The Rhinovirus (HRV) belongs to the Enterovirus genus in the Picornaviridae family and is a positive-sense single-stranded RNA virus. Commonly accountable for respiratory tract infections, which include common colds. It is yet unknown how to treat HRV infection.
MethodsThis study employed robust immunoinformatics techniques to predict the B-cell, CTL, and HTL epitopes on the Genome Polyprotein. Both non-allergic and antigenic epitopes were chosen in order to produce a subunit vaccine that patients could receive.
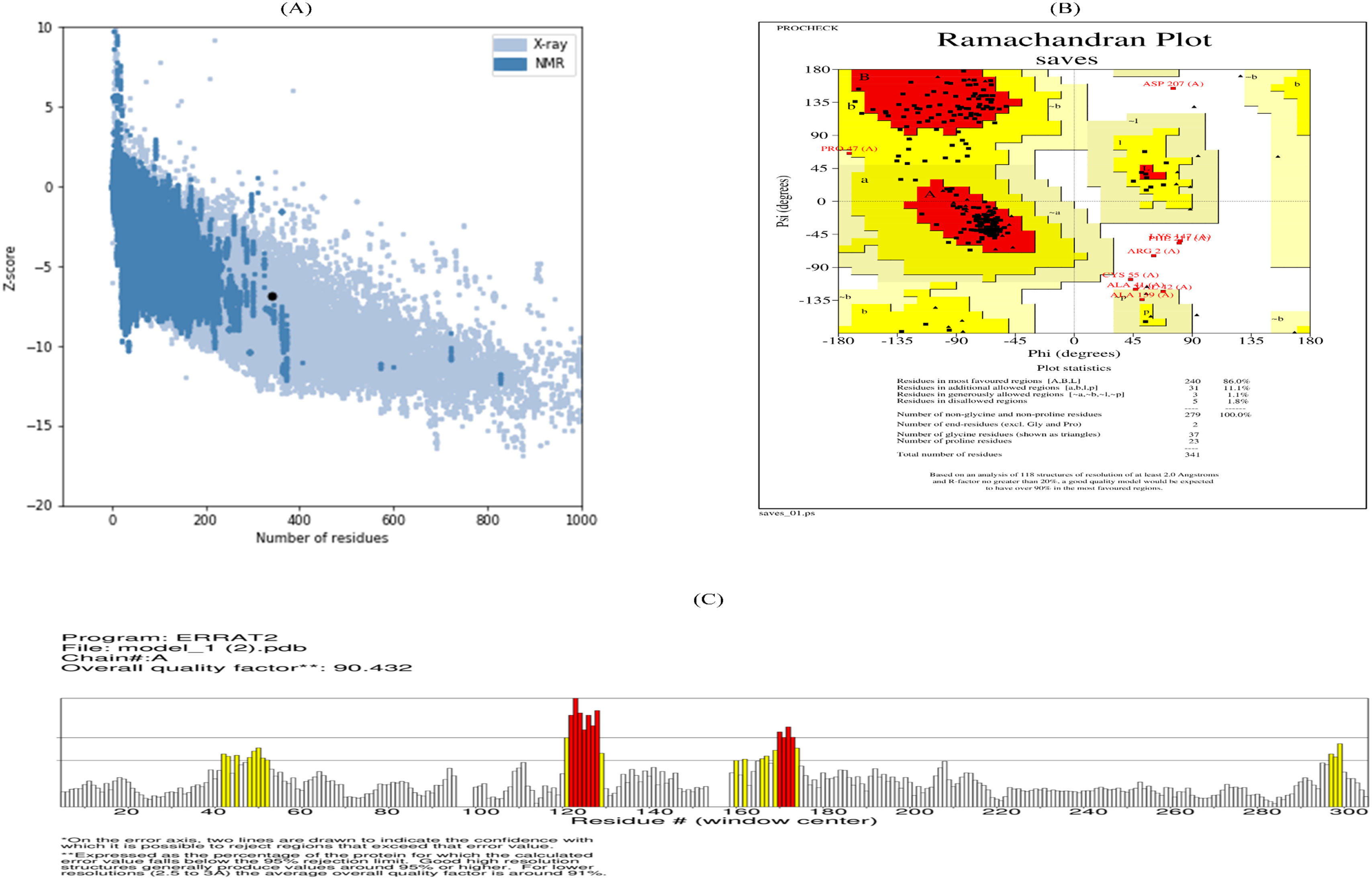
ResultsThe vaccine's immunogenicity score was reported as −4.46838, and its antigenic ratio yielded values of 0.5625 and 0.450999, respectively, using ERRAT, Rampage, and ProSa-web servers to validate the vaccine model. Consequently, the Z-score was −6.85, the ERRAT score was 90.432, and the Ramachandran plot value was generated as 86.0%. When TLR-7 was utilized to dock the vaccine, it revealed a good interaction with 151 non-bonding components, 7 hydrogen bonds, and 1 salt bridge. Using MD modeling, the stability of the docked complex was assessed. The vaccine had a GC content of 48.4% and a CAI value of 0.99% when it was reverse-translated. To implement the concept in a wet laboratory, the reverse translated vaccine sequence was cloned in pET28a (+) vector.
ConclusionThe vaccine developed in this work has to be experimentally validated in order to ensure its efficacy against the disease. The final application of this new research will be in the treatment of HRV-related illnesses as well as in upcoming experimental testing to verify the safety and immunogenicity of the suggested vaccine design.
El rinovirus (HRV) pertenece al género de los enterovirus de la familia picornavirus, y es un virus de ARN de cadena única de sentido positivo. Siendo un responsable habitual de las infecciones del tracto respiratorio, que incluyen el resfriado común, aún se desconoce el modo de tratar la infección por HRV.
MétodosEste estudio utilizó técnicas inmunoinformáticas sólidas para predecir los epítopos de células B, CTL y HTL en la poliproteína genómica. Se eligieron epítopos no alérgicos y antigénicos, a fin de producir una vacuna de subunidad que pudieran recibir los pacientes.
ResultadosSe reportó una puntuación de inmunogenicidad de la vacuna de −446,838, arrojando su ratio antigénico valores de 0,5625 y 0,450,999, respectivamente, utilizando los servidores ERRAT, Rampage y ProSa-web para validar el modelo de la vacuna. En consecuencia, la puntuación Z fue de −6,85, la puntuación ERRAT fue de 90,432, y se generó un valor del gráfico de Ramachandran del 86%. Al utilizarse TLR-7 para acoplar la vacuna, se revela una buena interacción con 151 componentes sin uniones específicas, 7 enlaces de hidrógeno, y 1 puente de sal. Utilizando la modelación MD, se evaluó la estabilidad del complejo acoplado. La vacuna tuvo un contenido de GC del 48,4% y un valor CAI del 0,99% al traducirse de manera inversa. Para implementar el concepto en un laboratorio húmedo se clonó la secuencia de la vacuna inversamente traducida en un vector pET28a (+).
ConclusiónLa vacuna desarrollada en este estudio ha de ser validada experimentalmente, a fin de garantizar su eficacia frente a la enfermedad. La aplicación final de esta nueva investigación será el tratamiento de las enfermedades relacionadas con HRV, así como la prueba experimental venidera para verificar la seguridad e inmunogenicidad del diseño de la vacuna sugerido.