Attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) is a common, complex, multifactorial neurodevelopmental disorder. In this study, conducted by experts in the management of ADHD in adults, a set of recommendations have been developed based on a review of the available evidence, with the aim of improving the clinical care of these patients.
Materials and methodsThis study was conducted in full compliance with the consensus methodology developed by the RAND Corporation/University of California Los Angeles (RAND/UCLA). The 29 proposed statements were evaluated using a 2-round iterative Delphi process. Of the 18 invited panellists, 15 completed both rounds (83.3% response rate).
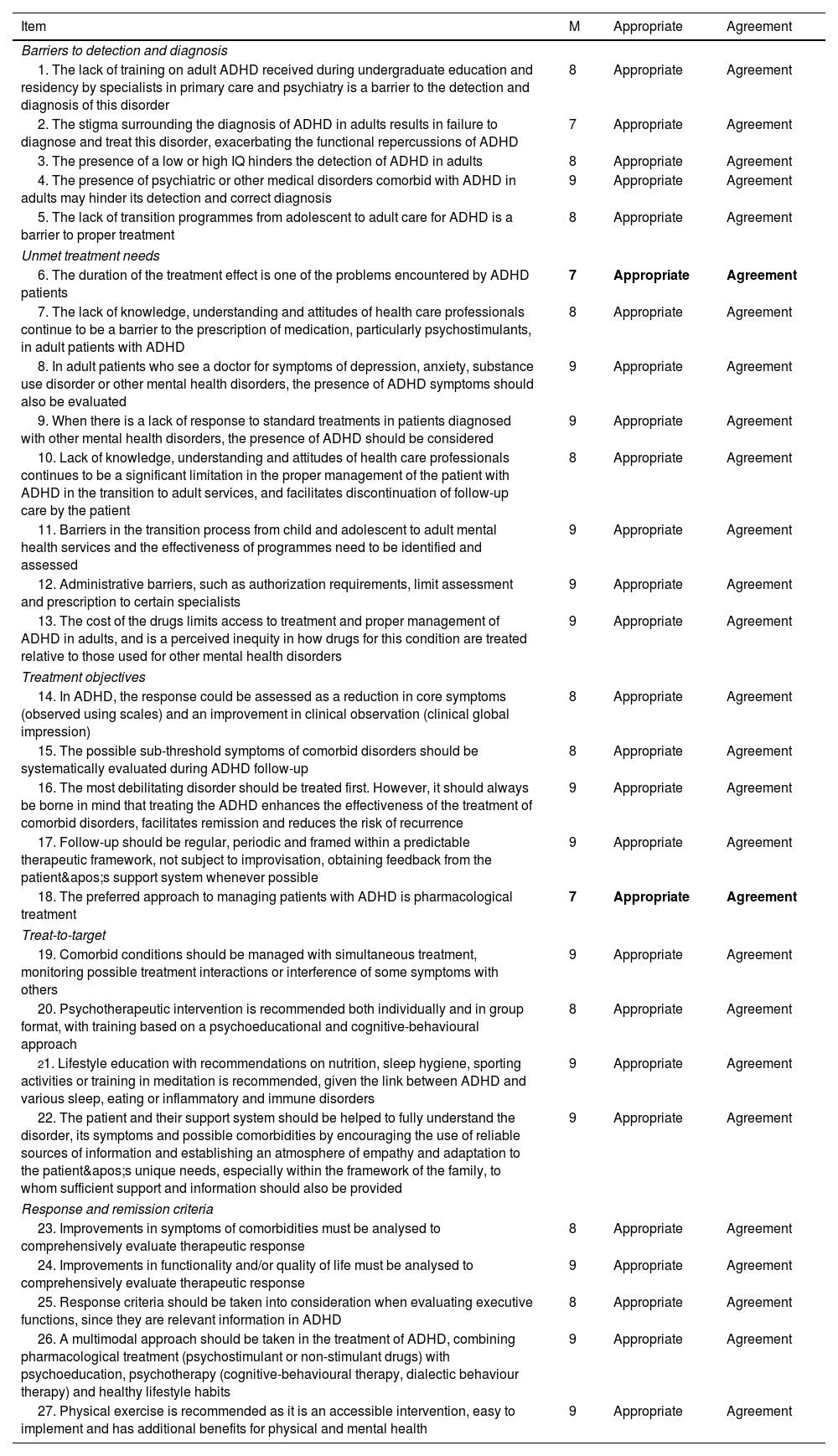
ResultsAfter 2 rounds of voting, the expert panel reached consensus, either in agreement or disagreement, on 93.1% of the statements (a total of 27 of the 29 proposed). These included proposals on important topics in the management of ADHD in adults, such as barriers to detection and diagnosis, unmet treatment needs, treatment objectives, the treat-to-target approach, and response and remission criteria.
ConclusionsThis study has sought to reinforce the importance of a structured and multidisciplinary approach in the management of ADHD in adulthood, focused on the patient and their needs. The recommendations presented here aim not only to mitigate the adverse outcomes associated with untreated ADHD, but also to facilitate a substantial improvement in the quality of life of individuals living with this disorder.
Article
(Sociedad Española de Psiquiatría y Salud Mental)
Diríjase al área de socios de la web de la SEPSM, (https://sepsm.org/revista/) y autentifíquese.