A 43-year-old male with alcoholic cirrhosis underwent EGD for hematemesis which revealed bleeding, grade II, lower esophageal varices that were endoscopically ligated with 6 bands. All the bands remained attached to varices at the completion of EGD. Despite apparent initial hemostasis, balloon tamponade was performed one hour later for suspected continued bleeding. Due to suspected continuing bleeding, EGD was repeated 4 h after initial EGD, and 3 h after balloon tamponade. This EGD revealed the esophageal varices; none of the bands remaining on esophageal mucosa; multiple mucosal stigmata likely from trauma at initial site of variceal bands before dislodgement; and 3 dislodged bands in gastric body, duodenal bulb, or descending duodenum. The patient expired 17 h thereafter from hypovolemic shock. This single report may suggest an apparently novel, balloon tamponade complication: dislodgement of previously placed, endoscopic bands. The proposed pathophysiology is release of bands by stretching entrapped, esophageal mucosa during esophageal balloon tamponade. This complication, if confirmed, might render balloon tamponade a less desirable option very soon after band ligation.
Balloon tamponade is a relatively effective temporizing measure for treating esophageal variceal bleeding that is sometimes used when other therapies are unavailable or are being arranged. An apparently novel complication of balloon tamponade therapy for esophageal varices is reported and a biologically plausible pathophysiology of this complication is proposed.
Case ReportA 43-year-old-male with alcoholic cirrhosis and known esophageal varices presented with hematemesis. Physical examination revealed blood pressure = 105/37 mmHg; pulse = 117 beats/min; pallor; soft, nontender, and protuberant abdomen with shifting dullness; and melena. Blood tests showed: hemoglobin = 2.2 g/dL, platelets = 116,000/mL, albumin = 1.1 g/dL, total-bilirubin = 1.4 mg/dL, and INR = 3.5 [MELD1 (Model-for-end-stage-liver-disease) score = 22]. The patient was intubated; administered octreotide and antibiotics; and transfused multiple units of packed erythrocytes and fresh-frozen-plasma. EGD (esophagogastroduodenoscopy) revealed massively bleeding, grade II, lower esophageal varices, and nonbleeding portal hypertensive gastropathy. An expert, attending endoscopist successfully deployed six bands (Speed-Band-Superview-Super-7, Boston-Scientific, Spencer, IN) on esophageal varices with initial hemostasis. At the conclusion of EGD all 6 bands were identified as still attached to esophageal mucosa. One hour later the same endoscopist, who had considerable experience in Sengstaken-Blakemore tubes, inserted a 16-French, Sengstaken-Blakemore tube (Bard-Inc., Covington City, Georgia 20014) per os for suspected continued bleeding. After verifying proper gastric balloon placement radiographically, the gastric balloon was inflated with 250-cc air, traction was applied, and esophageal balloon tamponade was applied at 40-mmHg-pressure.
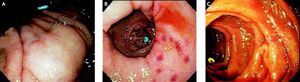
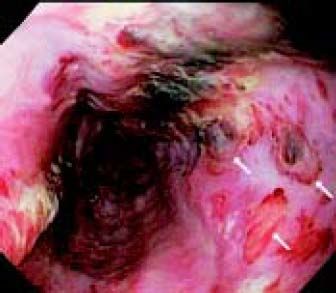
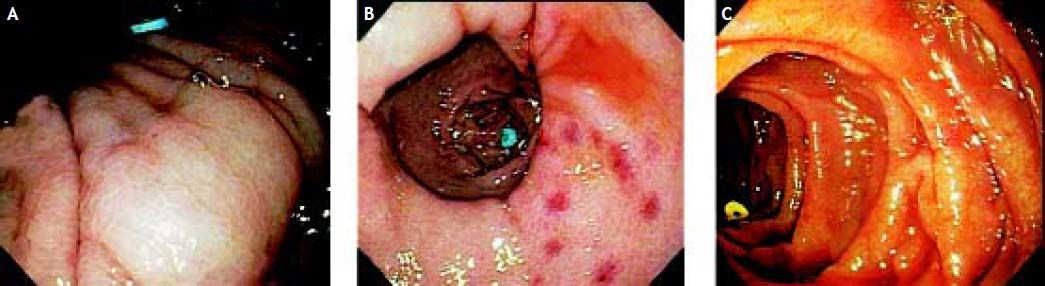
On transfer to William Beaumont Hospital for persistent borderline hypotension and suspected continued bleeding, repeat EGD, performed 4 h after initial EGD and 3 h after Sengstaken-Blakemore tube insertion showed esophageal varices; none of the 6 bands remaining on esophageal mucosa (Figure 1); multiple endoscopic stigmata of mucosal trauma likely at prior band attachment sites (Figure 1, arrows); and 3 dislodged bands in lumen of gastric body, duodenal bulb, or descending duodenum (Figure 2). In consultation with patient’s family, an interventional radiologist declined to perform TIPS (transjugular-intrahepatic-portosystemic-shunt) due to MELD score rising to 24.1 The patient expired 17 h later from hypovolemic shock.
Repeat esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), performed in a patient who underwent initial EGD with placement of 6 variceal bands 4 h earlier and esophageal balloon tamponade 3 h earlier, reveals grey, esophageal varices, and dislodgement of all six variceal bands. Three annular, macular/ mucosal, erythematous, distal esophageal lesions [each about the size and shape of mucosa captured by an endoscopic band (arrows)] likely represent endoscopic stigmata of mucosal trauma at initial site of variceal bands before dislodgement.
Three dislodged variceal bands are identified at EGD: blue band in proximal gastric body (A), blue band in duodenal bulb seen through widely-opened pylorus (B), and yellow band in descending duodenum (C). The finding of three bands still in stomach or duodenum is consistent with recent band dislodgement because of normally rapid, gastroduodenal emptying. Figure 2A also reveals a prominent, pale, snakeskin-patterned lesion, characteristic of portal hypertensive gastropathy. The proposed pathophysiology of the reported, extremely early, dislodgement of all 6 bands (< 4 h after endoscopic placement) is release of bands by stretching entrapped esophageal mucosa during esophageal balloon tamponade.
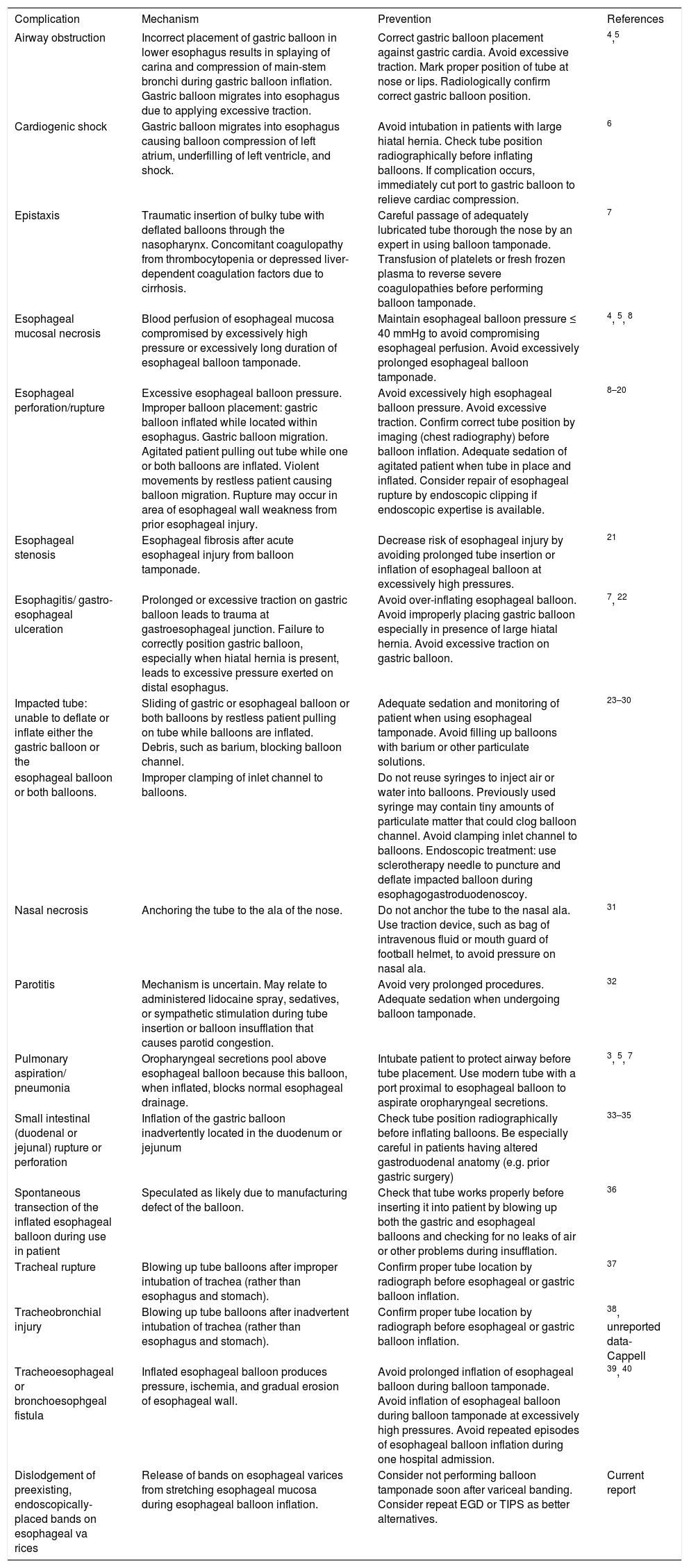
Esophageal variceal bleeding is a common, life-threatening, complication of cirrhosis. Endoscopic banding is the primary initial therapy, often followed by TIPS for the 10-20% of cases when endoscopic banding fails.2 Balloon tamponade is sometimes used as a temporizing measure because of short-term efficacy,3 but is generally considered second-line therapy because of moderately frequent complications (Table 1).3–40
Reported complications of esophageal tamponade for esophageal variceal bleeding.
| Complication | Mechanism | Prevention | References |
|---|---|---|---|
| Airway obstruction | Incorrect placement of gastric balloon in lower esophagus results in splaying of carina and compression of main-stem bronchi during gastric balloon inflation. Gastric balloon migrates into esophagus due to applying excessive traction. | Correct gastric balloon placement against gastric cardia. Avoid excessive traction. Mark proper position of tube at nose or lips. Radiologically confirm correct gastric balloon position. | 4,5 |
| Cardiogenic shock | Gastric balloon migrates into esophagus causing balloon compression of left atrium, underfilling of left ventricle, and shock. | Avoid intubation in patients with large hiatal hernia. Check tube position radiographically before inflating balloons. If complication occurs, immediately cut port to gastric balloon to relieve cardiac compression. | 6 |
| Epistaxis | Traumatic insertion of bulky tube with deflated balloons through the nasopharynx. Concomitant coagulopathy from thrombocytopenia or depressed liver-dependent coagulation factors due to cirrhosis. | Careful passage of adequately lubricated tube thorough the nose by an expert in using balloon tamponade. Transfusion of platelets or fresh frozen plasma to reverse severe coagulopathies before performing balloon tamponade. | 7 |
| Esophageal mucosal necrosis | Blood perfusion of esophageal mucosa compromised by excessively high pressure or excessively long duration of esophageal balloon tamponade. | Maintain esophageal balloon pressure ≤ 40 mmHg to avoid compromising esophageal perfusion. Avoid excessively prolonged esophageal balloon tamponade. | 4, 5, 8 |
| Esophageal perforation/rupture | Excessive esophageal balloon pressure. Improper balloon placement: gastric balloon inflated while located within esophagus. Gastric balloon migration. Agitated patient pulling out tube while one or both balloons are inflated. Violent movements by restless patient causing balloon migration. Rupture may occur in area of esophageal wall weakness from prior esophageal injury. | Avoid excessively high esophageal balloon pressure. Avoid excessive traction. Confirm correct tube position by imaging (chest radiography) before balloon inflation. Adequate sedation of agitated patient when tube in place and inflated. Consider repair of esophageal rupture by endoscopic clipping if endoscopic expertise is available. | 8–20 |
| Esophageal stenosis | Esophageal fibrosis after acute esophageal injury from balloon tamponade. | Decrease risk of esophageal injury by avoiding prolonged tube insertion or inflation of esophageal balloon at excessively high pressures. | 21 |
| Esophagitis/ gastro-esophageal ulceration | Prolonged or excessive traction on gastric balloon leads to trauma at gastroesophageal junction. Failure to correctly position gastric balloon, especially when hiatal hernia is present, leads to excessive pressure exerted on distal esophagus. | Avoid over-inflating esophageal balloon. Avoid improperly placing gastric balloon especially in presence of large hiatal hernia. Avoid excessive traction on gastric balloon. | 7, 22 |
| Impacted tube: unable to deflate or inflate either the gastric balloon or the | Sliding of gastric or esophageal balloon or both balloons by restless patient pulling on tube while balloons are inflated. Debris, such as barium, blocking balloon channel. | Adequate sedation and monitoring of patient when using esophageal tamponade. Avoid filling up balloons with barium or other particulate solutions. | 23–30 |
| esophageal balloon or both balloons. | Improper clamping of inlet channel to balloons. | Do not reuse syringes to inject air or water into balloons. Previously used syringe may contain tiny amounts of particulate matter that could clog balloon channel. Avoid clamping inlet channel to balloons. Endoscopic treatment: use sclerotherapy needle to puncture and deflate impacted balloon during esophagogastroduodenoscoy. | |
| Nasal necrosis | Anchoring the tube to the ala of the nose. | Do not anchor the tube to the nasal ala. Use traction device, such as bag of intravenous fluid or mouth guard of football helmet, to avoid pressure on nasal ala. | 31 |
| Parotitis | Mechanism is uncertain. May relate to administered lidocaine spray, sedatives, or sympathetic stimulation during tube insertion or balloon insufflation that causes parotid congestion. | Avoid very prolonged procedures. Adequate sedation when undergoing balloon tamponade. | 32 |
| Pulmonary aspiration/ pneumonia | Oropharyngeal secretions pool above esophageal balloon because this balloon, when inflated, blocks normal esophageal drainage. | Intubate patient to protect airway before tube placement. Use modern tube with a port proximal to esophageal balloon to aspirate oropharyngeal secretions. | 3, 5, 7 |
| Small intestinal (duodenal or jejunal) rupture or perforation | Inflation of the gastric balloon inadvertently located in the duodenum or jejunum | Check tube position radiographically before inflating balloons. Be especially careful in patients having altered gastroduodenal anatomy (e.g. prior gastric surgery) | 33–35 |
| Spontaneous transection of the inflated esophageal balloon during use in patient | Speculated as likely due to manufacturing defect of the balloon. | Check that tube works properly before inserting it into patient by blowing up both the gastric and esophageal balloons and checking for no leaks of air or other problems during insufflation. | 36 |
| Tracheal rupture | Blowing up tube balloons after improper intubation of trachea (rather than esophagus and stomach). | Confirm proper tube location by radiograph before esophageal or gastric balloon inflation. | 37 |
| Tracheobronchial injury | Blowing up tube balloons after inadvertent intubation of trachea (rather than esophagus and stomach). | Confirm proper tube location by radiograph before esophageal or gastric balloon inflation. | 38, unreported data-Cappell |
| Tracheoesophageal or bronchoesophgeal fistula | Inflated esophageal balloon produces pressure, ischemia, and gradual erosion of esophageal wall. | Avoid prolonged inflation of esophageal balloon during balloon tamponade. Avoid inflation of esophageal balloon during balloon tamponade at excessively high pressures. Avoid repeated episodes of esophageal balloon inflation during one hospital admission. | 39, 40 |
| Dislodgement of preexisting, endoscopically-placed bands on esophageal va rices | Release of bands on esophageal varices from stretching esophageal mucosa during esophageal balloon inflation. | Consider not performing balloon tamponade soon after variceal banding. Consider repeat EGD or TIPS as better alternatives. | Current report |
EGD: esophagogastroduodenoscopy. TIPS: transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt.
This report suggests an apparently novel complication of balloon tamponade: dislodgement of recently-placed, endoscopic bands (Table 1). If confirmed, this complication might render balloon tamponade a relatively undesirable option soon after variceal banding. A second EGD to diagnose and treat the cause of rebleeding or TIPS might generally be better alternatives in industrialized countries where these options are available. However, balloon tamponade may still be considered for severe, active bleeding if the endoscopic banding equipment or TIPS is not readily available, such as hospitals in developing countries or local, community hospitals in industrialized countries. Although one, prospective, controlled trial demonstrated that the efficacy of immediate sclerotherapy is comparable to that of delayed sclerotherapy preceded by balloon tamponade,41 a literature review revealed a lack of data concerning the efficacy of balloon tamponade after endoscopic band ligation failure. This situation is unlikely to change because of decreasing use of balloon tamponade in industrialized countries where TIPS is increasingly used as an alternative to balloon tamponade.
This report has limitations. It is retrospective, comprises one case, and cannot completely exclude band dislodgement before esophageal tamponade. However, the dislodgement of all 6 bands and their extremely early dislodgement (< 4 h after placement) argues for an association between balloon tamponade and band dislodgement. The proposed pathophysiology for band dislodgement is band release by stretching entrapped esophageal mucosa during esophageal balloon tamponade.
Important considerations in preventing complications from balloon tamponade include:
- •
Confirmation of proper location of the balloons before balloon inflation; and
- •
Employment of an expert team with considerable experience in deployment and maintenance of balloon tamponade.
Proper balloon location is confirmed by bedside radiography, ultrasonography,42 or endoscopic placement.43 Physicians and nurses can readily maintain their clinical skills related to balloon tamponade in developing countries where this procedure is still commonly performed. Physicians and nurses in industrialized countries are experiencing decreasing clinical exposure to balloon tamponade due to development of more effective endoscopic or interventional radiologic therapies during the last 20 years. It is important for clinical teams to maintain expertise and quality in balloon tamponade insertion and maintenance in countries in which it is infrequently used. Expertise can be promoted by periodic workshops or review of publications on proper physician and nursing techniques for intubation and maintenance of balloon tamponade.44,45
Financial Disclosure/Conflicts of InterestNone. In particular, Dr. Cappell does not divulge in this paper any confidential, proprietary, pharmaceutical data received in conjunction with his consultancy for the FDA Advisory Committee on Gastrointestinal Drugs.
IRB: case report received hospital IRB exemption/ approval, September 24, 2013.




![Repeat esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), performed in a patient who underwent initial EGD with placement of 6 variceal bands 4 h earlier and esophageal balloon tamponade 3 h earlier, reveals grey, esophageal varices, and dislodgement of all six variceal bands. Three annular, macular/ mucosal, erythematous, distal esophageal lesions [each about the size and shape of mucosa captured by an endoscopic band (arrows)] likely represent endoscopic stigmata of mucosal trauma at initial site of variceal bands before dislodgement. Repeat esophagogastroduodenoscopy (EGD), performed in a patient who underwent initial EGD with placement of 6 variceal bands 4 h earlier and esophageal balloon tamponade 3 h earlier, reveals grey, esophageal varices, and dislodgement of all six variceal bands. Three annular, macular/ mucosal, erythematous, distal esophageal lesions [each about the size and shape of mucosa captured by an endoscopic band (arrows)] likely represent endoscopic stigmata of mucosal trauma at initial site of variceal bands before dislodgement.](https://static.elsevier.es/multimedia/16652681/0000001300000006/v1_201906150917/S1665268119309883/v1_201906150917/en/main.assets/thumbnail/gr1.jpeg?xkr=ue/ImdikoIMrsJoerZ+w96p5LBcBpyJTqfwgorxm+Ow=)