Hyperprolactinaemia and sexual dysfunction are common adverse effects of antipsychotic drugs, particularly with dopamine D2 receptor antagonists. Long-acting injectables such as paliperidone palmitate (PP) and risperidone ISM may differ in their endocrine safety profiles, especially across sexes. We aimed to compare prolactin levels and clinically significant sexual dysfunction in patients treated with risperidone ISM vs monthly PP.
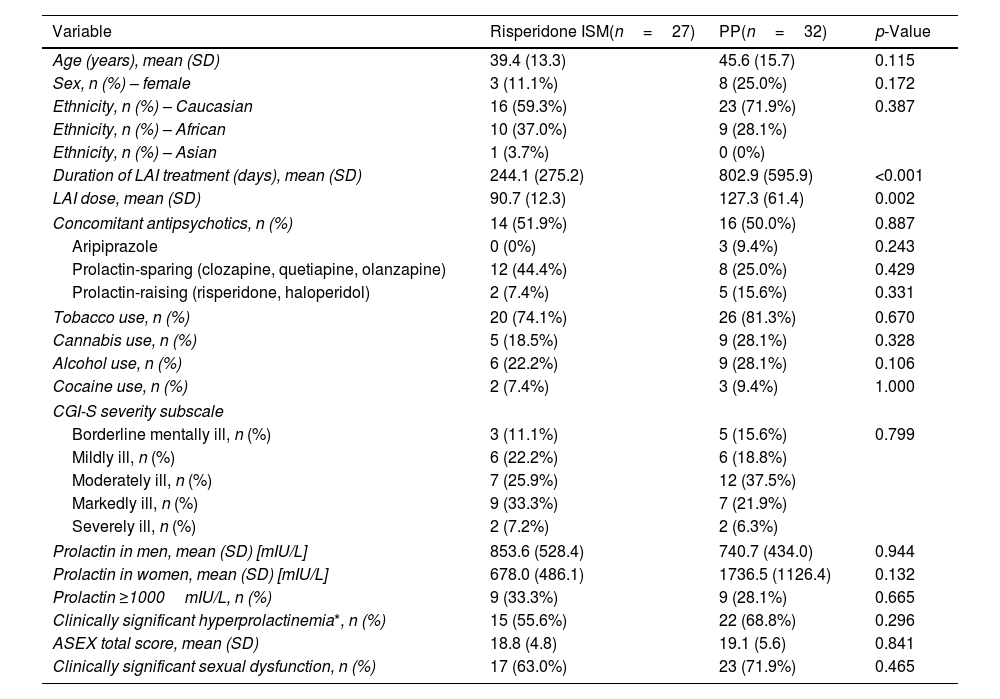
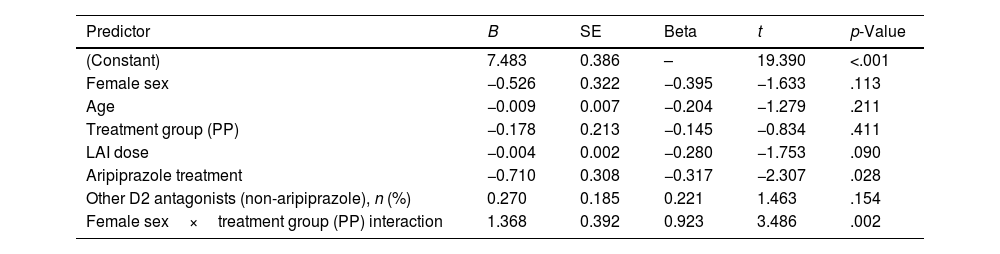
MethodsWe conducted a cross-sectional study including 59 patients with psychotic disorders (27 on risperidone ISM, 32 on PP). Clinically significant hyperprolactinaemia was defined as prolactin levels above sex-specific thresholds along with hypogonadism and/or sexual dysfunction. The Arizona Sexual Experience Scale was used to assess sexual function. Hormonal assays included prolactin, testosterone, and oestradiol. Prolactin values were log-transformed for regression models. Multiple linear regression assessed predictors of prolactin, including treatment, sex, age, dose, co-treatment with aripiprazole or other antipsychotics, and sex-by-treatment interaction. An exploratory logistic regression examined predictors of clinically significant hyperprolactinemia (with either hypogonadism or sexual dysfunction).
ResultsWomen on PP showed significantly higher prolactin levels vs those on risperidone ISM (interaction between female sex and PP; p=0.002). Aripiprazole co-treatment was associated with lower prolactin levels (p=0.020). Clinically significant hyperprolactinaemia was present in 55.6% of the risperidone ISM group vs 68.8% of the PP group. The exploratory logistic regression model revealed no significant predictors of clinically significant hyperprolactinaemia.
ConclusionRisperidone ISM may be associated with a more favourable prolactin profile in women vs PP. Findings support the relevance of sex and adjunctive strategies in managing antipsychotic-induced endocrine side effects.
Article
(Sociedad Española de Psiquiatría y Salud Mental)
Diríjase al área de socios de la web de la SEPSM, (https://sepsm.org/revista/) y autentifíquese.