Although there has been an improved management of invasive candidiasis in the last decade, controversial issues still remain, especially in the diagnostic and therapeutic approaches.
AimsWe sought to identify the core clinical knowledge and to achieve high level agreement recommendations required to care for critically ill adult patients with invasive candidiasis.
MethodsA prospective Spanish survey reaching consensus by the DELPHI technique was made. It was anonymously conducted by electronic mail in a first term to 25 national multidisciplinary experts in invasive fungal infections from five national scientific societies, including intensivists, anesthesiologists, microbiologists, pharmacologists and infectious diseases specialists, who answered to 47 questions prepared by a coordination group after a strict review of the literature in the last five years. The educational objectives spanned five categories, including epidemiology, diagnostic tools, prediction rules, and treatment and de-escalation approaches. The level of agreement achieved among the panel experts in each item should exceed 75% to be selected. In a second term, after extracting recommendations from the selected items, a face to face meeting was performed where more than 80 specialists in a second round were invited to validate the preselected recommendations.
ResultsIn the first term, 20 recommendations were preselected (Epidemiology 4, Scores 3, Diagnostic tools 4, Treatment 6 and De-escalation approaches 3). After the second round, the following 12 were validated: (1) Epidemiology (2 recommendations): think about candidiasis in your Intensive Care Unit (ICU) and do not forget that non-Candida albicans–Candida species also exist. (2) Diagnostic tools (4 recommendations): blood cultures should be performed under suspicion every 2–3 days and, if positive, every 3 days until obtaining the first negative result. Obtain sterile fluid and tissue, if possible (direct examination of the sample is important). Use non-culture based methods as microbiological tools, whenever possible. Determination of antifungal susceptibility is mandatory. (3) Scores (1 recommendation): as screening tool, use the Candida Score and determine multicolonization in high risk patients. (4) Treatment (4 recommendations): start early. Choose echinocandins. Withdraw any central venous catheter. Fundoscopy is needed. (5) De-escalation (1 recommendation): only applied when knowing susceptibility determinations and after 3 days of clinical stability. The higher rate of agreement was achieved in the optimization of microbiological tools and the withdrawal of the catheter, whereas the lower rate corresponded to de-escalation therapy and the use of scores.
ConclusionsThe management of invasive candidiasis in ICU patients requires the application of a broad range of knowledge and skills that we summarize in our recommendations. These recommendations may help to identify the potential patients, standardize their global management and improve their outcomes, based on the DELPHI methodology.
This article is also published in Spanish in this issue. It can be found in 10.1016/j.riam.2013.05.005
Aunque en la última década ha mejorado el manejo de la candidiasis invasiva, todavía persisten aspectos controvertidos, en especial por lo que respecta a la estrategia diagnóstica y terapéutica.
ObjetivosIdentificar los conocimientos clínicos esenciales y formular unas recomendaciones con la obtención de un alto grado de consenso, necesarias en la asistencia de pacientes adultos no neutropénicos en estado crítico con candidiasis invasiva.
MétodosSe preparó una encuesta prospectiva cuyo texto se redactó en español, y se obtuvo un consenso mediante técnica DELPHI (un método de reestructuración de un proceso de comunicación con el que se obtiene un grado de consenso de los especialistas sobre el problema planteado). En primer término, se envió de forma anónima por correo electrónico a 25 especialistas nacionales de diferentes disciplinas médicas, expertos en infecciones fúngicas invasivas, de 5 sociedades científicas nacionales, incluidos intensivistas, anestesistas, microbiólogos, farmacólogos e infectólogos, que respondieron a 47 preguntas preparadas por el grupo de coordinación, tras una revisión exhaustiva de los estudios publicados durante los 5 últimos años. Los objetivos educativos contemplaron 5 categorías: epidemiología, instrumentos diagnósticos, scores, estrategias terapéuticas y de desescalada. Para ser seleccionado, el grado de acuerdo alcanzado entre los expertos del panel en cada uno de los ítems debía superar el 75%. En segundo término, después de extraer las recomendaciones de los ítems seleccionados, se celebró una reunión presencial donde se invitó a participar en una segunda ronda a más de 80 especialistas y se les solicitó la validación de las recomendaciones preseleccionadas.
ResultadosEn primer término, se realizó una preselección de 20 recomendaciones (epidemiología 4, scores 3, diagnóstico de laboratorio 4, tratamiento 6 y desescalada 3). Después de la segunda ronda, se validaron las 12 recomendaciones siguientes: 1) Epidemiología (2 recomendaciones): en la Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos considere la candidiasis y no olvide la existencia de especies de Candida diferentes de Candida albicans. 2) Técnicas diagnósticas (4 recomendaciones): ante la más mínima sospecha, es preciso practicar hemocultivos cada 2–3 días y, en caso de obtener un cultivo positivo, cada 3 días, hasta obtener el primer resultado negativo. Si es posible, se obtendrán muestras de fluidos y tejidos estériles (es importante el examen microscópico directo de las muestras). Siempre que sea posible, como instrumentos microbiológicos, deben emplearse métodos diferentes del cultivo. La determinación de la sensibilidad antifúngica es obligatoria. 3) Scores (una recomendación): como instrumento de cribado, se recomienda utilizar el Candida score y determinar la multicolonización en pacientes en alto riesgo. 4) Tratamiento (4 recomendaciones): debe instaurarse el tratamiento de forma precoz. Las equinocandinas son el tratamiento de elección. Es recomendable retirar cualquier vía venosa central insertada. Debe realizarse un estudio del fondo de ojo. 5) Desescalada (una recomendación): solo aplicable cuando se confirme la sensibilidad a fluconazol y después del transcurso de 3 días de estabilidad clínica. El mayor acuerdo se alcanzó en la optimización de los instrumentos microbiológicos y en la retirada del catéter, mientras que el menor correspondió al de desescalada y a los scores.
ConclusionesEn pacientes ingresados en la Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, el manejo de la candidiasis invasiva requiere la aplicación de la amplia serie de conocimientos y habilidades resumidas en nuestras recomendaciones. Estas pueden ayudar a identificar a los pacientes potenciales, estandarizar su manejo global y mejorar su desenlace, en función de la metodología DELPHI.
Este artículo está publicado en español en este mismo número. Puede encontrarlo en 10.1016/j.riam.2013.05.005
The incidence of candidemia in non-neutropenic critically ill patients has significantly increased in the past years.7–9 In our country, the estimated incidence of candidemia is 4.3 episodes/105 habitants,5 of which 33–55% of the cases are located in the Intensive Care Units (ICU),11 although this percentage may have decreased in the last few years.
In addition to the increased incidence, a change in the distribution of the different Candida species has been observed.47Candida albicans continues to be the predominant species in the ICU,35 representing approximately half of the isolates. According to a recent epidemiological study published,49Candida parapsilosis and Candida glabrata are the second and third most common isolated species in our country.
In addition to the important financial burden on the health systems, Candida infections and candidemia are associated to elevated high mortality rate in critically ill patients. Candidemia is associated in the United States with a 14.5% increase of the mortality rate in adults, and a 10% increase in pediatric patients.66 On the other hand, the crude mortality rates and mortality rates associated to invasive candidiasis have been established at 40–78% and 20–40%, respectively.18,56
During the last few years, new antifungal agents have offered different alternatives in the treatment of invasive candidiasis. However, and due to the heterogeneity of the recommendations from the different scientific societies,2,15,47 the most effective therapeutic strategy has not yet been established, resulting in a remarkable lack of consensus when establishing the diagnosis and most appropriate treatment for this patient population.
The main objective of this research study is to analyze the present situation in the management of invasive candidiasis in non-neutropenic critically ill patients in our country's hospitals. For this purpose, between January and September 2012, a panel of specialists from 5 scientific societies was formed – The Spanish Association of Mycology (AEM) as promoter, the Spanish Society of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology (SEIMC); the Spanish Society of Anesthesiology, Reanimation and Pain Therapeutics (SEDAR); The Spanish Society of Critical, Intensive and Coronary Medicine Units (SEMICYUC); and the Spanish Society of Chemotherapy (SEQ) – with extensive experience in the treatment of non-neutropenic critically ill patients, who were requested to complete a questionnaire elaborated by the 5 coordinators responsible for the research, after having made a thorough review of the literature of the last five years. In the cases in which no consensus was reached, the experts detailed the reasons for the divergent opinions.
Once the coordinating group selected several recommendations, a second face to face meeting was held with 80 specialists from the entire national geography, who commonly care for critically ill adult patients with invasive candidiasis, who voted and validated the preselected recommendations.
MethodsThe panel of specialists was composed of 25 specialists with a wide geographical distribution in our country, pertaining to the five scientific societies collaborating in the research. The criteria of inclusion were based on their experience in the research of candidemia and on the prognostic and clinical management of non-neutropenic critically ill patients with a suspected or confirmed onset of invasive candidiasis.
The DELPHI technique was used to carry out the study with the objective of optimizing the consultation process of the 25 panel members. Specifically, the DELPHI methodology enables group opinions, and not merely individual opinions, from the experts in the different areas of information provided by the coordinators. A consensus greater than 75% (19–25 participants) was required in each of the questions formulated. In the cases in which the majority of the responses to a given question were shared by 15–18 participants, the degree of consensus was established as medium, whereas in those cases in which consensus was only shared by 14 or less experts, the degree of consensus was defined as low.
The 47 total questions elaborated by the coordinators (Table 1) are distributed in five different sections or specialties: Epidemiological section, 6 questions (developed by E.M. and P.L.); Scores section, 5 questions (developed by A.R. and R.Z.); Laboratory diagnosis section, 14 questions (developed by R.Z. and A.R.); Treatment section, 11 questions (developed by P.L. and E.M.); and Therapeutic de-escalation section, 9 questions (developed by R.F. and R.Z.).
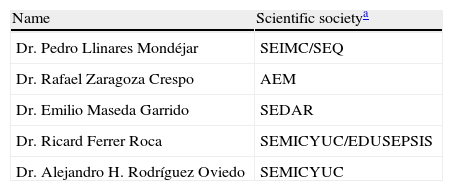
Épico Study. List of coordinators.
| Name | Scientific societya |
| Dr. Pedro Llinares Mondéjar | SEIMC/SEQ |
| Dr. Rafael Zaragoza Crespo | AEM |
| Dr. Emilio Maseda Garrido | SEDAR |
| Dr. Ricard Ferrer Roca | SEMICYUC/EDUSEPSIS |
| Dr. Alejandro H. Rodríguez Oviedo | SEMICYUC |
EDUSEPSIS: Proyecto Educacional en Sepsis Español.
The Spanish Association of Mycology (AEM) as promoter, the Spanish Society of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology (SEIMC); the Spanish Society of Anesthesiology, Reanimation and Pain Therapeutics (SEDAR); The Spanish Society of Critical, Intensive and Coronary Medicine Units (SEMICYUC); and the Spanish Society of Chemotherapy (SEQ).
The study was carried out in two phases. In the first one, and with the objective of detecting the degree of consensus, between May 18 and 29, 2012, the 25 specialists (Table 2) completed anonymously on Internet the categorical and metric scale questionnaire (majority). The coordinators responsible for the systematic search of the literature to elaborate the questions did not answer the questionnaire.
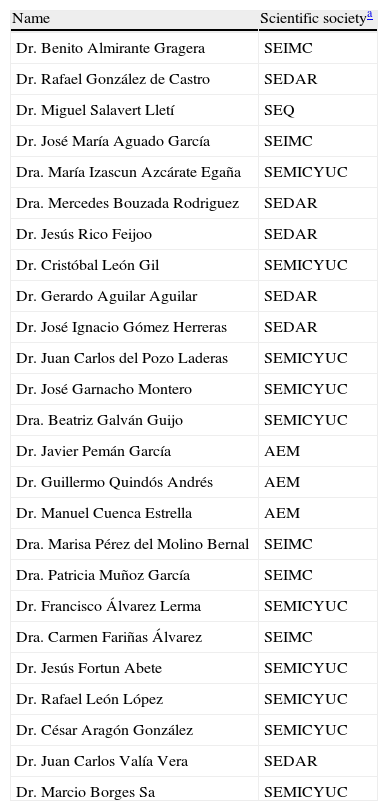
List of experts who participated in the Épico Study.
| Name | Scientific societya |
| Dr. Benito Almirante Gragera | SEIMC |
| Dr. Rafael González de Castro | SEDAR |
| Dr. Miguel Salavert Lletí | SEQ |
| Dr. José María Aguado García | SEIMC |
| Dra. María Izascun Azcárate Egaña | SEMICYUC |
| Dra. Mercedes Bouzada Rodriguez | SEDAR |
| Dr. Jesús Rico Feijoo | SEDAR |
| Dr. Cristóbal León Gil | SEMICYUC |
| Dr. Gerardo Aguilar Aguilar | SEDAR |
| Dr. José Ignacio Gómez Herreras | SEDAR |
| Dr. Juan Carlos del Pozo Laderas | SEMICYUC |
| Dr. José Garnacho Montero | SEMICYUC |
| Dra. Beatriz Galván Guijo | SEMICYUC |
| Dr. Javier Pemán García | AEM |
| Dr. Guillermo Quindós Andrés | AEM |
| Dr. Manuel Cuenca Estrella | AEM |
| Dra. Marisa Pérez del Molino Bernal | SEIMC |
| Dra. Patricia Muñoz García | SEIMC |
| Dr. Francisco Álvarez Lerma | SEMICYUC |
| Dra. Carmen Fariñas Álvarez | SEIMC |
| Dr. Jesús Fortun Abete | SEMICYUC |
| Dr. Rafael León López | SEMICYUC |
| Dr. César Aragón González | SEMICYUC |
| Dr. Juan Carlos Valía Vera | SEDAR |
| Dr. Marcio Borges Sa | SEMICYUC |
The Spanish Association of Mycology (AEM) as promoter, the Spanish Society of Infectious Diseases and Clinical Microbiology (SEIMC); the Spanish Society of Anesthesiology, Reanimation and Pain Therapeutics (SEDAR); The Spanish Society of Critical, Intensive and Coronary Medicine Units (SEMICYUC); and the Spanish Society of Chemotherapy (SEQ).
The questions that did not achieve the necessary consensus – the answers of the majority of the participants should coincide with at least 19–25 experts to reach a consensus of 75%, usually required in the DELPHI studies – were included in the second phase, carried out between June 8 and 14, 2012 on Internet, with the anonymous participation of 22 of the 25 specialists included in the initial phase.
The second phase aimed to identify the reasons that explained for the different opinions among the experts. Likewise, the coordinators, responsible for the analysis and identification of the questions with greatest deviation of opinion, were not included in the second phase.
After this, as explained above, the list of recommendations was validated in the face to face meeting held on September 15, 2012.
ResultsFirst phase – DELPHI expertsEpidemiological section1.-Among the risk factors that may affect critically ill patients, in your opinion, to what extent do you believe the development of invasive candidiasis is important?
Rationale: Candida species are a significant cause of infection in critically ill patients.31,34,56,63 The results of the EPIC II study, carried out with 13,796 adult patients admitted to 1265 ICUs in 76 countries, evidenced that 51% of the patients presented an infectious process, with Candida being the third microorganism responsible of the infection (17% of the patients infected) after Staphylococcus aureus (20.5%) and Pseudomonas (19.9%).29 In USA, Candida infection was the main cause of fungal infection in hospitalized patients.66 In addition, the incidence of Candida infections in the ICUs has increased in different countries throughout the last few years.9
A large majority of the experts consulted (88%) confirmed the importance of suffering candidiasis among the risk factors that could affect critically ill patients. Specifically, and based on a 0–10 point scale, where 10 represents the maximum level of importance, 22 experts granted 7 or more points to candidiasis. The average score was established at 7.7 points, with a standard deviation of 1.9 points. The consensus level achieved was high (>75%).2.-To what extent do you consider candidemia an important factor of mortality associated with critically ill patients?
Rationale: Invasive candidiasis is a major cause of direct and indirect mortality in neutropenic and non-neutropenic critically ill patients. The crude mortality rates associated with invasive candidiasis are 40–78% and 20–40%, respectively.18,56 In USA, candidemia is associated with a 14.5% increase of mortality in adults, as well as 10% in pediatric patients.66 Nevertheless, invasive candidiasis in immunocompromised patients with cancer can be a severe marker, whereas it is difficult to differentiate mortality directly attributable to invasive candidiasis from that of a concurrent infection or an underlying tumor disease.
Seventy-six percent of the expert panel members considered candidemia a very important mortality factor associated with critically ill patients. Specifically, and based on a scale of 0–10 points, 19 experts granted 7 or more points to candidemia as a mortality factor. The average score was 7.4 points, with a standard deviation of 2.2 points. The degree of consensus reached by the experts was high (>75%).3.-To what extent do you consider the distribution of Candida species in the last few decades, as well as its impact on the antifungal susceptibility patterns, important factors?
Rationale: In the last few years, a change in the distribution of Candida species in ICUs has been experimented.47,60C. albicans is still the predominant species in the ICUs,35 followed by C. parapsilosis and C. glabrata59, and approximately 15% has a low susceptibility to fluconazole. Also, the distribution of species varies with age: the incidence of candidemia due to C. glabrata increases with age, opposite to what occurs with C. parapsilosis and Candida tropicalis.52
Approximately 85% of the experts consulted consider the change in the distribution of Candida species in the last few years very relevant, as well as its impact on the antifungal susceptibility patterns. Specifically, and using a 0–10 point scale, 21 experts granted 7 or more points to the change in the distribution of the Candida species. The average score was 7.6 points, with a standard deviation of 1.8 points. The degree of consensus achieved was high (>75%).4.-To what extent do you consider important the identification of risk factors predisposing to Candida infections when the species might be other than C. albicans?
Rationale: Studies have identified several factors predisposing to infections caused by other species of Candida different from C. albicans (predominantly C. glabrata and Candida krusei). Among these, prior triazole therapy, gastrointestinal tract surgery in the 30 days prior to the onset of candidemia, as well as patients over 65 years of age, can be highlighted.60 These factors should be taken into account since C. glabrata and C. krusei are both potentially resistant to fluconazole.24 For its part, the emergence of C. parapsilosis has been associated with younger ages, the administration of echinocandins and deficient control practices, while C. tropicalis is particularly common in neutropenic patients with an underlying hematological disease.52,59
The vast majority of the specialists consulted (92%) consider the identification of risk factors that may favor the emergence of Candida species, other than C. albicans, of utmost importance. Specifically, being 10 points the highest score and 0 the lowest, 23 experts granted 7 or more points to the importance of identifying these risk factors. The average score was 8.5 points, with a standard deviation of 1.4 points. The degree of consensus achieved was again very high (>75%).5.-To what extent do you consider important the evaluation of the clinical features of critically ill patients, taking into account that they can condition the presentation of invasive candidiasis?
Rationale: Invasive candidiasis can present as isolated candidemia, non-documented invasive candidiasis or a combination of both. Prior surgery and patients with solid tumors are significantly more frequent in patients with invasive candidiasis, while prior antibiotic therapy, neutropenia and hematological tumors are significantly more common in patients with candidemia.34 Additionally, the crude mortality rate due to candidemia in critically ill patients remains high and is related to the host (diagnosis upon admission to the ICU), and not to the variables of the treatment.56 Metastatic processes occur in a considerable proportion of the patients in the ICU with candidemia and care must be given to possible secondary foci.
A large majority of the experts consulted (88%) highlighted the importance of evaluating the clinical features of critically ill patients, since they can condition the appearance of candidiasis. Specifically, and based on a scale of 0–10, where 10 represents the maximum level of importance, 22 experts granted 7 or more points to the evaluation of clinical features. The average score was established at 8.2 points, with a standard deviation of 1.4 points. The degree of consensus reached was high (>75%).6.-Indicate your level of agreement with the following statements: (1) Candida species are a determining factor in mortality associated with invasive candidiasis. (2) The underlying disease is a determining factor in mortality associated with invasive candidiasis
Rationale: In addition to an adequate control of the infectious focus, the infectious process is conditioned by three factors: the susceptibility of the infecting organism23,61; the virulence of the organism6,26; and the severity of the underlying disease.20,23C. krusei, C. tropicalis and C. glabrata have been associated with an elevated rate of mortality, while C. parapsilosis has been associated with a low pathogenicity. The severity of the underlying disease is an important mortality factor and, in fact, the total mortality is greater in candidemic critically ill patients, than in the general population. In the study of Marriott et al.,36 the age, the diagnoses upon admission to the ICUs (other than polytraumatisms) and the mechanical ventilation upon onset of the candidemia, were independent mortality factors in the multivariate analysis. Recent studies have evidenced that the use of echinocandins and the early administration of antifungal therapy resulted in lower mortality rates of invasive candidiasis.6 Perhaps the benefits of optimized antifungal treatment are hidden in ICU patients by a severe underlying disease affecting mortality.
(1) Close to 85% of the panel members consider Candida species a determining factor of mortality associated with candidiasis. Specifically, on a scale of 1–5 points, in which 5 represents the maximum level of agreement, 21 experts granted 4 or 5 points in favor. The average score was established at 4.1 points. A high degree of consensus was reported (>75%).
(2) When considering an underlying disease as a determining factor of mortality associated with candidiasis, total consensus was achieved. Based on 1–5 point scale, the 25 experts consulted granted 4 or 5 points in favor, establishing an average of 4.8 points.
Scoresection1.-On what factors do you base the initiation of antifungal therapy in patients with severe sepsis, fever, broad-spectrum antibiotic treatment and negative culture results?
The coordinators responses: Risk Factors, Candida Score, Multicolonization, Markers, Poor evolution.
The majority of the experts consulted based the initiation of antifungal treatment in patients with severe sepsis, fever, broad-spectrum antifungal therapy and negative blood culture results on risk factors (8 experts) or the Candida Score (8 experts). Only 1 specialist claimed to base treatment on markers, while multicolonization or poor evolutions were options selected in each case by 4 of the experts. A medium degree of consensus was achieved (>50% and <75%).2.-Multicolonization is one of the factors contemplated in the Candida Score. Do you consider the evaluation of multicolonization indispensable to use the Candida Score?
Rationale: Studies published in the literature have demonstrated that multicolonization is a prognostic factor in proven candidiasis,32 and the colonization index is directly correlated to invasive fungal infection.3
An ample majority of the experts consulted (83%) considered indispensable the evaluation of multicolonization to use the Candida Score. Specifically, based on a 0–10 point scale, where 10 is of utmost importance, 21 experts granted 7 or more points to the evaluation of clinical features. The average score was 8.0 points, with a standard deviation of 1.9 points. A high degree of consensus was achieved (>75%).3.-To what extent do you use the corrected colonization index (CCI) to guide the treatment of invasive candidiasis?
Rationale: The Pittet Index or CCI (ratio of highly positive samples/total number of samples analyzed) was described in surgical patients and demonstrated that a corrected colonization with a threshold of >0.4 has a positive predictive value54 and a 100%55 negative predictive value on the development of invasive candidiasis.
Seventy-six percent of the experts consulted confirmed they do not use the corrected colonization index (CCI) to guide the treatment of invasive candidiasis, or only used it sporadically. Specifically, 10 experts confirmed the use of CCI ‘in some cases’ and 9 did not use it ‘in any case’, while 6 admitted its use ‘in the majority of the cases’. A high degree of consensus was reached (>75%).4.-In how many cases out of ten, concerning patients at risk of acquiring invasive fungal infection, do you use the Candida Score to guide the treatment of invasive candidiasis?
Rationale: The Candida Score is useful to evaluate the risk of developing invasive fungal infections, with a low positive predictive value and a very high negative predictive value. Therefore, it is highly improbable that non-neutropenic critically ill patients colonized with Candida, having a Candida Score below 3, are at risk of developing invasive candidiasis.33 Then, only patients with a Candida Score exceeding 2.5 will be benefited from the administration of early antifungal therapy.32
Seventy-two percent of the experts consulted confirmed the use of the Candida Score to evaluate the risk of developing invasive fungal infections. Specifically, 18 of the experts confirmed that they used this score in at least 7 out of 10 non-neutropenic critically ill patients with Candida spp. colonization, while 3 used it in 6 patients, 2 in 5 patients, 1 in 4 patients and 1 expert in no case. The experts reached a medium degree of consensus (>50% and <75%).
Taking into account that the question did not achieve a minimum degree of consensus in accordance with the DELPHI technique, it was included in the second phase, in which the experts were asked to explain why they did not use the Candida Score on a regular basis in these situations. Among the explanations offered, we highlight: (1) ‘It has a poor positive predictive value; it's only useful to not administer antifungal therapy, since the negative predictive value is very good’. And (2) ‘There are difficulties for obtaining surveillance cultures; even when they have been performed, since results are only obtained after 72hours, early treatment that reduces the rate of mortality is impeded’.5.-To what extent do you agree on only using a rectal sample and urine to detect colonization?
Rationale: An important contribution resulting from the CAVA Study33 is the independent identification of predictive values of invasive candidiasis, from each of the colonization sample locations, limiting the number of samples for colonization evaluation to those that are significant: rectal sample and urine.
Eighty percent of the experts consulted considered the use of a rectal sample and urine sufficient for detecting colonization. Specifically, based on a 0–10 point scale, where 10 is the maximum level of importance, 20 experts granted 7 or more points to the exclusive use of both samples. The average score was 7.4 points, with a standard deviation of 2.5 points. A high degree of consensus was achieved.
Laboratory diagnostic section1.-In your opinion, and in suspected cases of invasive candidiasis, which frequency would you recommend to perform blood cultures?
Rationale: At present, hemocultures are the gold standard in diagnosing invasive candidiasis.16,17,51 However, this technique only offers a sensitivity of 50% in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis.51 Therefore, a higher number of tests could increase this diagnostic rate.
Ninety-two percent of the experts consulted recommended performing hemocultures on a daily basis or, at least, every two or three days. Specifically, 6 experts advocated performing them on a daily basis and 16 every two or three days, while 1 specialist recommended performing hemocultures once a week, and 2 to perform only one hemoculture and wait for results. A high degree of consensus was achieved (>75%).2.-Indicate to what extent you request each of the following two diagnostic tests to diagnose non-candidemic invasive candidiasis
2.1.-Test on sterile fluids and/or tissue specimens
2.2.-Direct microscopy of sterile fluids and/or tissue specimens
Rationale: Nowadays, it is very difficult to diagnose non-candidemic invasive candidiasis with certainty,25 since it requires the histological identification of Candida tissue invasion and/or evidence of the yeast presence in sterile fluids.16,22
Regarding question 2.1, the large majority (96%) of the experts consulted considered very important to request the test on sterile fluids and/or tissue to accurately diagnose invasive candidiasis. Specifically, based on a scale of 0–10 points, where 10 represents the highest level of importance, 24 experts granted 7 or more points to this diagnostic test. The average score was 9.1 points, with a standard deviation of 1.3 points.
With respect to question 2.2, 84% of the experts consulted considered the direct microscopy of sterile fluids and/or tissue samples to diagnose invasive candidiasis very relevant. Specifically, based on a 0 to 10 point scale, 21 experts granted 7 or more points to this diagnostic test. The average score was 8.2 points, with a standard deviation of 1.4 points. Both questions achieved a high degree of consensus (>75%).
2.3.-In the case of a patient with suspected peritonitis caused by Candida, to what extent do you consider necessary sending perioperative samples to the Microbiology laboratory?
Rationale: In cases of suspected peritonitis caused by Candida spp., the diagnosis should be preferably based on the analysis of perioperative samples of fluid and/or peritoneal tissue,43,62,69 a diagnostic test that has demonstrated a high prognostic value.19
The complete panel considered necessary sending perioperative samples of fluids and/or peritoneal tissue in cases of suspected peritonitis caused by Candida necessary. In fact, the entire panel granted 7 or more points to this statement, for which a high degree of consensus was achieved.3.-Do you consider the isolation of Candida from respiratory samples a diagnosis of candidiasic pneumonia?
Rationale: Sixty percent of the non-neutropenic critically ill patients are colonized with Candida when the stay in ICU exceeds 7 days.25 However, and despite the remarkable frequency of isolation of Candida in the respiratory tract, Meersseman et al.,39 in a study that lasted 2 years, observed the complete absence of cases of candidiasic pneumonia in the autopsies performed on patients with evidences of pneumonia, thus confirming that pneumonia caused by Candida is extremely unusual in patients in ICUs.16
All of the experts consulted did not consider the isolation of Candida in the respiratory tract samples of critically ill patients sufficient to diagnose candidiasic pneumonia. Specifically, 18 experts did not consider isolation in any case, while 7 confirmed that they could consider this option only in certain specific cases. The highest degree of consensus was reached, 100%.4.-In accordance with the epidemiological changes in invasive candidiasis, do you consider that in cases of proven invasive candidiasis, it is important to know the susceptibility pattern to the different antifungal agents?
Rationale: During the last decades, the main epidemiological trend in invasive candidiasis in ICUs and Oncology Units has been the decrease of Candida albicans, contrasting with the increase of non-C. albicans–Candida species, very especially C. glabrata, C. tropicalis, C. krusei and C. parapsilosis.35,47,60,66 In this context, the IDSA guidelines published in 2009 established the recommendation of carrying out susceptibility studies only in cases of treatment failure, as well as testing fluconazole in those with C. glabrata isolates.47
The vast majority (96%) of the experts consulted highlighted the relevance of knowing the susceptibility to the different antifungal agents in cases of confirmed invasive candidiasis. Specifically, based on a 0–10 point scale to value its importance, 24 experts granted 7 or more points to the need of establishing the susceptibility to the drug treatment. The average score was 8.8 points, with a standard deviation of 1.2 points. The level of consensus achieved was high, exceeding 75%.5.-In your opinion, to what extent do you consider useful the measurement of procalcitonin in serum for the diagnosis of suspected candidemia?
Rationale: Procalcitonin measurement in serum seems to be very precise discerning between bacteremia and non-infectious inflammatory conditions in critically ill patients with clinical signs of sepsis.13 Two studies performed in non-neutropenic and/or surgical patients determined that seric procalcitonin is lower in candidemia than in bacteremia, both presenting high negative predictive values below 2 and 5ng/ml.12,37
Seventy-six percent of the experts consulted highlighted the usefulness of procalcitonin measurement in the diagnosis of suspected candidemia. Specifically, 4 specialists consider it ‘very useful’, while 15 define the procalcitonin measurement as ‘quite useful’. A high degree of consensus was achieved, exceeding 75%.6.-At present, to what extent do you consider the use of non-culture based methods of microbiological diagnostic techniques necessary for the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis?
Rationale: The combination of traditional diagnostic methods with non-culture based microbiological tools could be the clue to improve the diagnosis and prognosis of fungemias in critically ill patients.25,50,51,62 To date, results published on the detection of (1,3)-β-d-glucan, galactomannan, mannan and anti-mannan, Candida albicans germ tube antibodies or nucleic acid are promising and could be very useful to guide early antifungal treatment. In general, it is recommended as screening once or twice a week in critically ill patients with risk factors, especially in surgical patients, after 5–7 days of hospitalization.50 However, and still today, non-culture based methods for microbiological diagnosis are not available in the majority of the hospitals in our country.
Eighty percent of the experts consulted considered the use of non-culture based methods for the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis very necessary. Specifically, based on a scoring scale of importance from 0 to 10 points, 19 experts granted 7 or more points to the need for this microbiological diagnosis. The average score was 8.0 points, with a standard deviation of 1.7 points. A high degree of consensus was reached.7.-To what extent would you use the combined detection of mannan antigen and antimannan antibodies for the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis, if this technique was available in your hospital?
Rationale: The detection of mannan antigen and antimannan antibodies against Candida antigen in an ELISA format has been useful in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis16,51 and has been commercialized for many years. Also, with the objective of avoiding the poor performance of these techniques when used separately, the joint implementation of these tests in all patients with suspected invasive candidiasis is recommended.41
The majority of the experts consulted did not share a general opinion regarding the convenience of using combined detection of mannan antigen and anti-mannan antibodies in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis. Specifically, 5 and 8 specialists, respectively, considered their use in ‘almost all cases’ and ‘in the majority of the cases’. On the contrary, 12 experts considered that their use is only convenient ‘in some cases’. A medium degree of consensus was achieved, 52% (>50% and <75%). Therefore, this question was included in the second phase of the DELPHI study.8.-To what extent do you use the (1,3)-β-d-glucan detection as a diagnostic tool for invasive candidiasis?
Rationale: The detection of betaglucan, by means of a technique presently available in the market, offers high specificity16,25,42,51 and positive predictive value (PPV)1,33,45 in patients with probable or confirmed IFI.
The responses revealed a divergent behavior among the experts consulted with respect to how often (1,3)-β-d-glucan testing should be used in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis. Specifically, 16 experts, 64% of the sample, considered its use in ‘only some cases’ or ‘in no case’, while 7 and 2 specialists responded that it should be used ‘in the majority of the cases’ or ‘in almost all cases’. A medium degree of consensus of 64% was reached, so the question was selected for the second phase of the DELPHI study.9.-To what extent do you use the indirect immunofluorescence method (C. albicans IFA IgG, Vircell) for the detection of anti-mycelial antibodies in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis, if this technique is available in your hospital?
Rationale: Indirect immunofluorescence (C. albicans IFA IgG, Vircell) for the detection of Candida albicans germ tube antibodies (CAGTA) shows high sensitivity and specificity in cases of candidemia,51,67,68 which could be crucial in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis in surgical ICU patients.59
The majority of the experts consulted did not share a general pattern of behavior in relation to how often they used CAGTA detection in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis. Only 13 experts, 52% of the sample, considered its use in ‘only some cases’ or ‘in no case’, while 9 and 3 specialists, respectively, responded that they use it ‘in the majority of the cases’ or ‘almost always’. A medium degree of consensus was reached. The question was selected for the second phase of the DELPHI Study.10.-To what extent do you use nucleic acids detection in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis, if molecular methods of polymerase chain reaction (PCR) techniques are available in your hospital?
Rationale: New molecular detection methods of real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), as evidenced in numerous articles in the literature,16,30,38,51,65 are an interesting alternative for the quick diagnosis of invasive candidiasis.
The answers reveal the absence of a general pattern of behavior among the majority of the experts consulted. Only 13 experts, 52% of the sample, consider the detection of nucleic acids in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis necessary in ‘only some cases’ or ‘in no case’, while 7 and 5 specialists, respectively, answered that it should be performed ‘in the majority of the cases’ or ‘in almost all cases’. A medium degree of consensus was achieved, 52%, for which the question was selected to be included in the second phase of the study.
Since the questions regarding the non-culture based method of microbiological techniques, questions 7–10, did not achieve the minimum consensus in the DELPHI technique, the 22 experts participating in the second phase of the study were consulted on the mannan antigen and anti-mannan antibody techniques, (1,3)-β-d-glucan detection, anti-mycelial antibody detection, and nucleic acids detection. They answered about which of these tests they would recommend for the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis. The responses identified (1,3)-β-d-glucan detection, chosen by 10 experts, and the detection of nucleic acids, chosen by 8 experts, as the techniques most widely recommended by the specialists consulted.11.-Indicate your level of agreement with the following statements: (1) The combination of several non-culture based microbiological methods can provide a better diagnosis of invasive candidiasis and, (2) The combination of scores of clinical prediction, together with the use of nonculture based methods of microbiological techniques, can be adequate strategies to initiate early invasive candidiasis treatment.
Rationale: The use of the different non-culture based methods, such as the mannan antigen/antimannan antibodies, beta-glucan detection and, very especially, the detection of nucleic acids by PCR, may significantly assist in the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis.4 Also, the combination of the tests with traditional diagnostic methods could be the clue to improve both the diagnosis, as well as the prognosis of invasive candidiasis in critically ill patients.51
1) Ninety-six percent of the experts consulted indicated that combining various techniques can provide a better diagnosis in invasive candidiasis. Specifically, based on a scale of 1–5 points, where 5 represents the highest score, 24 experts granted 4 or 5 points to the statement. The average score was 4.8 points. A high degree of consensus was achieved, exceeding 75%.
2) The combination of scores and non-culture based methods of microbiological techniques was considered an adequate strategy, achieving full consensus. Based again on a scale of 1–5 points, the 25 experts consulted granted 4 or 5 points to the statement, establishing an average of 4.8 points.
Treatment section1.-Do you consider the use of echinocandins as a first-line choice of treatment for invasive candidiasis?
Rationale: The recommendations established in the Clinical Practice Guidelines of the different national and supranational societies2,15,47 have caused some controversy on the treatment of invasive candidiasis. In this context, a work carried out by Andes et al.6 demonstrated that the treatment with echinocandins is associated to a significant decrease of the mortality rate due to invasive candidiasis.
Seventy-six percent of the experts consulted, 19 out of the 25 specialists, consider that echinocandins should be the first-choice antifungal therapy for invasive candidiasis in all cases, regardless of whether the patient had a history of recent azole exposure. A high degree of consensus was reached (>75%).
The specialists who agreed that echinocandins should be the first-line antifungal therapy only in patients, who have received prior azole therapy, were consulted in the second phase of the study and explained the reasons that justify their answer. We display below two of the reasons offered by the specialists: (1) ‘It depends on the epidemiology of the center and the characteristics of the patient. If the patient is stable and has not received previous azole therapy in a hospital with prevalence of C. albicans strains, I find no reason to administer echinocandins’. And (2) ‘It is evident that the affirmative response to the statement, ‘do you consider necessary prior azole therapy’ is not correct. I believe that there are certain specific situations in which fluconazole could be indicated in patients with documented candidemia with sensitivity to this antifungal agent (in 70–80% of the occasions) and with clinical stability (…)’.2.-To what extent do you agree with the administration of echinocandins at higher doses than the standard recommended for the treatment of endocarditis caused by Candida or other types of invasive candidiasis?
Rationale: Clinical trials have demonstrated the efficacy and confirmed the safety of the echinocandin therapy at higher doses than the standard-dose therapy in the management of invasive candidiasis.10,48 Thus, IDSA guidelines published in 2009 established the possibility of administering higher doses of echinocandins for the treatment of endocarditis caused by Candida.47
The responses reveal the divergent opinions encountered among the experts consulted with respect to administering higher doses of echinocandins in the treatment of endocarditis caused by Candida. Specifically, based on a scale from 1 to 5 points, where 5 represents the highest level of agreement, only 13 specialists (52%) claimed to be ‘somewhat in agreement’ or ‘totally in agreement’, granting 4 or 5 points to the administration of higher doses. The average was 3.4 points and a medium degree of consensus was reached (>50% and <75%).
The question did not achieve the minimum consensus contemplated in the DELPHI technique, for which it was selected to be included in the second phase of the study, where the experts who favored the administration of higher doses of echinocandins in the treatment of endocarditis caused by Candida or other types of invasive candidiasis, were asked to indicate their motives. We display two of the reasons the specialists mentioned: (1) ‘It is considered in clinical trials and experts’ opinions. Also, it is mentioned in the IDSA guidelines published in 2009 regarding the treatment of endocarditis.’ And (2) ‘Due to the seriousness of invasive candidiasis or endocarditis, optimization of the treatment, according to the Pk/Pd target based on the AUC/MIC ratio, is a priority in reaching levels of the focus. Also, these drugs have linear pharmacokinetics and few adverse effects’.3.-In the case of a critically ill patient on an echinocandin therapy, with C. parapsilosis isolates detected in blood cultures, please indicate your level of agreement with each of the following two statements: (1) echinocandin therapy should be substituted by fluconazole, regardless of the patient's clinical evolution, and (2) fluconazole should be administered together with an echinocandin, until clinical improvement is observed.
Rationale: The recommendations established in the Clinical Practice Guidelines of different national societies2,47 have raised some controversy regarding the treatment of choice for invasive candidiasis due to C. parapsilosis. In this context, while Pfaller et al.53 concluded that fluconazole was superior to candins in the treatment of C. parapsilosis due to the mutations of the fks genes of Candida, the Kale-Pradhan et al. study demonstrated the non-inferiority of the efficacy of echinocandins against other antifungal agents in the treatment of invasive candidiasis caused by C. parapsilosis.28
(1) Sixty percent of the experts consulted disagreed with the convenience of changing the treatment. Specifically, based on a scale of 1–5 points, where 5 is the highest score, 15 experts granted 1 or 2 points to this statement. The average score was 2.6 points. A medium degree of consensus was achieved. The question was selected to be included in the second phase of the DELPHI study, in which the degree of divergence was similar.
(2) Sixty-four percent of the experts consulted disagreed with the convenience of combining fluconazole and an echinocandin. Specifically, based on a scale of 1–5 points to evaluate the level of disagreement, 16 experts granted 1 or 2 points to the statement. The average score was established at 2.3 points. A medium degree of consensus was reached.4.-In case you consider that patients with candidemia should receive an ophthalmological evaluation, when would you carry it out?
Rationale: Few studies in the literature address eye disorders during candidemia. In this context, while chorioretinitis is the most common disorder described (9–16%), a much lower percentage of cases of endophthalmitis have been reported (1.6%).27,46 However, and contrary to that established in the recommendations of the Clinical Practice Guidelines,15,47 the need for an ophthalmological evaluation in all patients with candidemia is considered in few situations.
The large majority of the experts consulted (96%) considered an ophthalmological evaluation necessary in patients with candidemia, either during the first week or between the first and second weeks. Only one specialist indicated that the ophthalmological evaluation should not be carried out on a conscious patient without clinical signs. Therefore, a high degree of consensus was achieved.5.-In the case of a patient with candidemia on an echinocandin therapy with ocular involvement, should the treatment be switched to another antifungal agent?
Rationale: The eye is a protected compartment, for which the degree of penetration of systemic antifungal agents varies significantly.47 According to evidence reported by Ridell et al.,57 neither echinocandins nor posaconazole achieve adequate therapeutic concentrations in the vitreous. In contrast, voriconazole has been defined as the most effective antifungal agent in the treatment of ocular manifestations.
Seventy-two percent of the experts consulted considered that, in patients with candidemia and ocular involvement treated with echinocandins, treatment should switch to another antifungal agent ‘in all cases’ or ‘in the majority of the cases’. On the contrary, 3 specialists considered that the change of treatment should only be made ‘in some cases’, 3 that the change ‘does not necessarily need to be made’, and 1 that the change ‘depends on the clinical evolution’. A high degree of consensus was reached.6.-In your opinion, should the central venous catheter be removed in all critically ill patients with candidemia?
Rationale: The convenience of withdrawing or maintaining the central venous catheter (CVC) in patients with candidemia has raised controversy in different publications. Specifically, and while studies have not demonstrated the benefit associated with the withdrawal of the CVC,44 several articles confirm that its removal has reported a statistically significant improvement in the survival of the patients.6,40,60
Absolute consensus among the experts consulted on the need to withdraw the central venous catheter in all cases of candidemia was achieved (100%).7.-In your opinion, to what extent does the risk of hepatotoxicity affect the election of a specific echinocandin?
Rationale: The degree of hepatic dysfunction (child) can condition the election and dosage of each of the echinocandins, due to their distinct metabolism and pathway of elimination. The Wang et al.64 study showed that 9.3% of the patients treated with echinocandins presented high liver enzyme levels, although there was no need to interrupt the treatment.
Fifty-six percent of the experts consulted considered that the risk of hepatotoxicity has ‘considerable influence’ or ‘much influence’ on the election of the type of echinocandin administered. Specifically, based on a scale of 1–5 points, where 5 is the maximum level of influence, 15 experts granted 4 or 5 points. The average score was established at 2.6 points. A medium degree of consensus was achieved.8.-Please indicate your level of agreement with the following statement: ‘Empirical therapy of fluconazole in critically ill patients with invasive candidiasis should not be used. It should only be administered in cases where the species and susceptibility of Candida have been established in hemodynamically stable patients’
Rationale: The indication for fluconazole treatment in critically ill patients has changed in the last few years.2,15 Both C. glabrata and C. krusei are potentially fluconazole-resistant.24
Sixty percent of the specialists consulted agree with the statement. Specifically, based on a scale of 1–5 points to evaluate the level of agreement, 15 experts granted 4 or 5 points to this statement. The average was 3.6 points and a medium degree of consensus was achieved.9.-Do you consider that all patients with candidemia should be screened for endocarditis by a transesophageal echocardiography?
Rationale: The possibility of candidemia causing an infective endocarditis is a critical component in its clinical management, requiring a longer treatment, and valve surgery should be seriously considered in the majority of the patients.23
Seventy-two percent of the experts consulted considered that the transesophageal echocardiography for screening endocarditis in patients with candidemia should only be performed in exceptional cases. In contrast, 3 and 4 specialists hold that it should be carried out ‘in all cases’ and ‘in the majority of the cases’, respectively. A medium level of consensus was reached.10.-Can the type of antifungal agent administered in the treatment of invasive candidiasis reduce the mortality rate associated to invasive candidiasis?
Rationale: Numerous publications have demonstrated that the election of the antifungal agent plays an essential role in the survival of critically ill patients with invasive candidiasis. Echinocandin therapy is associated with significantly reduced mortality.6 On the other hand, prior therapy with azoles is considered a mortality risk factor.26,60
An ample majority of the experts consulted (92%) considered that the type of antifungal agent used in the treatment of invasive candidiasis can reduce the mortality associated with invasive candidiasis. Therefore, based on a scale of 1–5 points, where 5 represents the maximum level of agreement, 23 experts granted 4 or 5 points to this statement.11.-Can early invasive candidiasis treatments reduce mortality rates associated with invasive candidiasis?
Rationale: Delayed invasive candidiasis treatment in critically ill patients is associated to increased mortality.23,61 In this context, however, the Marriott et al. study36 did not observe any relationship between the rate of mortality and the start date of the treatment.
All the experts consulted (100%) considered that early invasive candidiasis treatment can reduce mortality associated with invasive candidiasis. A high degree of consensus was reached.
Therapeutic de-escalation section
Rationale: Susceptibility patterns to antifungal agents vary depending on the Candida species. C. albicans, C. tropicalis and C. parapsilosis are usually susceptible to fluconazole, while C. glabrata is generally susceptible dose-dependent or resistant, and C. krusei is intrinsically resistant.70 Fluconazole achieved better results than candins in the treatment of C. parapsilosis due to mutations in the fks genes of Candida.53
In the treatment of candidemia in non-neutropenic patients, fluconazole is recommended in stable patients with no history of azole exposure. In hemodynamically unstable patients (APACHE II≥15) or patients with criteria of severe sepsis or having received previous azole therapy or suspected azole-resistant candidemia, empirical echinocandin therapy is recommended.15,47
Determining the susceptibility to antifungal agents could be useful for optimizing antifungal treatment, including de-escalation to fluconazole.14,58 However, susceptibility in vitro tests are not carried out in all centers for several reasons, such as the delay in receiving the results and their cost. The identification of the species, as well as the determination of the susceptibility to antifungal agents, requires 5 days on average. On the other hand, determining the susceptibility to antifungal agents has proven to be cost-effective in the context of candidemia and could help to identify patients with drug-resistant Candida species receiving inappropriate treatment and patients who would be candidates for de-escalation to fluconazole.58
Based on experts’ opinions, IDSA Guidelines suggest that susceptibility testing of fluconazole should routinely be performed against C. glabrata and other Candida species that do not respond to empirical antifungal therapy or if resistance to azole antifungals is highly suspected.47
The de-escalation of antifungal therapy is not usually well protocolized; it is not done on a regular basis and there is a lack of supportive scientific evidence, especially in critically ill patients. To optimize the appropriate use of antimicrobials to achieve the maximum effectiveness, reduce the adverse effects and administer a cost-effective treatment, we must ensure the correct initial antifungal therapy, but also de-escalate when possible in terms of antimycotic efficacy and reduced costs.14,58
Antifungal de-escalation should be guided by microbiological results, antifungal susceptibility, the concomitant medication the patient is taking and clinical evolution. This information is usually not available until after 5 days, so the decision to de-escalate is often taken late.1.-In proven invasive candidiasis caused by C. albicans in patients on empirical echinocandin therapy, should treatment always be de-escalated to fluconazole, regardless of the clinical condition?
Rationale: Antifungal therapy should be based on the Candida species and clinical condition of the patient.58 Therefore, empirical echinocandin therapy is recommended in hemodynamically unstable patients (APACHE II≥15) or patients with criteria of severe sepsis.15,47 Also, the Andes et al.6 study demonstrated that echinocandin therapy was associated to significantly decreased mortality due to invasive candidiasis.
Seventy-six percent of the experts consulted did not agree that it is always convenient to de-escalate to fluconazole, regardless of the patient's clinical condition, in proven invasive candidiasis due to C. albicans in patients on empirical echinocandin therapy. Specifically, based on a scale of 1–5 points, where 5 represents the maximum level of agreement, 19 experts granted 1 or 2 points to the statement. The average score was established at 2.0 points. A high degree of consensus was achieved (>75%).2.-Can treatment be de-escalated, regardless the isolate is susceptible to fluconazole or not, in proven invasive candidiasis due to C. albicans in patients on empirical echinocandin therapy?
Rationale: The susceptibility of C. albicans to fluconazole is very high. In the study of Zulaga et al.70, 95.2% of the isolates of C. albicans were susceptible to fluconazole, and no resistant isolates were identified.
Eighty percent of the experts consulted considered that in proven invasive candidiasis due to C. albicans in patients receiving empirical echinocandin therapy de-escalation should not be considered without determining the susceptibility to fluconazole. Specifically, based on a 1–5 point scale to evaluate the level of agreement, 20 experts granted 1 or 2 points to the statement. The average score was 2.0 points, and a high degree of consensus was achieved.3.-In proven invasive candidiasis caused by C. glabrata in patients receiving empirical echinocandin therapy, always de-escalate to fluconazole, regardless of the patient's clinical condition.
Rationale: The use of fluconazole is recommended in the treatment of candidemia in non-neutropenic stable patients, without prior azole therapy. The use of empirical echinocandin therapy is recommended in hemodynamically unstable patients (APACHE II≥15) or those with criteria of severe sepsis, prior azole therapy or suspected invasive candidiasis due to azole-resistant Candida.15,47
The vast majority of the experts consulted (96%) considered that the clinical condition of the patient must be considered before de-escalating to fluconazole in proven invasive candidiasis caused by Candida glabrata in patients receiving empirical echinocandin therapy. Thus, based on a 1–5 point scale, where 5 represents the maximum level of agreement, 24 experts granted 1 or 2 points to this statement. A high degree of consensus was achieved.4.-In proven invasive candidiasis caused by C. glabrata in patients receiving empirical echinocandin therapy, de-escalation can be performed regardless of determining the susceptibility to fluconazole.
Rationale: The 2009 IDSA guidelines recommend performing antifungal susceptibility tests only in cases of therapeutic failure, although they also recommend these tests for fluconazole susceptibility in those C. glabrata isolates recovered from the patients.47 As reported in the study of Garnacho-Montero et al.,24C. glabrata is potentially fluconazole-resistant. On the other hand, the study of Collins et al.14 concluded that performing fluconazole susceptibility tests in those C. glabrata isolates from patients with proven invasive candidiasis provided improved outcomes, not only in economic, but clinical terms.
Ninety-six percent of the experts consulted considered that in proven invasive candidiasis due to C. glabrata in patients receiving empirical echinocandin therapy, de-escalation should not be performed without previously determining the fluconazole-susceptibility. Specifically, based on a 1–5 point scale to evaluate the level of agreement, 24 experts granted 1 or 2 points to the statement. The average score was 1.2 points. Once again, a high degree of consensus was achieved.5.-Patients with infection caused by C. krusei with favorable evolution and receiving empirical echinocandin therapy should be de-escalated to voriconazole.
Rationale: C. krusei is intrinsically fluconazole-resistant.22 On its part, voriconazole presents a superior activity than fluconazole against C. krusei.21
Seventy-six percent of the specialists consulted considered that in patients with an infection caused by C. krusei, with favorable evolution and on empirical echinocandin therapy, de-escalation to voriconazole is not adequate. Specifically, based on a 1–5 point scale, where 5 represents the maximum level of agreement, 19 experts granted 1 or 2 points to the statement. The average score was 1.8 points and a high degree of consensus was reached.
The question was selected for the second phase of the DELPHI Study to learn about the reasons why some experts considered de-escalation to voriconazole adequate under the already mentioned circumstances. We display below two of the reasons offered by the specialists: (1) ‘If the clinical evolution is good, C. krusei also displays high susceptibility to voriconazole and very low MICs, for which it would be a very good option’. And (2) ‘This is a fully valid alternative, accepted in different guidelines. If there are not contraindications for the use of voriconazole (and as long as we have plasma level determinations), de-escalating or switching to oral therapy is always an alternative.6.-In patients receiving antifungal therapy for suspected but unproven invasive candidiasis, after 5 days of good clinical evolution, what action would you take?
The responses showed enormous disparity between the opinions of the experts consulted in relation to the measures to be taken in this situation. Thus, 7 specialists (28%) would opt for suspending the antifungal therapy; 6 experts (24%) would continue with the same treatment during 14 days; 6 specialists would de-escalate to an azole; and 2 experts (8%) did not know what measure to take. In conclusion, a low degree of consensus was achieved (<50%).7.-In patients receiving antifungal therapy for suspected but unproven invasive candidiasis, after 10 days without good clinical improvement, what action would you take?
Seventy-six percent of the experts consulted think that in patients with antifungal therapy due to suspected but unproven invasive candidiasis, in whom clinical improvement is not observed after 10 days, the antifungal therapy should be stopped and the patient should be checked again. Also, 3 specialists assured they would only modify the treatment, while 2 would continue treatment for 14 days and 1 would add another antifungal agent. The degree of consensus achieved was high.8.-In patients with candidemia caused by a fluconazole-susceptible Candida species, initially treated with an echinocandin and being the patient stable, when do you believe the treatment should be changed to fluconazole oral therapy?
The large majority of the experts consulted (84%) believe that in patients with candidemia caused by a fluconazole-susceptible species of Candida, who have initially received echinocandin therapy and that are stable, fluconazole oral therapy should be given within a maximum period of two or three days after stabilization. A high degree of consensus was established.
Although the question achieved sufficient consensus in accordance with the DELPHI methodology, the 4 experts that considered necessary a period longer than 2–3 days after stabilization, were asked in the second phase of the current study to indicate the motives that justify their response. We display below two of the reasons provided by the specialists: (1) ‘First of all, in the context of a critically ill patient, oral therapy can only be administered on few occasions, despite its excellent absorption by the digestive tract. In second place, and although there are no supportive studies, I believe that 2 or 3 days is a very short period. The guidelines recommend 7 to 10 days. Personally, I do it after 5–7 days, as long as the evolution is favorable, the CVC has been removed in case of being the origin of the infection and it is fluconazole-susceptible’. And (2) ‘The basic issue of this question is the underlying belief that the patient can have an infection due to fluconazole-resistant species. The microbiological susceptibility testing in vitro is not exactly equivalent to that in vivo. Therefore, I do not believe that linking the stability of the patient and the antifungal susceptibility to the same result is reasonable’.9.-In general, critically ill patients with invasive candidiasis should not be de-escalated.
Seventy-two percent of the experts consulted considered adequate to de-escalate in invasive candidiasis in critically ill patients. Specifically, based on a 1–5 point scale, where 5 represents the maximum level of agreement, 18 experts granted 1 or 2 points to the statement. A medium degree of consensus was reached, below 76%.
First phase recommendationsAfter having the results of the DELPHI methodology applied to non-neutropenic critically ill patients with suspected or proven invasive candidiasis, the following 20 recommendations were developed (Table 3) based on the questions that achieved a high level of agreement, subsequently validated in the meeting in person with the hospital panel experts.
First 20 recommendations.
| Epidemiological section |
| 1. Since the incidence of patients with invasive candidiasis admitted to intensive care units has increased in the last decades, consider early treatment in critically ill patients with an infectious process |
| 2. The most common fungal infections in critically ill patients are caused by Candida species and, although C. albicans is still the species that produces the majority of the candidiasis, consider that non C. albicans–Candida species are found with increased frequency, exceeding C. albicans in some series |
| 3. While it is essential to know the local epidemiology in critically ill patients with invasive candidiasis, consider the possibility of fluconazole-resistant Candida species in neutropenic patients with chronic renal failure, who have received previous triazole therapy |
| 4. Since certain Candida species, such as C. tropicalis, C. krusei and C. glabrata have been associated with high mortality in critically ill patients, consider the early use of efficient antifungal agents against these species |
| Scores section |
| 1. Determining the Candida Score should be a screening tool in all critically ill patients with invasive candidiasis |
| 2. Investigate the presence of multicolonization in all patients at risk |
| 3. Associate biomarkers detection to the Candida Score |
| Diagnostic laboratory section |
| 1. Perform blood cultures at the time of suspected invasive candidiasis and every 2–3 days, provided the infection persists. In case of a positive result, perform controls until a negative result is obtained |
| 2. Submit sterile fluids and tissues for fungal culture and use direct microscopy whenever possible |
| 3. In patients with suspected invasive candidiasis, use the routine non-culture based microbiological technique, if available in your center |
| 4. In patients with proven invasive candidiasis, request an antifungal susceptibility study |
| Treatment section |
| 1. Start early treatment at the time of considering the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis, since early treatment is associated to lower mortality rates |
| 2. An echinocandin should be the first-choice empirical treatment in critically ill patients, regardless of prior administration of azole therapy |
| 3. Only in special situations in hemodynamically stable patients without prior azole therapy and with knowledge of a local epidemiology, treatment with azoles can be considered |
| 4. At least one ophthalmological evaluation is recommended in all patients with candidemia at risk of developing chorioretinitis and endophthalmitis, since an ocular involvement is a marker of prolonged treatment |
| 5. The antifungal treatment should be changed in patients with ocular involvement and on echinocandin therapy, due to its poor penetration |
| 6. Whenever possible, remove the central catheter in patients with candidemia |
| Therapeutic de-escalation section |
| 1. In critically ill patients with proven invasive candidiasis due to C. albicans or C. glabrata receiving empirical echinocandin therapy, consider de-escalating to fluconazole treatment if clinical stability is present and the species is fluconazole-susceptible |
| 2. In critically ill patients with proven invasive candidiasis by a fluconazole-susceptible Candida species that are receiving empirical echinocandin therapy, consider de-escalating to fluconazole 2 or 3 days after achieving clinical stability |
| 3. In patients receiving antifungal therapy due to suspected invasive candidiasis that has not been proven by the tenth day and show no clinical improvement, suspend the antifungal treatment and reevaluate the patient |
Using the same methodology, 80 experts met in person to vote the recommendations described in Table 3. Only those that achieved a consensus over 75% were chosen. Please, find the final recommendations in Table 4.
The 12 Épico final recommendations.
| Epidemiological section |
| 1. Since the incidence of patients with invasive candidiasis admitted to intensive care units has increased in the last decades, consider early treatment in critically ill patients with an infectious process |
| 2. While it is essential to know the local epidemiology in critically ill patients with invasive candidiasis, consider the possibility of fluconazole-resistant Candida species in neutropenic patients with chronic renal failure, who have received previous triazole therapy |
| Scores section |
| 1. As a screening tool, investigate the presence of candidiasic multicolonization and determine the Candida Score in all critically ill patients with suspected invasive candidiasis |
| Laboratory diagnostic section |
| 1. Perform blood cultures at the time of suspected invasive candidiasis and every 2–3 days, provided the infection persists. In case of a positive result, perform hemoculture controls until a negative result is obtained |
| 2. Submit sterile fluids and tissues for fungal culture and use direct microscopy whenever possible |
| 3. In patients with suspected invasive candidiasis, use the routine non-culture based microbiological technique, if available in your center |
| 4. In patients with proven invasive candidiasis, request an antifungal susceptibility study |
| Treatment section |
| 1. Start early treatment, at the time of considering the diagnosis of invasive candidiasis |
| 2. An echinocandin should be the first-line choice of empirical therapy in critically ill patients |
| 3. At least one ophthalmological evaluation is recommended in all patients with candidemia. In case of ocular involvement, consider the poor penetration of echinocandins |
| 4. Whenever possible, remove the central catheter in patients with candidemia |
| Therapeutic de-escalation section |
| 1. In critically ill patients with proven invasive candidiasis by a fluconazole-susceptible Candida species that are receiving empirical echinocandin therapy, consider de-escalating to fluconazole after 2 or 3 days of clinical stability |
The management of patients with suspected or proven invasive candidiasis requires a great deal of knowledge. The recommendations developed, based on the DELPHI methodology, summarize this knowledge for educational purposes and can assist in the early identification of potential patients, standardize its management and improve prognostic performance.
Conflict of interestsThis consensus has been sponsored by MSD Laboratories, Spain.
Carmen Romero and Ainhoa Torres (Entheos editorial group) for their excellent work and dedication to this project.
LIST OF COORDINATORS, PARTICIPANTS AND PRACTICING PHYSICIANS COORDINATORS
COORDINATORS
Rafael Zaragoza Crespo
Servicio de Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario Dr. Peset. Valencia
Pedro Llinares Mondéjar
Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Complejo Hospitalario Universitario A Coruña
Emilio Maseda Garrido
Servicio de Anestesiología, Hospital Universitario La Paz. Madrid.
Ricard Ferrer Roca
Servicio de Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario Mútua de Terrassa. Barcelona
Alejandro H. Rodríguez Oviedo
Servicio de Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario Juan XXIII. Tarragona
EXPERTS
Benito Almirante Gragera
Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Universitari Vall d’Hebron. Barcelona
Rafael González de Castro
Servicio de Anestesiología, Hospital Universitario de León. León.
Miguel Salavert Lletí
Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Universitario y Politécnico La Fe. Valencia
José María Aguado García
Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre: Madrid
María Izascun Azcárate Egaña
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario de Donostia. Guipúzcoa
Jesús Rico Feijoo
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital Universitario Río Hortega. Valladolid
Cristóbal León Gil
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario de Valme. Sevilla.
Gerardo Aguilar Aguilar
Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital Clínico Universitario de Valencia
José Ignacio Gómez Herreras
Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital Clínico Universitario de Valladolid
Juan Carlos del Pozo Laderas
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario Reina Sofia. Córdoba
José Garnacho Montero
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Virgen del Rocio. Sevilla
Beatriz Galván Guijo
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario La Paz. Madrid
Javier Pemán García
Microbiología, Hospital Universitario La Fe. Valencia
Guillermo Quindós Andrés
Inmunología, Microbiología y Parasitología, Facultad de Medicina y Odontología, Universidad del País Vasco
Manuel Cuenca Estrella
Microbiología, Centro Nacional de Microbiología, Instituto de Salud Carlos III. Madrid.
Maria Luisa Pérez del Molino Bernal
Microbiología y Parasatología, Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Santiago de Compostela
Patricia Muñoz García
Microbiología y Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Universitario Gregorio Marañón. Madrid
Francisco Álvarez Lerma
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitari del Mar. Barcelona
Carmen Fariñas Álvarez
Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla. Santander
Jesús Fortún Abete
Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Ramón y Cajal. Madrid.
Rafael León López
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario Reina Sofía. Córdoba
César Aragón González
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Carlos Haya. Málaga
Juan Carlos Valía Vera
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Consorcio Hospital General Universitario de Valencia
Marcio Borges Sa
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Son Llàtzer. Palma de Mallorca
Mercedes Bouzada
Servicio de Anestesiología de Reanimación y Tratamiento del Dolor. Hospital Clínico Universitario de Santiago de Compostela
PRACTICING PHYSICIANS
Luis Suárez Gonzalo
Unidad de Reanimación y Cirugía Cardiotorácica, Hospital La Paz. Madrid
Cruz Soriano Cuesta
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital La Paz. Madrid
Esther López Ramos
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Universitario Príncipe de Asturias. Madrid
Fernando Arméstar Rodríguez
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Germans Trias i Pujol de Badalona. Barcelona
Eva Benveniste Pérez
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Germans Trias i Pujol de Badalona. Barcelona
Francisco Javier González de Molina Ortíz
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario Mútua Terrassa. Barcelona
Jordi Vallés Daunis
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Parc Taulí. Barcelona
Susana Sancho Chinesta
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Universitario Dr. Peset. Valencia
Roberto Reig Valero
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital General de Castelló. Castellón
Francisco López Medrano
Unidad de Enfermedades Infecciosas, Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre. Madrid
Miguel Angel Alcalá Llorente
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario Fundación Jimenez Díaz. Madrid
María José Pérez-Pedrero Sánchez-Belmonte
Servicio de Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Virgen de la Salud. Toledo
Mercedes Catalán González
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario 12 de Octubre. Madrid.
Paula Vera Artazcoz
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital de la Santa Creu i Sant Pau. Barcelona
Montserrat Vallverdú Vidal
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario Arnau de Vilanova Lleida
Alejandra García Roche
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitari Vall d’Hebron. Barcelona
Manuel Jesús Rodríguez Carvajal
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Juan Ramón Jimenez. Huelva
Angel Caballero Sáez
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital San Pedro. Logroño
Emilio Díaz Santos
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital de Sant Joan Despí Moisès Broggi. Barcelona
Teresa Tabuyo Bello
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Complejo Hospitalario Universitario A Coruña
Juan Ramón Fernández Villanueva
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Clínico Univertisario de Santiago de Compostela
María Teresa Rey Rilo
Anestesiología, Hospital Universitario Fundación Jiménez Díaz-Capio. Madrid
Vicente Torres Pedrós
Anestesiología, Hospital Universitario Son Espases. Palma de Mallorca
María Aranda Pérez
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Son Llàtzer. Palma de Mallorca
Ángel Arenzana Seisdedos
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Virgen Macarena. Sevilla
Rafael García Hernández
Servicio de Anestesiología, Hospital Universitario. Puerta del Mar. Cádiz
Antonio Ayelo Navarro
Servicio de Anestesiología, Hospital General Almansa. Albacete
José Luis Antón Pascual
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital San Juan de Alicante
Carlos Castillo Arenal
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital de Txagorritxu. Álava
Nuria Gonzalez Jorrín
Unidad de Reanimación, Hospital Donostia. Guipúzcoa
Francisco Esteve Urbano
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario de Bellvitge. Barcelona
Francisco Álvarez Lerma
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitari del Mar. Barcelona
Gonzalo Tamayo Medel
Unidad de Reanimación, Hospital Universitario Cruces. Vizcaya
Unai Bengoetxea Uriarte
Unidad de Reanimación, Hospital Universitario Basurto, Vizcaya
Juan Carlos Pardo Talavera
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Morales Meseguer. Murcia
Roberto Jiménez Sánchez
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital General Universitario Santa Lucía. Murcia
Guillermo Quindós Andrés
Inmunología, Microbiología y Parasitología, Facultad de Medicina y Odontología, Universidad del País Vasco
Violeta Fernández García
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital Universitario Central de Asturias. Oviedo
Pedro Picatto Hernández
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital Universitario Central de Asturias. Oviedo
Armando Blanco Vicente
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario Central de Asturias. Oviedo
José Castaño Pérez
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Virgen de las Nieves. Granada
María Victoria de la Torre Prados
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Virgen de la Victoria. Málaga
José Manuel Soto
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Clínico Universitario San Cecilio. Granada
César Aragón González
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Regional Sas Carlos Haya. Málaga
Ana Loza Vázquez
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario de Valme. Sevilla
Fernando Maroto Monserrat
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital San Juan de Dios. Sevilla
José Garnacho Montero
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Virgen del Rocío. Sevilla
Estrella Terradillos Martín
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital Gregorio Marañón. Madrid
José Peral Gutiérrez de Ceballos
Medicina Intensiva, UCI, Hospital General Universitario Gregorio Marañón. Madrid
Luis Quecedo Gutiérrez
Servicio de Anestesiología, Hospital de la Princesa. Madrid
Javier García Cortés
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital Universitario de Gran Canaria Dr. Negrín. Las Palmas de Gran Canaria
Catalina Sánchez Ramírez
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario de Gran Canaria Dr. Negrín. Las Palamas de Gran Canaria
Marta Gurpegui Puente
Medicina Intensiva, UCI Polivalente, Hospital Universitario Miguel Servet. Zaragoza
Pilar Luque Gómez
Medicina Intensiva y Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Clínico Universitario “Lozano Blesa” de Zaragoza
María Reyes Iranzo Valero
Servicio de Anestesiología, Hospital Universitario Puerta de Hierro. Madrid
Isidro Prieto del Portillo
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Ramón y Cajal. Madrid
Luis Gajate Martín
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital Ramón y Cajal. Madrid
Manuel Cervera Montes
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Arnau de Vilanova. Valencia
María Ángeles Ballesteros Sanz
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario Marqués de Valdecilla. Santander
María del Valle Ortiz
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Universitario de Burgos
Eduardo Tamayo Gómez
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital Clínico de Valladolid
Felipe Bobillo de Lamo
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Clínico de Valladolid
María Clara García Bernardo
Servicio de Anestesiologíanestesia y Reanimación, Hospital del Río Ortega. Valladolid
Miguel Angel Pereira Loureiro
Servicio de Anestesiología y, Reanimación y UCI, Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Vigo
María Milagros Cid Manzano
Servicio de Anestesiología, Complexo Hospitalario de Ourense
María Elena Vilas Otero
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Vigo
Jorge Ángel Pereira Tamayo
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Vigo
Marina Varela Durán
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Complejo Hospitalario Universitario de Pontevedra
José Ricardo Gimeno Costa
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitai i Politecnic La Fe. Valencia
Ignacio Moreno Puigdollers
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital Universitari i Politecnic La Fe. Valencia
María Teresa Recio Gómez
Medicina Intensiva, Complejo Hospitalario de Cáceres
Juan Francisco Machado Casas
Medicina Intensiva, Complejo Hospitalario de Jaén
Rafael Léon López
Medicina Intensiva, Hospital Universitario Reina Sofía. Córdoba
Silverio Salvador Antoni
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital General Universitario de Alicante
Carolina Giménez Esparza
Unidad de Cuidados Intensivos, Hospital Vega Baja de Orihuela. Alicante
Joaquín Lobo Palanco
Medicina Intensiva, Complejo Hospitalario de Navarra
Rocío Armero Ibáñez
Servicio de Anestesiología y Reanimación, Hospital Universitario Dr. Peset. Valencia