombotic prophylaxis | Double antiaggregation clopidogrel + ASA | Anticoagulation Enoxaparin 90 mg/24 h | Prophylactic anticoagulation 10 days after discharge. | — | Enoxaparin 80 mg/24 h/one month. Treated with ASA 100mg | Enoxaparin 40 mg/12 h/2 months. On ASA which she was taking before |
| Survival (months) | 3 (alive) | 14 (died) | 17 (died) | 0 (died) | 27 | 7 |
| DFT (months) | No (3) | Yes (11) | Yes (19) | — | No (27) | Yes (7) |
| Type of recurrence | — | Metastasis | Liver metastasis | — | — | Local and metastasis (bone and lungs) |
ASA: Aspirin, DFT: Disease-free time; SIML: Supra- and infra-umbilical median laparotomy; PTFE: Polytetrafluoroethylene; IVC: Inferior vena cava.
The most common reconstruction technique was cavoplasty in 83.3%, using cryopreserved vascular graft3, PTFE prosthesis1 and Dacron®prosthesis1.
The rate of R0 resection (free surgical margins) was 66.67%, the rate of suspected R1 microscopic disease was 33.33%.
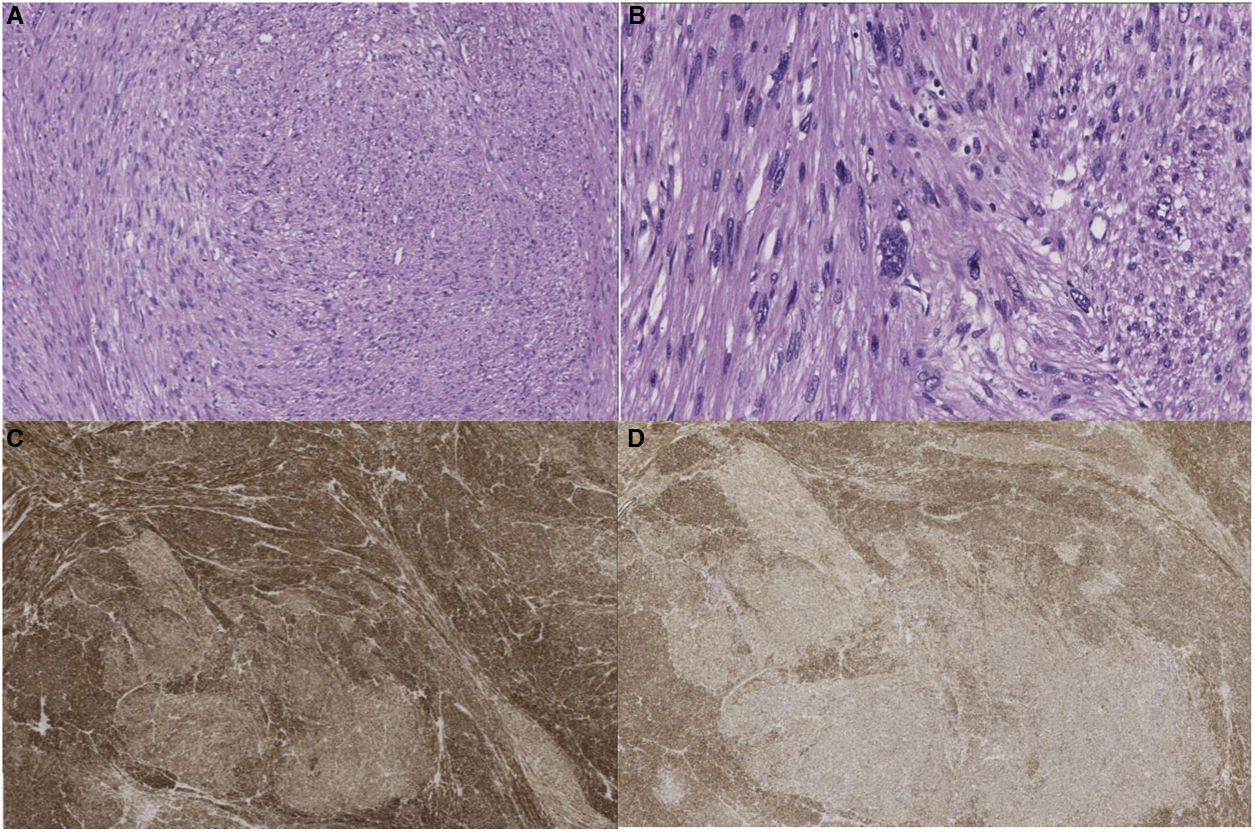
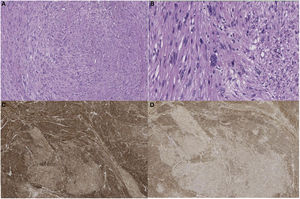
Pathological anatomyThe surgical specimens were fixed with 10% formaldehyde solution, embedded in paraffin, 3 μm sections were obtained and H&E stained. Automated immunohistochemistry was performed with BOND Polymer Refine Detection (Leica), using monoclonal or polyclonal antibodies against smooth muscle specific actin, desmin, caldesmon, CD-31, Ki-67, calponin and CD-34 (Fig. 2).
MorbimortalityThere was major morbidity in only one patient, who died intraoperatively due to haemodynamic instability. As minor morbidity, one patient presented a transient ischaemic stroke due to paradoxical embolism with an unknown patent foramen ovale that resolved conservatively, and a second patient presented a mild retroperitoneal haematoma that did not require invasive management.
There was no thrombosis of either artificial or biological grafts in the series presented. The most used anticoagulant-antiplatelet therapy was enoxaparin at treatment doses, which was replaced at one month by antiplatelet therapy, most commonly ASA 150 mg/24 h.
Adjuvant therapyOf the 6 patients, only one received neoadjuvant radiotherapy (patient 5). Two patients received adjuvant. Patient 2, who received adriamycin and trabectedin. Patient 3 received adjuvant radiotherapy and chemotherapy; the chemotherapy agents used first line were ifosfamide and adriamycin, and after recurrence, trabectedin.
SurvivalAt the end of follow-up (median follow-up of 10.7 months) 50% of the patients were still alive. Overall survival was 11.3 ± 10.0 months. Of the 6 patients, 3 had recurrence. The median DFI was 9.5 ± 2.4 months; the remaining 2 at the time of the study had 3 and 27 months of follow-up, with no signs of recurrence.
DiscussionMalignant tumours of the wall of the great vessels are rare. They occur more frequently in women7,8 in patients between 50 and 60 years of age7,8. These data are like those of our series, summarised in Tables 1 and 2.
Anatomopathological study.
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tumour AP characteristics | Desmin and smooth muscle actin positive.Necrosis 10% | Cystification.Extensive necrosis | Extensive areas of dedifferentiation.Actin, desmin and caldesmon+ (in dedifferentiated areas), CD34+.Necrosis 20% | Desmin+, caldesmon+, SMA+.Necrosis 40% | Expression of desmin and caldesmon.Necrosis 30% | Moderately differentiated with moderate pleomorphism and focal necrosis.SMA, desmin and calponin+ |
| Grades of malignancy | G2 | Not available | Not available | G3 | G3 | G3 |
| Ki-67 | 20% | Not available | 70% | 80% | 20% | 30% |
SMA: Smooth muscle actin; PA: Pathological anatomy.
Inferior vena cava leiomyosarcomas can be classified according to their location following the scheme used by Kulaylat et al.4 as described above, some can be classified as level 1,2; level 2,3 or even level 1,2,3. These tumours are termed “bi-level” or “tri-nivel”4. Other classifications exist, such as that of Stilidi et al.9 (who divide the inferior vena cava into 6 levels), or that of Kieffer et al.10, although they are not as widely used. This anatomical classification is also important because the presenting symptoms may vary depending on the segment in which the tumour is located11.
The growth pattern can be classified as predominantly extraluminal, predominantly intraluminal or hourglass, with significant both intraluminal and extraluminal growth4,7. In some cases the origin of the tumour is obvious, and is easily identified with a pedicle attaching the extraluminal mass to the vein wall. In others, it is firmly attached to the wall and requires resection for radical excision8. They have classically been considered slow growing in most cases, but growth has been shown to be rapid. They metastasise late and are mainly found in the liver and lungs, although virtually no organ is unaffected4. Speed of growth was difficult to determine in a series of six cases. However, we can contrast our data with those in the literature. As in the literature, the most common finding was Kulaylat et al.4 level 2 involvement, with predominantly extravascular growth3.
Symptoms are very non-specific, and the condition may be a chance finding after an imaging test. The most frequent symptom is abdominal discomfort7,8, in line with the data from our centre, where 4 of the 6 patients started with these symptoms. There are other possible manifestations: Budd-Chiari syndrome, DVT, respiratory symptoms, oedema of the lower limbs, weight loss, back pain, fever, etc.7. Imaging tests are necessary for diagnosis, generally CT and MRI, which can help define the origin and extent of the tumour. On CT, the tumour is low density, with a solid or heterogeneous mass; there may be an area of necrosis; it is useful to find internal calcification secondary to this necrosis, but this is an infrequent finding4,12,13. MRI shows similar information to CT, but provides more information about the extent of the tumour and thrombi present4. Despite the information they can provide, to confirm the diagnosis, preoperative CT or ultrasound-guided core needle biopsy is indicated to rule out other diseases that are not candidates for surgery. Straker et al.14 performed a retrospective cohort study, using data from 2620 patients with retroperitoneal sarcomas from the National Cancer Database, in which they concluded that preoperative biopsy has no negative effect on survival. It may indirectly improve survival outcomes by facilitating neoadjuvant therapy and increase complete tumour resection. Preoperative biopsy was performed in all but one patient in our centre. In our preoperative protocol, preoperative biopsy is always performed to plan the treatment according to the histology, which in the case of leiomyosarcoma of the vena cava is primary resection, patients also undergo anaesthetic assessment combined with angio-CT or angio-MRI, and a protocol is established with the National Transplantation Organisation to acquire cryopreserved grafts as the first choice. Therefore, patient selection is fundamental to a good prognosis. In our series, the only patient who died intraoperatively was a borderline indication, which was agreed with the patient and the multidisciplinary committee.
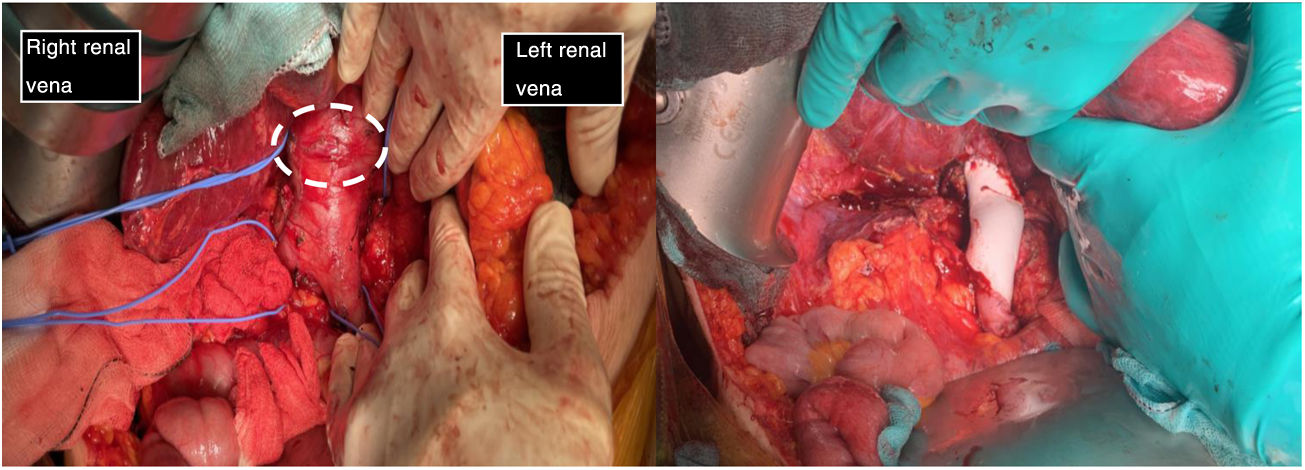
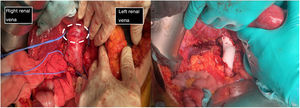
Although there are several therapeutic options, surgical resection with margins (Fig. 3) can lengthen survival, and is currently the only possibility of cure11,15,16. Despite extensive tumour resection, recurrences occur in many patients, but most are haematogenous metastases and not locoregional recurrences16. There are many possibilities for surgical intervention. Due to the small number of cases, it was not possible to determine the best material for cavoplasty, nor the ideal size16,17; we choose cryopreserved grafts. The diameter of the graft is important as it determines flow velocity and adaptability to the native vessel. The use of a prosthesis of a slightly smaller calibre than the inferior vena cava improves flow velocity and the anastomosis on the ring of the prosthesis limits the compression phenomenon11,16. The synthetic materials that can be used include PTFE o Dacron®. PTFE prostheses are currently the most widely accepted for inferior vena cava replacement, ahead of biological grafts10,11. In our case series, cryopreserved pulmonary artery was the most frequently used material for cavoplasty (60%) versus Dacron® (20%) and PTFE (20%) (Fig. 3). In future interventions, it would be interesting to note the calibre of the prosthesis used to evaluate its influence on the results of the intervention. Adjuvant or neoadjuvant treatment with chemotherapy and radiotherapy is controversial15,16. In our centre only one patient received neoadjuvant treatment with radiotherapy. Adjuvant was administered in two patients (adriamycin and trabectedin).
The first image shows the moment when structures were identified prior to excision of the leiomyosarcoma. It depicts the vascular control in the retrohepatic and infrarenal cava and both renal veins prior to tumour removal (tumour marked with white dashed line). The second image shows the presence of a PTFE prosthesis to replace the IVC, both renal veins have been preserved, reinserting the left one.
Great vessel sarcomas (aorta, pulmonary arteries and veins, venae cavae) are classified as luminal and mural18. The former originate from the intima. They are undifferentiated neoplasms more frequent in the thoracic aorta or pulmonary arteries. Histologically they can be similar to leiomyosarcomas, through immunohistochemistry they are positive for markers such as actin and vascular markers such as CD-31 negative for desmin. Sarcomas originating from veins are most often leiomyosarcomas18. Venous leiomyosarcomas are most common in the IVC. Histologically they are identical to leiomyosarcomas found in other sites, and are positive for vimentin, smooth muscle actin, muscle-specific actin and desmin19, and negative for vascular markers such as CD-31.
Examination of the excised tumour reveals a typical pattern of interlacing spindle-shaped cells with eosinophilic cytoplasm and central nuclei. The tumour cells show positivity for desmin, vimentin and smooth muscle cell actin, but not for s-100 protein, alpha inhibin or CD1174,20. It can be classified into different stages according to FNCLCC criteria: grades I, II and III. However, this histological grade does not correlate with worse disease-free time or shorter survival3. In contrast, tumour size does show an association with decreased disease-free time and survival7.
After surgery, some authors recommend long-term anticoagulation to improve patency of the prosthesis; others, however, have reported good results without the need for oral anticoagulation11. The patients in our series in whom prostheses were used had different anticoagulation regimens, followed by permanent low-dose antiplatelet therapy. In the case of the patient who underwent cavorrhaphy, anticoagulation was limited to 10 days postoperatively.
Five years after surgery, 55% remain alive; however, only a minority of patients live longer than 10 years. This survival is not homogeneous and is influenced by a multitude of factors, some of which have already been mentioned7. Almost all patients have recurrence of the disease, mainly haematogenous as in our series. Disease-free survival at 5 years in the published series is only 6%, which is consistent with our series7.
ConclusionLeiomyosarcoma of the vena cava is a rare disease whose diagnostic and therapeutic management cannot be standardised. It constitutes a surgical challenge and surgery should be performed in referral units that include multidisciplinary committees specialised in the management of sarcomas. Surgical resection is currently the main treatment with acceptable results in referral units. Multicentre studies are necessary to gather as much experience as possible in this rare disease.
Conflict of interestsThe authors have no conflict of interests to declare.
Please cite this article as: Pérez-de-Villar JM, Arjona-Sanchez A, Rufián-Andujar B, Valenzuela-Molina F, Sánchez-Hidalgo JM, Rodriguez-Ortiz L, et al. Tratamiento quirúrgico de los leiomiosarcomas de vena cava. Serie de casos en un hospital de tercer nivel y revisión de la literatura. Cir Esp. 2022;100:481–487.