To investigate the effect of testicular histopathology on the success of microscopic testicular sperm extraction (mTESE) and the factors that could predict the success of mTESE in patients with non-mosaic Klinefelter syndrome (KS).
Material and methodsForty-one KS patients diagnosed with non-obstructive azoospermia (NOA) who had undergone mTESE at our clinic were included in the study. The patients were divided into 5 groups according to the histopathology results: hyalinisation of tubules (HT), sertoli cell only (SCO), early maturation arrest (EMA), late maturation arrest (LMA), and hypospermatogenesis (HS). The groups were compared with regard to age, duration of infertility, hormone profile, testicular volume, and sperm retriveal rate. The clinical features of the patients with mTESE from whom sperm could or could not be obtained were also compared with the aim of investigating the predictive value of testicular histopathology and the other variables for prediction of the success of mTESE.
ResultsSperm could be obtained through mTESE in 13 out of 41 patients (31.7%). A statistically significant difference was determined between the groups with regard to the rate of sperm collection. No significant difference was determined between the histopathology groups with regard to the other variables. A statistically significant difference was determined between the groups from whic sperm could be collected or not with regard to age, Johnsen criteria, SCO, EMA and LMA variables. Multi-variate analysis revealed that age and Johnsen score were the independent variables predictive for success of mTESE.
ConclusionThe present study has revealed that impairment in testicular histopathology negatively affects the success of mTESE and that it is a predictive factor for the success of mTESE in patients with KS. Increased patient age was also determined to negatively affect the success of mTESE and the operation was demonstrated to be more successful before 34 years of age.
Estudiar el efecto de la histopatología testicular en el éxito de la extracción microscópica de espermatozoides testiculares (EETm) y los factores que podrían pronosticar el éxito de la EETm en pacientes con síndrome de Klinefelter (SK) sin mosaicismo.
Material y métodosEn el estudio se incluyó a 41 pacientes con SK diagnosticados de azoospermia no obstructiva (ANO) a quienes se les había realizado la EETm en nuestra clínica. Se dividió a los pacientes en 5 grupos, de acuerdo con los resultados de la histopatología: hialinización de túbulos (HT), células de Sertoli solamente (SCS), detención de la maduración temprana (DMT), detención de la maduración tardía (DMTa) e hipoespermatogénesis (HS). En los grupos se compararon la edad, la duración de la infertilidad, el perfil hormonal, el volumen testicular y la tasa de recuperación de esperma. También se compararon las características clínicas de los pacientes con EETm de los que se pudo obtener esperma o no con el objetivo de estudiar el valor pronóstico de la histopatología testicular y otras variables para pronosticar el éxito de la EETm.
ResultadosSe pudo obtener esperma a través de la EETm de 13 de 41 pacientes (31,7%). Se estableció una diferencia estadísticamente importante entre los grupos respecto a la tasa de recolección de esperma. No se estableció ninguna diferencia importante entre los grupos de histopatología respecto a las otras variables. Se estableció una diferencia estadísticamente importante entre los grupos de los cuales se pudo recolectar esperma o no respecto a la edad, a los criterios de Johnsen, SCS, DMT y DMTa. El análisis multivariante reveló que la edad y la puntuación de Johnsen fueron las variables independientes pronósticas del éxito de la EETm.
ConclusiónEl presente estudio ha revelado que el deterioro de la histopatología testicular afecta negativamente al éxito de la EETm, y que es un factor pronóstico para el éxito de la EETm en pacientes con SK. También se estableció que el aumento de la edad del paciente afectaba negativamente al éxito de la EETm, y se demostró que la operación tenía más éxito cuando se realizaba antes de los 34 años.
Klinefelter syndrome (KS) is the most common sex chromosome abnormality, with an estimated prevalence of 1:500–1:700 in new-born males.1 KS was first described in 1942 and is defined by a clinical phenotype comprised of tall stature with a feminine body type, gynaecomastia, small testes and infertility.2 KF is seen in 3% of infertile patients and in 11.9% of azoospermic patients.3 The disease has been observed in non-mosaic (47, XXY) and mosaic (47, XXY/46, XY) forms; 85% of patients have the non-mosaic form. The ejaculate of patients with the mosaic form contains sperm, whereas patients with the non-mosaic form are usually sterile. Testicular degeneration in patients with KS begins in foetal life and leads to testicular tissue degeneration and azoospermia in adulthood.4,5 Focal spermatogenesis may be seen despite testicular degeneration. These patients can father their own children through microscopic testicular sperm extraction (mTESE) or intra-cytoplasmic sperm injection (ICSI) methods. Reported rates of sperm retrieval using mTESE range from 16% to 56.7%.6
An unsuccessful mTESE operation can lead to emotional and financial effects in patients with KS. Awareness of the predictive factors for success of the operation is important to avoid unnecessary operations. In particular, knowledge of the degree of testicular degeneration is beneficial for planning of a second operation when the first operation has failed. No study has investigated the effect of testicular degeneration on the success of mTESE in patients with KS. Thus, we investigated the effect of testicular histopathology on the success of mTESE and the factors that predict the success of mTESE in patients with KS and non-obstructive azoospermia (NOA).
Materials and methodsPatients and study designWe retrospectively reviewed the medical data of 445 patients with the diagnosis of NOA who had undergone the mTESE operation consecutively in our institution between October 2008 and May 2017. This study was conducted in accordance with the Declaration of Helsinki and with approval from the institutional ethics committee. The diagnosis of NOA was confirmed by clinical findings, medical history, physical examination findings, serum hormone levels, genetic analysis and two semen analyses, as recommended in the World Health Organization guidelines. Semen for the analyses was obtained by masturbation after 3–4 days of sexual abstinence. The levels of serum total testosterone (T), follicular stimulating hormone (FSH), luteinising hormone (LH), 17β-oestradiol (E2) and prolactin (PRL), and the results of genetic (karyotype and Y chromosome microdeletion) analyses were evaluated. Blood for hormone profiling was drawn from patients’ antecubital veins after at least 8h of fasting. The microparticle enzyme immunoassay method (Cobas e601; Roche/Hitachi, Indianapolis, IN, USA) was used to determine all hormone levels. For the chromosome analysis, peripheral venous blood samples from the patients were subjected to 72h of phytohaemagglutinin-induced cell culture. In all patients, the karyotype was confirmed by cytological analysis and included evaluation of more than 30 peripheral blood lymphocyte metaphases. Y chromosome microdeletion analysis was performed for all patients before mTESE surgery, and mTESE was not recommended for patients with AZFa and AZFb deletions. Patients’ testicular volumes were measured by scrotal ultrasound. The external organs were examined to exclude additional anomalies. All mTESE operations were completed without complication.
Forty-one patients with KS and NOA who had undergone mTESE in our clinic were included in the study. Patients with other genetic anomalies, history of vasectomy, testicular trauma, malignant disease or obstructive azoospermia, and those who had undergone more than one mTESE operation were excluded from the study. No patient was given hormone therapy before mTESE. Biopsy samples obtained during mTESE were examined. According to histopathological findings, the patients were divided into five groups: hyalinisation of tubules (HT), Sertoli cells only (SCO), early maturation arrest (EMA), late maturation arrest (LMA) and hypospermatogenesis (HS). The groups were compared with regard to age, duration of infertility, hormone profile, testicular volume and the rate of sperm retrieval by mTESE.
The clinical features of patients from whom sperm were and were not retrieved with mTESE were also compared to investigate the predictive value of testicular histopathology and other variables for the success of mTESE.
TESE techniqueAdditional sperm samples were obtained on the day that the mTESE operation was planned, and the absence of sperm was confirmed. Informed consent was obtained from all patients before mTESE. All patients underwent spinal anaesthesia for mTESE. A midline scrotal incision was made, and the scrotal contents were pushed from the side of the larger testis. The tunica vaginalis was opened, and the tunica albuginea surrounding the testicle was visualised. After this stage, the operation was conducted under an operating microscope. As described by Schlegel,7 an avascular area was selected from the anti-mesenteric area to the tunica albuginea, and a 3-cm incision was made with a thin scalpel. Small samples were obtained from opaque, large, white tubules in the testicular parenchyma. Each sample was placed in a Petri dish filled with human tubal fluid. An embryologist evaluated all samples immediately under a microscope at 200× magnification to assess the presence of spermatozoa. The operation was terminated when suitable spermatozoa were found for ICSI. If spermatozoa were not detected in the first sample, additional samples were obtained from the same testicle. In cases where spermatozoa were not found in the samples from the larger testis, samples were obtained from the contralateral testis. Biopsy specimens were sent to the pathology laboratory intraoperatively to determine testicular histopathology.
Histopathological analysisAll testicular biopsy samples were fixed in Bouin's solution and embedded in paraffin blocks following tissue processing. Four-micrometre-thick sections were obtained, stained with haematoxylin and eosin and evaluated under a microscope at 400× magnification by the same pathologist with more than 10 years of experience. Germinal epithelia of at least 100 seminiferous tubules were evaluated for each biopsy sample. Tissue maturation and the spermatogenetic condition of the germinal epithelium were assessed using Johnsen's score (JS), which ranges from 1 to 10: 1, tubular necrosis; 2, SCO; 3, spermatogonia only; 4 and 5, arrest at the primary spermatocyte stage; 6 and 7, arrest at the early spermatid stage; 8 and 9, arrest at the late spermatid stage; and 10, full spermatogenesis.8 The mean JS was calculated for each sample. Testicular biopsy specimens were classified according to histopathological criteria as follows: normal spermatogenesis (NS; mean JS=10), HS (mean JS=8–9), LMA (mean JS=6–7), EMA (mean JS=3–5), SCO (mean JS=2) and HT (mean JS=1). The most predominant histopathological diagnosis from all specimens was used when a mixed pattern was observed.
Statistical analysisThe conformity of the variables to normal distribution was assessed with the Shapiro–Wilk test. Categorical variables are described using frequencies and percentages, and numerical variables are described using means and ranges. Student's t-test and the chi-squared test were used for inter-group analysis of continuous variables. More than two independent averages were compared with analysis of variance. We performed univariate and multivariate binary logistic regression analyses to identify factors associated with and predictive of positive sperm retrieval during mTESE. Logistic regression analysis was performed by creating a model that included age, T level, FSH level and JS. The ability of the variables to predict the presence of sperm obtained during the mTESE procedure was investigated by receiver operating curve (ROC) analysis, and threshold values were calculated using the Youden index. Data analysis was carried out using SPSS version 22.0 software (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA), and p-values <0.05 were considered to be significant.
ResultsSperm were obtained during mTESE in 13 of 41 (31.7%) patients. The mean age was 30.8±4.8 years, the mean duration of infertility was 6.2 years (range, 1–12 years), the mean total T level was 308.2±191.3ng/dL, the mean E2 level was 26.1±12.5pg/mL, the mean FSH level was 42.1±18.4mIU/mL, the mean LH level was 19.3±10.1mIU/mL, the mean PRL level was 10.9±4.8ng/mL and the mean JS was 2.95.
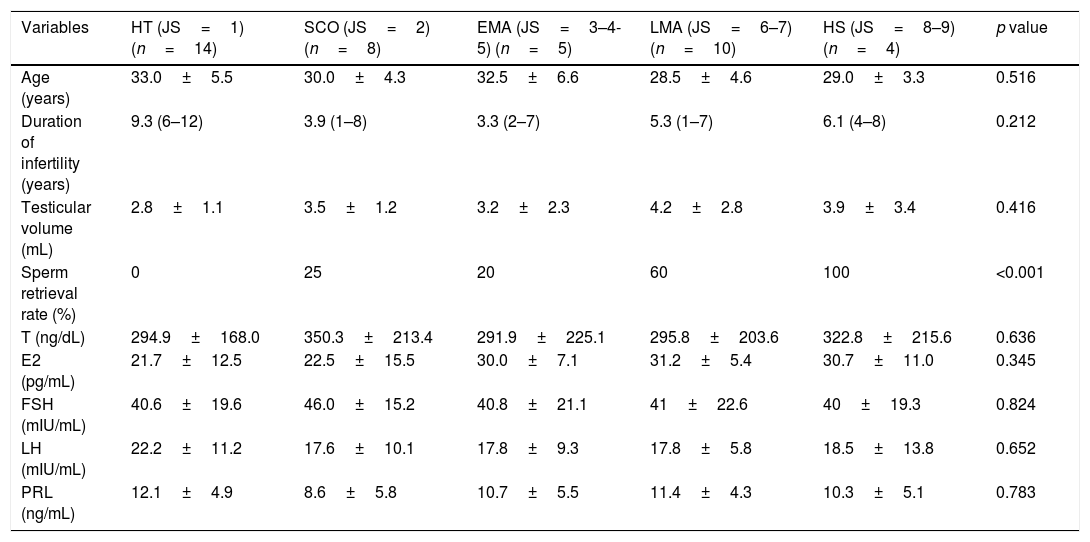
Histopathological examination showed HT in 14 (34.1%) patients, SCO in 8 (19.5%) patients, EMA in 5 (12.1%) patients, LMA in 10 (24.3%) patients and HS in 4 (9.7%) patients. NS was not observed in any patient. The sperm retrieval rates were 0% (0/14) in the HT group, 25% (2/8) in the SCO group, 20% (1/5) in the EMA group, 60% (6/10) in the LMA group and 100% (4/4) in the HS group. A significant difference in sperm retrieval rate was detected among groups (p<0.001). No significant difference in any other variable was identified among groups. Comparisons of the clinical and hormonal data, as well as mTESE outcomes, among the testicular histopathology groups are presented in Table 1.
The comparison of clinical, hormonal data and the TESE outcomes among testicular histopathology groups.
| Variables | HT (JS=1) (n=14) | SCO (JS=2) (n=8) | EMA (JS=3–4-5) (n=5) | LMA (JS=6–7) (n=10) | HS (JS=8–9) (n=4) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 33.0±5.5 | 30.0±4.3 | 32.5±6.6 | 28.5±4.6 | 29.0±3.3 | 0.516 |
| Duration of infertility (years) | 9.3 (6–12) | 3.9 (1–8) | 3.3 (2–7) | 5.3 (1–7) | 6.1 (4–8) | 0.212 |
| Testicular volume (mL) | 2.8±1.1 | 3.5±1.2 | 3.2±2.3 | 4.2±2.8 | 3.9±3.4 | 0.416 |
| Sperm retrieval rate (%) | 0 | 25 | 20 | 60 | 100 | <0.001 |
| T (ng/dL) | 294.9±168.0 | 350.3±213.4 | 291.9±225.1 | 295.8±203.6 | 322.8±215.6 | 0.636 |
| E2 (pg/mL) | 21.7±12.5 | 22.5±15.5 | 30.0±7.1 | 31.2±5.4 | 30.7±11.0 | 0.345 |
| FSH (mIU/mL) | 40.6±19.6 | 46.0±15.2 | 40.8±21.1 | 41±22.6 | 40±19.3 | 0.824 |
| LH (mIU/mL) | 22.2±11.2 | 17.6±10.1 | 17.8±9.3 | 17.8±5.8 | 18.5±13.8 | 0.652 |
| PRL (ng/mL) | 12.1±4.9 | 8.6±5.8 | 10.7±5.5 | 11.4±4.3 | 10.3±5.1 | 0.783 |
T, testosterone; E2, estradiol; FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; LH, luteinising hormone; PRL, prolactin; HT, hyalinisation of tubules; SCO, Sertoli cell only; EMA, early maturation arrest; LMA, late maturation arrest; HS, hypospermatogenesis.
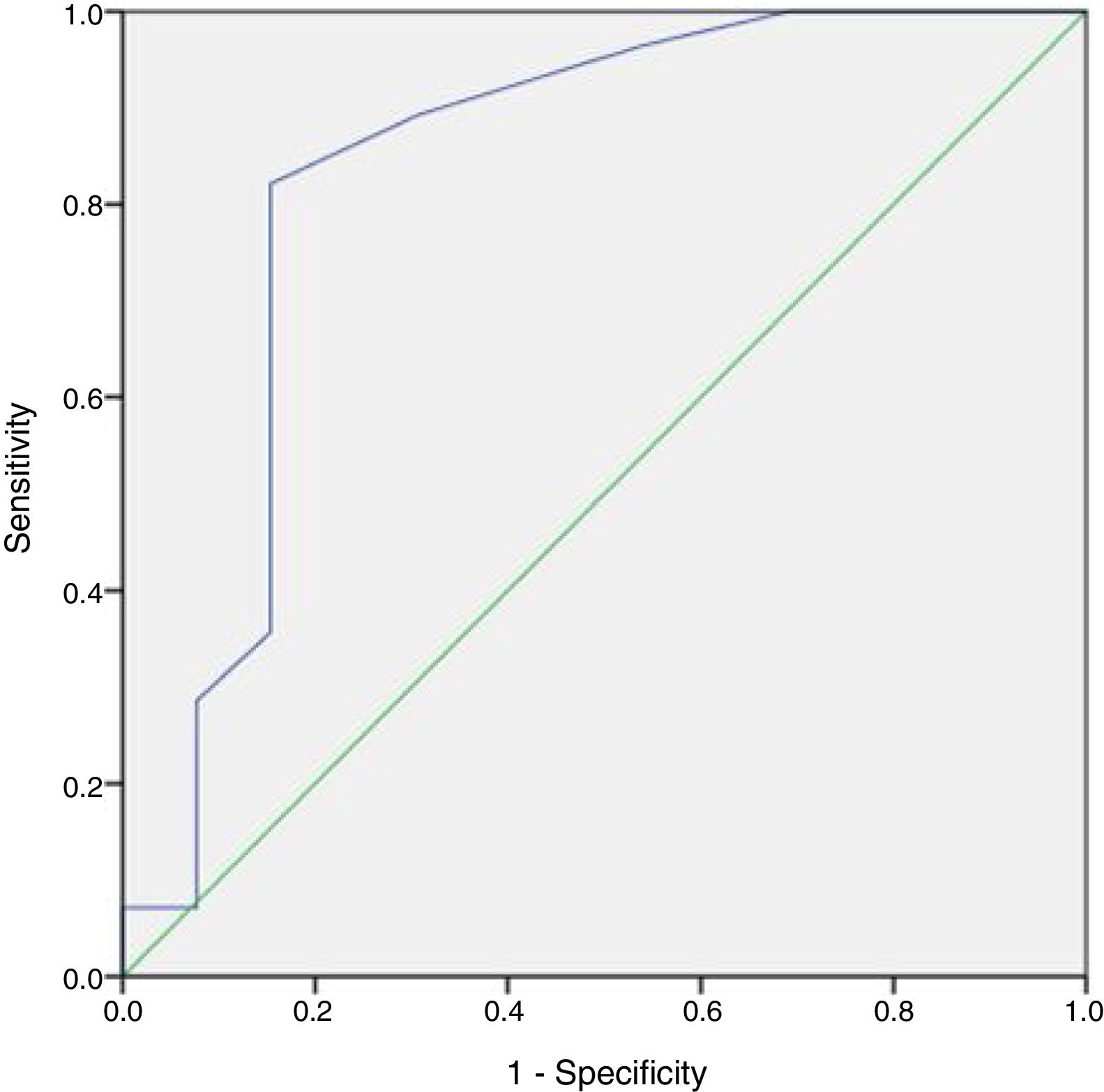
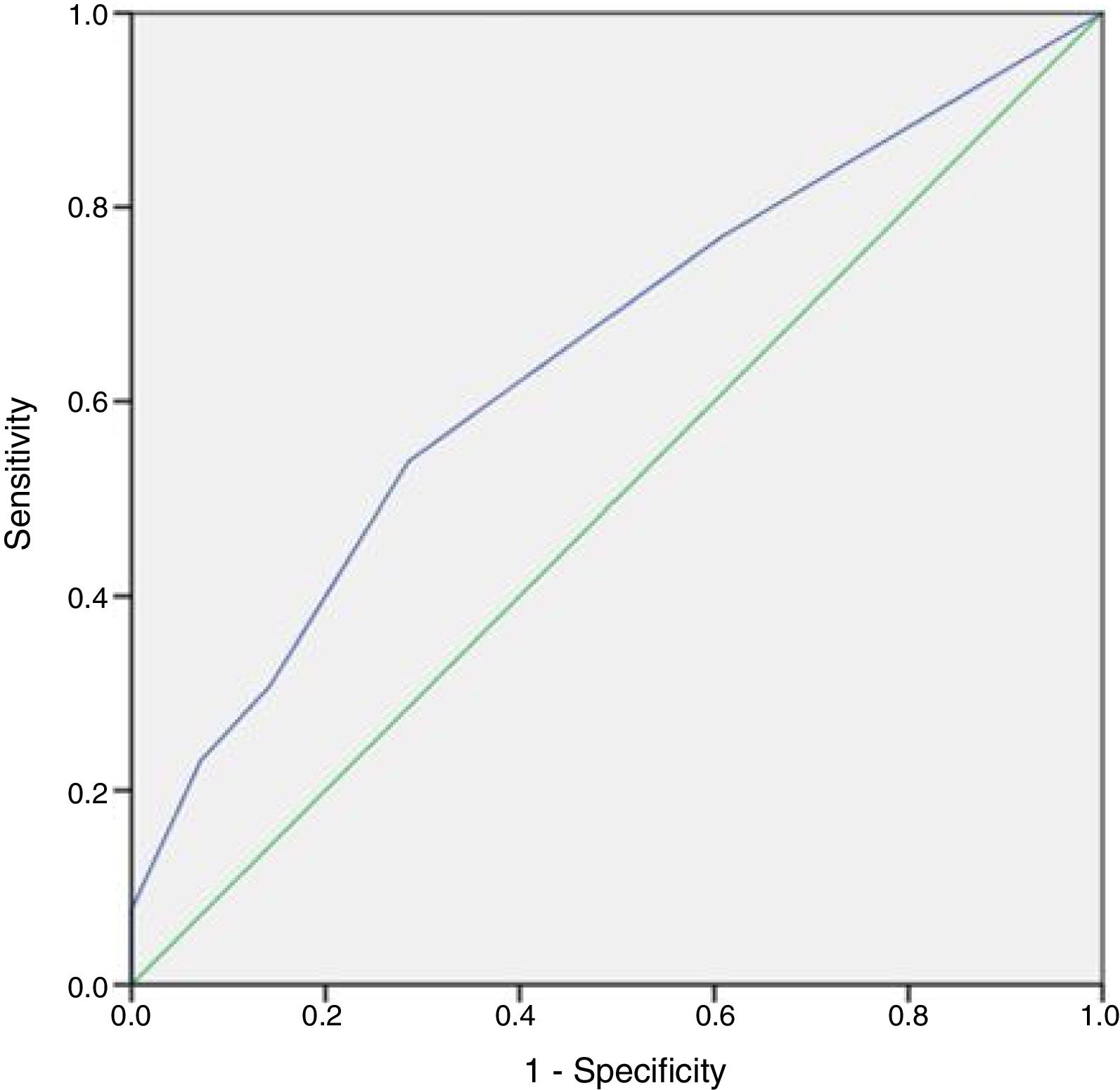
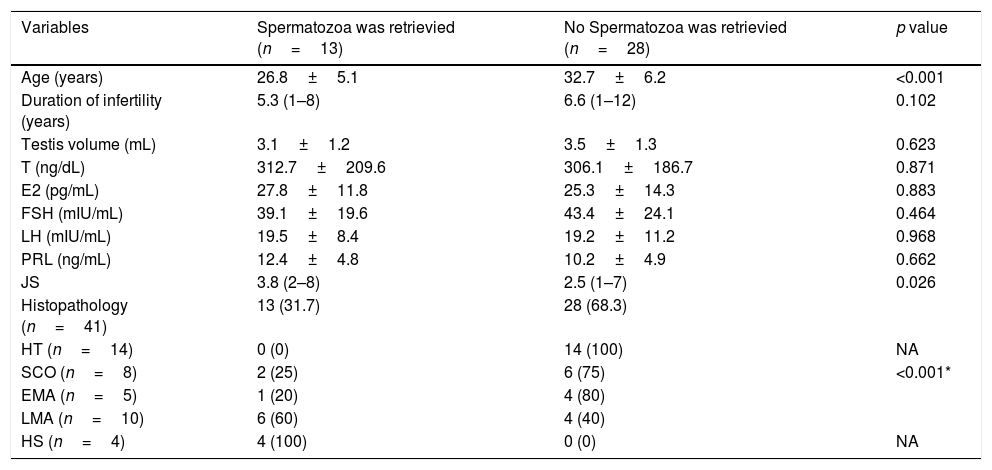
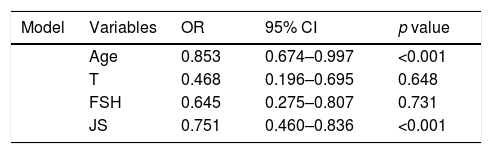
No patient had a history of cryptorchidism. No severe complication developed during the mTESE procedure or in the following 3 weeks. Significant differences were observed in age, JS, SCO, EMA and LMA between patient groups in which sperm could and could not be retrieved (Table 2). Statistical analysis could not be carried out for the HT and HS subgroups. Multiple logistic regression analysis was performed by creating a model that included age, T level, FSH level and JS (Table 3). The best cut-off value was 34 to predict the age for best sperm collection during mTESE (71.4% sensitivity, 92.3% specificity, p<0.001). The area under the ROC for patient age was 0.835 (Fig. 1). The best JS cut-off value to predict sperm retrieval during mTESE was 4.5 (69.2% sensitivity, 85.7% specificity, p<0.001). The area under the ROC for JS was 0.648 (Fig. 2).
Univariate analyses of patients according to sperm retrieval success.
| Variables | Spermatozoa was retrievied (n=13) | No Spermatozoa was retrievied (n=28) | p value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age (years) | 26.8±5.1 | 32.7±6.2 | <0.001 |
| Duration of infertility (years) | 5.3 (1–8) | 6.6 (1–12) | 0.102 |
| Testis volume (mL) | 3.1±1.2 | 3.5±1.3 | 0.623 |
| T (ng/dL) | 312.7±209.6 | 306.1±186.7 | 0.871 |
| E2 (pg/mL) | 27.8±11.8 | 25.3±14.3 | 0.883 |
| FSH (mIU/mL) | 39.1±19.6 | 43.4±24.1 | 0.464 |
| LH (mIU/mL) | 19.5±8.4 | 19.2±11.2 | 0.968 |
| PRL (ng/mL) | 12.4±4.8 | 10.2±4.9 | 0.662 |
| JS | 3.8 (2–8) | 2.5 (1–7) | 0.026 |
| Histopathology (n=41) | 13 (31.7) | 28 (68.3) | |
| HT (n=14) | 0 (0) | 14 (100) | NA |
| SCO (n=8) | 2 (25) | 6 (75) | <0.001* |
| EMA (n=5) | 1 (20) | 4 (80) | |
| LMA (n=10) | 6 (60) | 4 (40) | |
| HS (n=4) | 4 (100) | 0 (0) | NA |
T, testosterone; E2, estradiol; FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; LH, luteinising hormone; PRL, prolactin; HT, hyalinisation of tubules; SCO, Sertoli cell only; EMA, early maturation arrest; LMA, late maturation arrest; HS, hypospermatogenesis; JS, Johnsen score; NA, not applicable.
The regression analysis model and independent predictive factors that reflect possibility of sperm retrieval.
| Model | Variables | OR | 95% CI | p value |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age | 0.853 | 0.674–0.997 | <0.001 | |
| T | 0.468 | 0.196–0.695 | 0.648 | |
| FSH | 0.645 | 0.275–0.807 | 0.731 | |
| JS | 0.751 | 0.460–0.836 | <0.001 |
T, testosterone; JS, Johnsen score; FSH, follicle-stimulating hormone; OR, odds ratio; CI, confidence interval.
We concluded that testicular histopathology was associated with the success of mTESE in patients with KS and that it may be a predictor of the success of mTESE. The present study summarises our 8-year experience with mTESE in patients with KS. Testicular histopathology is impaired in KS, beginning from childhood.4,5 This impairment causes infertility, leading to NOA. The use of sperm obtained by mTESE for ICSI enables these patients to father their own children. However, few studies have investigated the effect of impaired testicular histopathology on the success of mTESE. Koga et al.9 reported collecting sperm from 16 of 17 (94.1%) patients who showed no sclerotic change in testicular tissue. Ozveri et al.3 reported obtaining sperm during mTESE in four of six (64%) patients with SCO histopathology and in two of two (100%) patients with HS histopathology, but they could not retrieve sperm from one patient with Leydig hyperplasia. In another study, histopathological examination results for 54 patients with KS who had undergone mTESE were evaluated and sperm were obtained from 24 of 34 (71%) patients with SCO histology; however, sperm could not be retrieved from 2 of 3 (67%) patients with HS histology, 3 of 9 (33%) patients with Leydig hyperplasia and 1 patient with MA.10 In contrast, JS, which more objectively classifies testicular histopathology, was used in our study. The patients were divided into five groups according to this classification. The likelihood of sperm retrieval was significantly greater in patients with HS and LMA histopathology. Furthermore, multivariate analysis revealed that JS was an independent variable that predicted the outcome of mTESE. Thus, we concluded that impaired testicular histopathology reduced the likelihood of the presence of mature sperm in the testes of patients with KS, consistent with the literature. Previous studies have shown that testicular histopathology is better in younger than in older individuals with KS.4,5 Although no significant difference was detected among testicular histopathology subgroups with regard to age in our study, the mean ages of patients with HS and LMA histopathology were lower than those of subjects with HT and SCO histopathology. This finding suggests that JS is more important than patient age for the determination of mTESE success in patients with KS. Further multicentre studies with larger samples should be conducted to determine the factors defining the success of mTESE.
In our study, the positive sperm recovery rate by mTESE was 31.7%, which is similar to the rates reported in previous series of 16–56.7%.6
Okada et al.11 reported that increased patient age was a negative factor and that an age of 35 years was critical for the success of mTESE. Similarly, Ferhi et al.6 found that only patient age was a predictive factor and that an age of 32 years was critical for the success of mTESE in patients with KS. We found that an age of 34 years was critical for the success of mTESE and that age was an independent variable that predicted the success of mTESE together with testicular histopathology.
Ozer et al.12 provided hormonal therapy to patients with KS and low T levels prior to mTESE. In contrast, we did not administer androgens before mTESE. Although androgen replacement therapy during the peri-pubertal period can have beneficial effects on normal pubertal development in patients with KS, therapy should be discontinued at least 6 months before mTESE.5 Alternative therapeutic options, such as the administration of aromatase inhibitors (anastrozol or testolactam), clomiphene or human chorionic gonadotropin, are often applied, but no controlled trial has been performed.
Knowledge of diagnostic testicular biopsy outcomes prior to the mTESE operation is valuable for predicting the success of sperm retrieval during mTESE. Diagnostic testicular biopsy has complications similar to those of the mTESE operation. Furthermore, sperm retrieval during subsequent mTESE cannot be assured by the retrieval of sperm during diagnostic testicular biopsy in patients with NOA. Diagnostic testicular biopsy is not recommended in clinical practice due to the additional cost, repetitive surgical procedures and invasive nature of the procedure, which increases the risk of complications.13 Here, testicular histology prior to mTESE was known only when the patient had undergone previous surgery. Knowledge of testicular histopathology following unsuccessful mTESE provides urologists with important data to predict the success of sperm retrieval for patients undergoing repeat mTESE.
The mean duration of infertility of the patients included in our study was quite long. The reason may be that the patient population that presents to our infertility clinic comes from rural areas with a low socioeconomic status; therefore, patients may have failed to seek the appropriate treatment at relevant health institutions in time.
Diagnostic testicular biopsy is not recommended before mTESE, as it results in similar complications as those of mTESE because it is an invasive procedure. Therefore, biopsy samples obtained during mTESE were evaluated in our study.
Our study had some limitations, such as its retrospective single-centre design, despite the large number of patients included. Not all sperm obtained by mTESE can be used in ICSI. The lack of post-ICSI fertility analyses in our study may be a limitation; however, ICSI outcomes are affected by many factors, including female fertility. The primary goal of our study was to identify factors affecting the success of mTESE; thus, we did not consider ICSI outcomes.
ConclusionsThe present study revealed that impaired testicular histopathology negatively affects the success of mTESE, and that testicular histopathology is a predictive factor for the success of mTESE in patients with KS. Advanced patient age negatively affected the success of mTESE, and the likelihood of success may increase in patients who have undergo mTESE before the age of 34 years.
Ethical disclosuresProtection of human and animal subjectsThe authors declare that no experiments were performed on humans or animals for this study.
Confidentiality of dataThe authors declare that they have followed the protocols of their work center on the publication of patient data.
Right to privacy and informed consentThe authors have obtained the written informed consent of the patients or subjects mentioned in the article. The corresponding author is in possession of this document.
Conflict of interestThe authors declare no conflict of interest.
We would like to thank to Ozgur Cakmak, Ertan Can and Taha Cetin for their contribution to the statistical analysis.