The current evidence indicates that inflammation is highly related to depression but not to anxiety in clinical samples. However, less understood is the relationship between inflammation and symptoms of depression and anxiety in a nonclinical sample. The aim of this study was to investigate the association between three inflammation markers and symptoms of depression and anxiety in a healthy sample without a history of psychiatric disorders.
MethodsSymptoms of depression and anxiety were evaluated in 74 healthy adults (mean age=42.3; SD=11.8) using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale. We assessed proinflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, IL-1β, and CRP), and morning cortisol levels using blood samples.
ResultsTNF-α correlates positively with depressive symptoms, but there were no significant relationships between anxiety scores and inflammation markers. Importantly, TNF-α relates to symptoms of depression independently of anxiety scores, age, body mass index, cortisol, and sex.
ConclusionsOur results indicate that TNF-α is associated with depressive symptoms, independently of anxiety, age, body mass index, cortisol, and sex, even in a sample of hospital health professionals without diagnosis or psychiatric history.
Substantial evidence indicates that anxiety and depressive symptoms are highly prevalent in the general population and are among the main reasons for disability and mortality.1–4 Importantly, symptoms of depression and anxiety are usually highly correlated, and patients with higher levels of both anxiety and depression show lower quality of life and poorer clinical outcomes.5–8 Research has shown that Generalized Anxiety Disorder (GAD) and panic disorder have the highest rates of comorbidity with Major Depressive Disorder (MDD).9–12 Together, these results support the idea that both depression and anxiety are correlated and highlight the difficulty of delimiting the symptoms associated with both conditions. Identifying markers that can differentiate between depression and anxiety symptoms is crucial to improving the early detection of both disorders, understanding the clinical course and the prognosis, leading to a better choice of treatment.
Although some authors consider that anxiety and depression present a similar etiology and pathophysiology; relying on common genetic polymorphisms, neurobiological vulnerability, and similar pathophysiological phenotypes,13–15 recent research has shown important and promising efforts to delineate the neurophysiological differences between depression and anxiety.16 The use of biomarkers has been proposed to increase diagnostic precision and identify differences and similarities between both disorders. Within this context, inflammatory markers have been investigated in relation to symptoms of depression and anxiety. Evidence for the depression-inflammation relationship comes from three different observations: Elevated levels of proinflammatory cytokines in patients with MDD, comorbidity of inflammatory diseases with MDD, and increased risk of MDD after cytokine treatments are administered.17–20 Recent meta-analyses have shown that the majority of subjects with depression show elevated levels of the cytokines IL-1, IL-6, tumor necrosis factor-a (TNF-α) and C-reactive protein (CRP).21–25 Notably, Wu et al.26 recently proposed that proinflammatory activity could be used as a prognostic biomarker of depression. Following the theory of social signal transduction, the authors argue that inflammatory activation in a psychosocial event is positively associated with depressive symptoms; that is, more proinflammatory cytokines would predict an increase in depressive symptoms over time. Along this line, the relationship between inflammation and depression is also supported by studies investigating postmortem brain tissues, cerebrospinal fluid, and positron emission tomography.27 These lines of research indicate the presence of central inflammation markers in people with a history of major depression. Together, the current evidence seems to support the relationship between inflammation and depression, and although there are some discrepancies, it seems that the most specific and sensitive immune biomarkers for depression are IL-6, TNF-α, and CRP.
In contrast to the large volume of studies showing a relationship between depression and inflammation, the association between inflammation and anxiety has shown mixed results. A recent meta-analysis that included 41 studies found an overall significant difference between controls and subjects with anxiety disorders in proinflammatory cytokines, specially by IL-1, IL-6, and TNF-α.28 However, when they investigated the moderating effect of the diagnosis, only individuals with post-traumatic stress disorder showed differences in inflammation. Michopoulos et al.,29 in an extensive review, reached a similar conclusion, indicating that there is limited support on the relationship between GAD, panic disorder, phobias, and inflammation.
Together, the current evidence indicates that inflammation is highly related to depression but not to anxiety in clinical samples. However, little is known regarding symptoms of depression and anxiety in nonclinical samples (participants without current or past diagnosis of depression and anxiety disorders). Within this context, more research is still needed to understand the relationship between inflammation and symptoms of depression and anxiety in nonclinical samples and, most importantly, whether the relationship between inflammation and symptoms of depression and anxiety in healthy participants is independent of anxiety and depression symptoms, respectively. Given that depression and anxiety symptoms are highly correlated and that anxiety and depression disorders usually show a high rate of comorbidity, investigating whether inflammation is independently related to depression or anxiety may offer critical information to improve the early detection and better understand the development of both disorders.
The objective of the study was to investigate whether IL-1β, TNF-α, and PCR, three inflammatory markers, are related to symptoms of depression and anxiety in a sample of participants without current or past diagnosis of depression and anxiety disorders, and who do not refer to symptoms of depression and anxiety. Based on the literature in clinical samples, we hypothesize that participants with more depressive symptoms will show larger values of proinflammatory cytokine. Importantly, we expect that, even though depression and anxiety will be highly correlated, the association between depression and inflammation will be independent of anxiety levels. On the other hand, we hypothesized that anxiety symptoms will not be associated with proinflammatory cytokines. Besides the relationship with inflammatory markers, previous research has also shown that depression and anxiety are associated with stress-related hormones such as cortisol (e.g., Vreeburg et al.30). Thus, in this study we controlled for cortisol levels at the moment of inflammation assessment.
MethodsParticipantsThe sample consisted of 74 health professionals. Participants were medical doctors and nurses from the Luis Lagomaggiore Hospital, a public hospital in Mendoza, Argentina. The volunteers were recruited using a convenience sampling method (non-probabilistic sampling) via post and emails to personnel from the hospital. The following exclusion criteria were considered: medication that could affect inflammatory variables (use of corticosteroids), and a history of any psychiatric disorder or other medical disorder that could affect work activity. See Table 1 for the characteristics of the study sample. A sample size estimation using G*Power showed that a sample of 73 participants is needed to observe a medium effect size (f2=0.15) with a statistical power=0.9. We selected a medium effect size based on the results observed by Osimo et al.,24 showing a medium to high effect size in the relationship between depression and inflammatory markers (including TNF-α and CRP).
Characteristics of the study sample.
| Mean (SD) or % | |
|---|---|
| Age | 42.39 (11.8) |
| Sex | Men: 25.7%Women: 74.3% |
| Body mass index | 26.21 (4.4) |
| Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale | |
| Depression | 5.54 (3.1) |
| Anxiety | 9.03 (3.3) |
| Inflammation | |
| PCR (mg/l) | 4.98 (5.7) |
| TNF-α (pg/ml) | 122.63 (219.2) |
| IL-1β (pg/ml) | 5.20 (1.05) |
| Endocrine | |
| Cortisol morning (μg/dl) | 15.76 (6.5) |
Symptoms of depression and anxiety were assessed using the Spanish version of the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale-HADS31 (Spanish-adaptation), one of the most widely used instruments to assess psychological distress in the clinical population and the general population. The HADS is a Likert-type scale (from 0 to 3) composed of two subscales that evaluate anxiety and depression levels. The score of each subscale ranges from 0 to 21. Higher scores indicate more symptoms of anxiety or depression.
InflammationBlood samples for cytokines and CRP were centrifuged for 10–15min at 3000rpm, and the serum was stored at −80°C until determinations were made. The autoanalyzer Immulite 1000 chemiluminescence Immunoassay System (Siemens Healthcare Diagnostics GmbH, Berlin, Germany) was used to detect the serum concentrations of IL 1β and TNF-α, according to the manufacturer's instructions. The system includes an ultracentrifugation washing method that eliminates the unlatched phase and minimizes nonspecific binding. The inter-assay precision of IL-1 β and TNF-α, were in the range 5.2–6.7% and 2.6–3.6%, respectively; and the intra-assay precision were in the range of 2.7–4.2% and 4.0–6.5%, respectively. The inferior detection limit<5pg/ml and <8.1pg/ml, respectively. CRP levels were obtained by PCR-Latex Test with inferior detection limit <6mg/l. The technique is a rapid slide agglutination test, and the determination is made by testing a latex suspension coated with anti-PCR antibodies, against the test sera.
CortisolCortisol levels were assessed by immunochemistry coupled to electrochemiluminescence in an Inmulite 1000 autoanalyzer (Siemens Medical Solutions Diagnostics, Los Angeles, CA, USA).
ProcedureThe study was approved by the medical ethical committee of the Luis Lagomaggiore Hospital (Mendoza, Argentina), and all the participants provided written informed consent. The study was carried out in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki.
The participants were asked to come to the laboratory at 7:30am with 12h fasting and in groups of 10 people. At the beginning of the session, the informed consent was signed. Participants were then asked to complete the HADS to measure symptoms of depression and anxiety. At 8:00 am, 10ml of blood were collected. Weight and height were measured during the session to compute the body mass index. Heart rate, blood pressure and dehydroepiandrosterone were also measured during the session, however, these measures were not a focus of interest in the current study and are not included in the analyses. All measurements were carried out by qualified medical doctors and nurses.
Data management and statistical analysesBivariate correlations were performed to investigate the unadjusted association between depression and anxiety scores with inflammation markers, and cortisol levels.
Residual scores showed a normal distribution (Kolmogorov–Smirnov test: all p>0.1) and therefore, the data was not log or sqrt transformed before the analyses.
All the statistical analyses were performed using the SPSS v25.0 software. A p≤0.05 was considered statistically significant.
ResultsBivariate correlation analysesTable 2 shows the unadjusted correlations between depression, anxiety, and biomarkers. We observed that higher levels of depression were significantly correlated with higher levels of anxiety (r=0.511). The results also indicate a positive and significant correlation between depression and TNF-α values (r=0.295). That is, the higher the depression score, the higher the TNF-α values. None of the other correlations with depression and anxiety scores were statistically significant (p=0.128).
Unadjusted correlation analyses between depression, anxiety, and biomarkers.
| Depression | Anxiety | |
|---|---|---|
| Depression | – | p<0.001, r=0.511* |
| PCR | p=0.554, r=−0.070 | p=0.571, r=−0.067 |
| TNF-α | p=0.011, r=0.295* | p=0.325, r=0.116 |
| IL-1β | p=0.547, r=−0.072 | p=0.502, r=−0.080 |
| Cortisol change | p=0.879, r=−0.018 | p=0.881, r=−0.018 |
The association between depression and IL-1β was also in line with our hypothesis. However, we observed that one participant showed extremely high IL-1β values (+3SD), and the investigation of Cook's distance indicated that this participant was an influential case (Cook's distance>0.5) for the association between depression and IL-1β. Therefore, this participant was excluded from the analyses with IL-1β. After the exclusion of this participant, the association between depression and IL-1β was no longer significant. No other influential cases were observed.
Regression analyses1Besides the possible influence of cortisol levels on inflammation, previous research has shown that age and sex may affect inflammation levels and depression and anxiety symptoms (e.g., Vogelzangs32). Moreover, the meta-analysis by Howren et al.,33 reported that studies that adjusted for body mass index found substantially smaller associations between depression and inflammation. Thus, in regression analyses we investigated whether the significant relationship between depression and TNF-α values (r=0.295) was independent of age, body mass index, cortisol levels, and sex (men=0, women=1). Moreover, to investigate whether TNF-α was associated with depression and anxiety independently of each other, anxiety was included in the regression analysis.
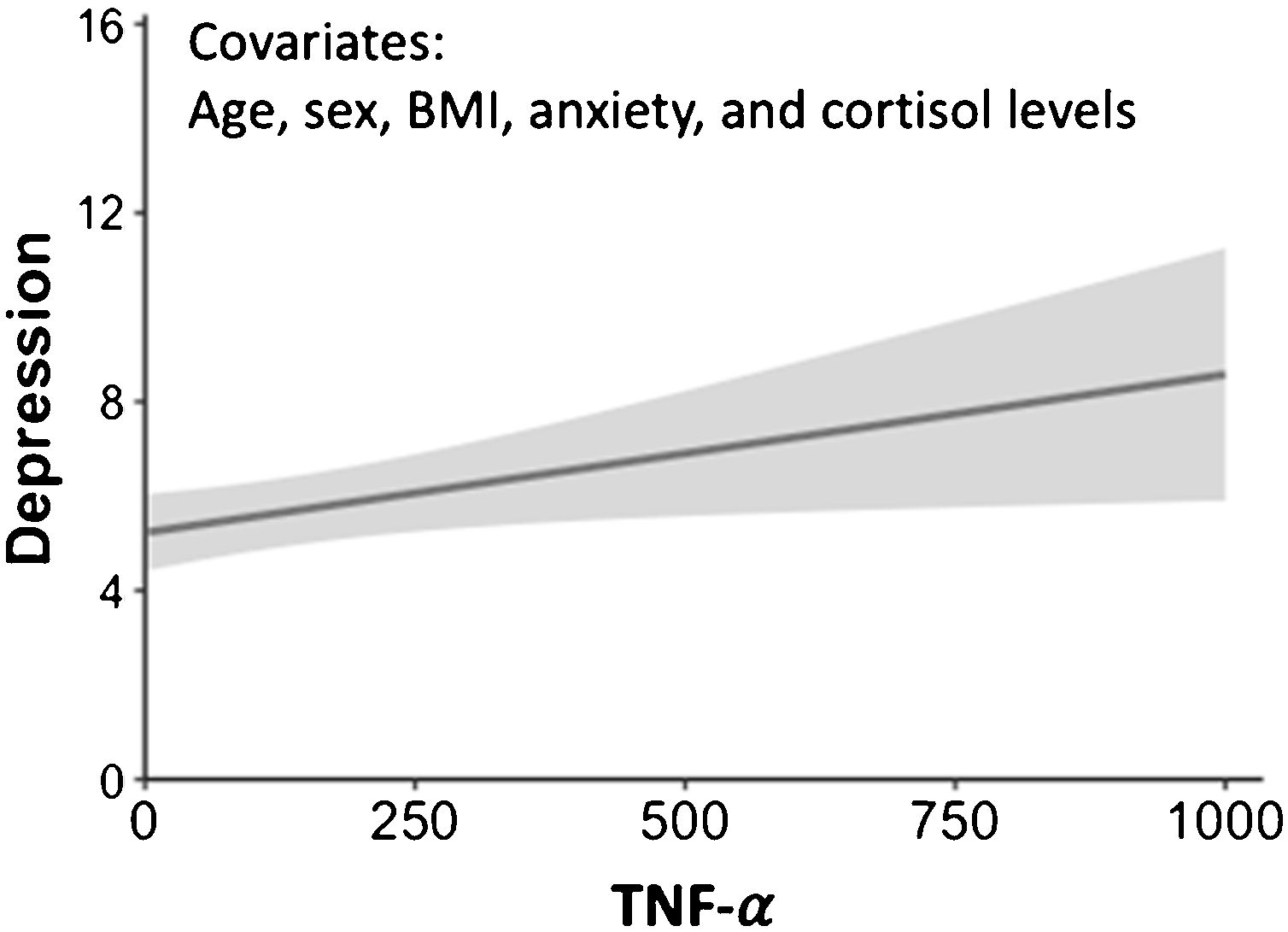
Given that correlation analyses showed a significant unadjusted association between depression and TNF-α values, we used regression analyses to investigate whether this association was still significant after controlling for age, sex, body mass index, cortisol levels, and anxiety scores. Depression was introduced as the dependent variable. We introduced TNF-α, age, sex, body mass index, cortisol levels, and anxiety scores as the predictors. The results indicate that higher TNF-α was significantly related to depression (β=0.223, p=0.038). Higher anxiety scores were also related to higher depressive symptoms (β=0.482, p<0.001). Age, sex, body mass index and cortisol levels were not related to depression (p>0.475). The results indicate that the model significantly explains 27% of the variance of depression symptoms (F=5.37, p<0.001). See Fig. 1 for a representation of the regression line and 95% confidence interval of the model.
Regression line and 95% confidence interval for the regression model with depression scores as the dependent variable, and TNF-α, age, sex, cortisol levels, body mass index, and anxiety scores as the predictors. Higher depression scores were related to higher TNF-α levels (β=0.223, p=0.038) and higher anxiety scores (β=0.456, p<0.001). Age, sex, cortisol levels and body mass index were not related to depression scores (p>0.475). The model explains 27% of the variance of depression scores. BMI=Body mass index.
This study aimed to investigate the relationship between inflammation markers (IL-1β, TNF-α, and CRP) and symptoms of depression and anxiety in a sample of 74 healthy adults. Our results indicate that higher TNF-α was related to more symptoms of depression. Importantly, this relationship was independent of age, sex, body mass index, and anxiety levels. Anxiety was not associated with inflammation markers.
We observed that higher TNF-α was associated with more symptoms of depression. This relationship was independent of age, sex, body mass index, and anxiety scores, and the model explains 27% of the variability in depression score. These results are consistent with previous studies showing a relationship between depression and a proinflammatory state.17,18,21–25 Recent research proposed that proinflammatory cytokines, particularly TNF-α, may play a central role in the clinic, pathophysiology, and working mechanisms of treatment in depressive disorders. TNF-α is one of the main proinflammatory cytokines produced by dendritic cells and macrophages and is an important activator of the inflammatory cascade.34 Central administration of TNF-α results in sickness behavior symptoms, similar to those observed in a depressive state.35 Moreover, a blockage of TNF-α can improve depressive symptomatology in humans and animal models,36 and in patients with MDD who present elevated levels of TNF-α, the efficacy of antidepressant treatments has been related to a decrease in TNF-α.37 Notably, the current literature suggests that the pathways between negative moods and inflammation are bi-directional. Thus, negative moods may activate peripheral physiologic mechanisms, leading to an up-regulation of systemic levels of inflammation, and peripheral inflammatory mediators signal the brain to affect behavioral, affective, and cognitive changes consistent with symptoms of MDD.38 Together, our results support the relationship between TNF-α and depressive symptoms, highlighting that this association may be observed even in a sample of healthy adults with no current or past diagnosis of depression.
It is important to note that, even though depression and anxiety were highly correlated, the association between TNF-α and depression was independent of anxiety scores. Moreover, anxiety symptoms were not significantly associated with inflammatory markers. These results are in line with recent meta-analyses and reviews showing that inflammation is related to posttraumatic stress disorder but not to other anxiety disorders.28,29 One previous study, however, observed a significant relationship between TNF-α and anxiety in a sample of health professionals when the participants were exposed to a highly stressful period (a period of medical residency exams).39 This result may suggest that the relationship between inflammation and anxiety can only be observed when stress levels exceed a specific threshold. The sample of the current study was also composed of health professionals, and when compared with the results observed by Chandrashekara et al.,40 our results indicate that our participants were not in a period of high levels of stress during the period when this study was carried out. However, given that we did not assess stress levels in our participants, we cannot investigate the moderation effect of this variable in the relationship between anxiety and inflammation. Future studies may benefit from including measures of stress.
The current study adds critical evidence of the inflammation-depression association, supporting the idea that depressive symptoms, and not anxiety, are associated with a proinflammatory state. Resonating with previous research, our results highlight the need for further research on the relationship between symptoms of depression and anxiety, and specific biomarkers of inflammation.
We did not observe a significant relationship between depression and the other two proinflammatory biomarkers, CRP and IL-1 β. This result is in line with the heterogeneity of findings presented in the different studies in relation to biomarkers and depression. Regarding CRP, a recent meta-analysis observed that approximately a quarter of patients with depression present evidence of low-grade inflammation, and more than half of patients show elevated CRP levels.25 In another meta-analysis, Ng et al.40 showed that CRP levels were higher in older people with depression than in controls, but this difference was not statistically significant. In 2019 Lamers et al.41 found bidirectional associations between depression and IL-6 levels in a large sample (n=2416). In contrast, CRP was not associated with depression. Notably, Del Giudice and Gangestad42 recently proposed that PCR has two isoforms, one produced locally in inflamed or damaged tissues, and another isoform that seems to have anti-inflammatory effects. Regarding IL1-β, recent studies and meta-analysis also showed inconsistent associations with depressive symptoms.22–24 Taken together, the association between CRP, IL1-β, and depression do not seem to be consistent, and our findings are in line with these results.
The main strength of this study is that it provides evidence of a positive association between inflammation and depressive symptoms independently of anxiety symptoms. In contrast to previous studies focused on psychiatric patients, we could demonstrate this independent association in participants without current or past diagnosis of depression and anxiety disorders. Our results suggest that people with depressive symptoms, even if they did not reach syndromic or psychopathological thresholds, would correlate with higher values of TNFa.
Besides the important results, some limitations should be considered. The exclusion of participants due to exclusion criteria was based on the self-report of the participants and we did not collect objective measures to exclude participants. Although we excluded participants with corticosteroid treatment, we did not assess the use of other anti-inflammatory drugs. Therefore, we could not exclude participants taking other medications that may affect the immune system. Also, regarding the study sample, given that medical doctors and nurses from an Argentine public hospital were recruited for this study using a convenience sampling, the generalizability of our results should be taken with caution. Although sex did not moderate the relationship between inflammatory markers and depression and anxiety (see footnote 1), future studies may benefit from including a similar number of men and women to test sex-related differences. Moreover, we did not measure IL-6 levels, an important inflammatory marker that has been related to psychological disorders in previous studies. Finally, the current study did not measure cholesterol, smoking or sedentary lifestyle, and other factors that may be considered as confounding factors in the relationship between TNF, anxiety and depression. Future studies may benefit from including these variables.
In conclusion, this study provides evidence that, in a healthy sample of hospital health professionals, higher symptoms of depression are associated with higher TNF-α. Importantly, although depression and anxiety were strongly associated, the relationship between depression and TNF-α was independent of anxiety levels. Thus, our findings suggest that individuals with higher TNF-α levels may benefit from training or prevention programs focused on reducing depressive symptoms.
FundingNone.
Conflict of interestNone.
The authors would like to thank the participants of this study.