To determine the protocols used by Spanish anaesthesiologists for thromboprophylaxis and anticoagulant or antiplatelet drugs management in neurosurgical or neurocritical care patients.
Materials and methodsAn online survey with 22 questions, with one or multiple options, launched by the Neuroscience Subcommittee of the Spanish Anaesthesia Society and available between June and October 2012.
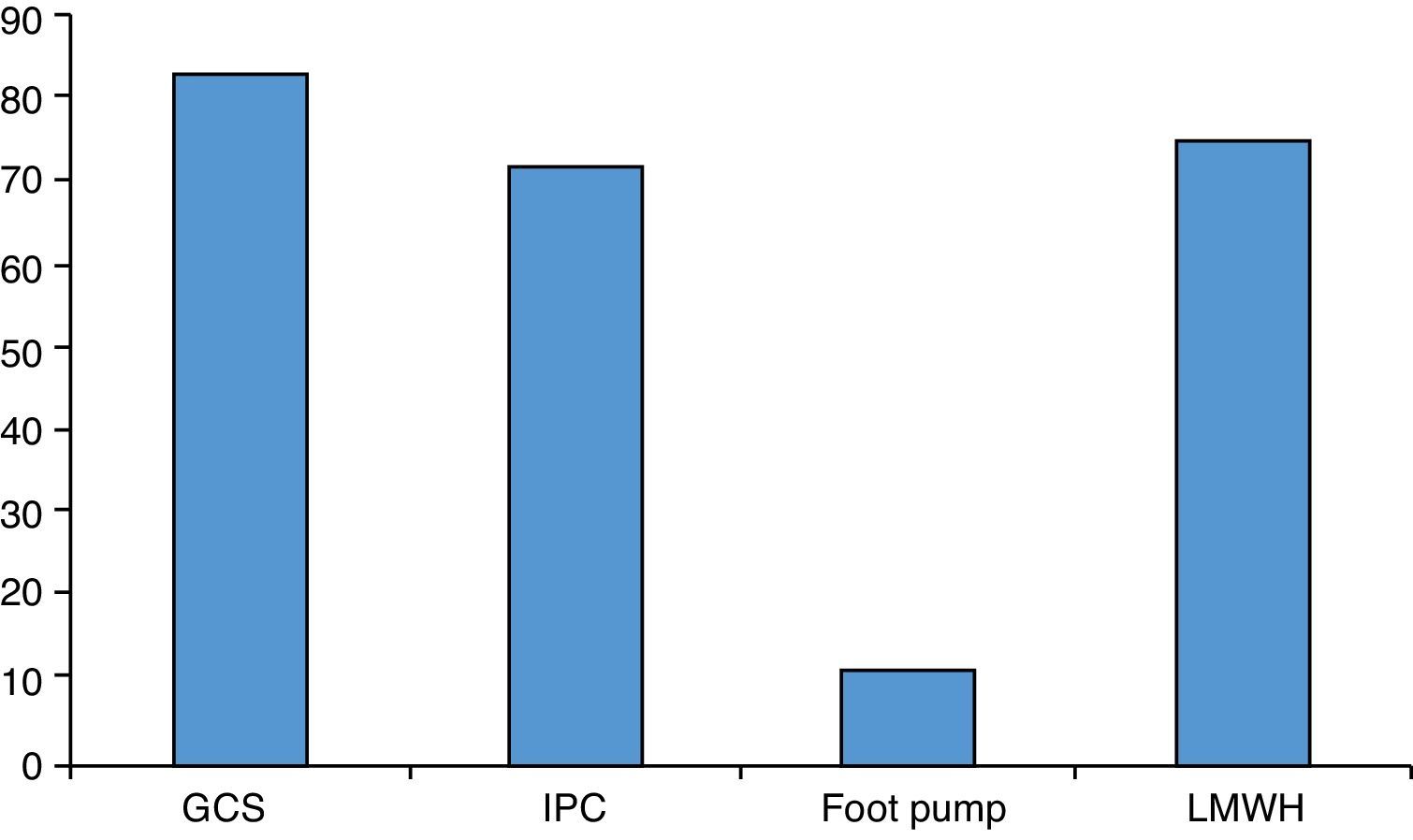
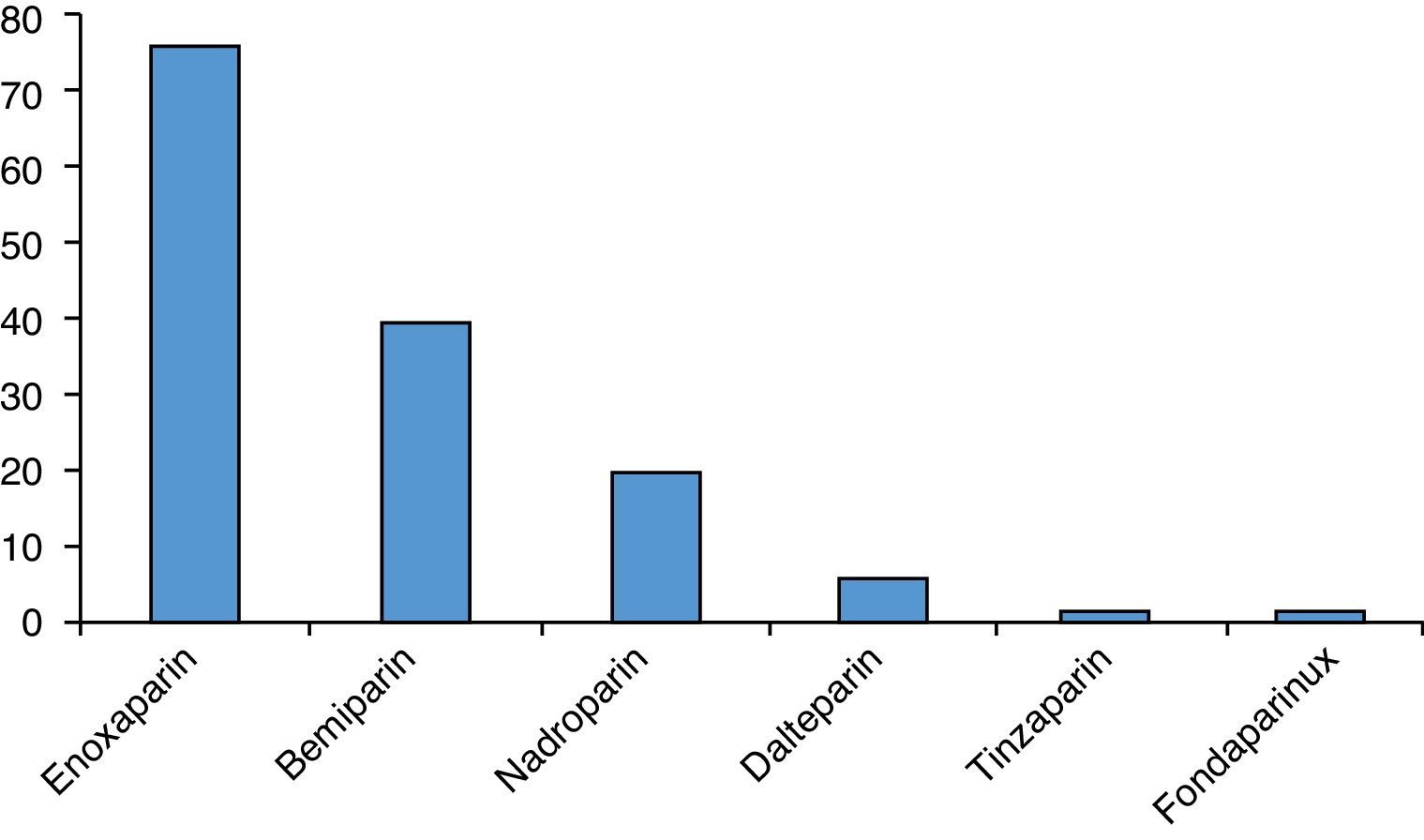
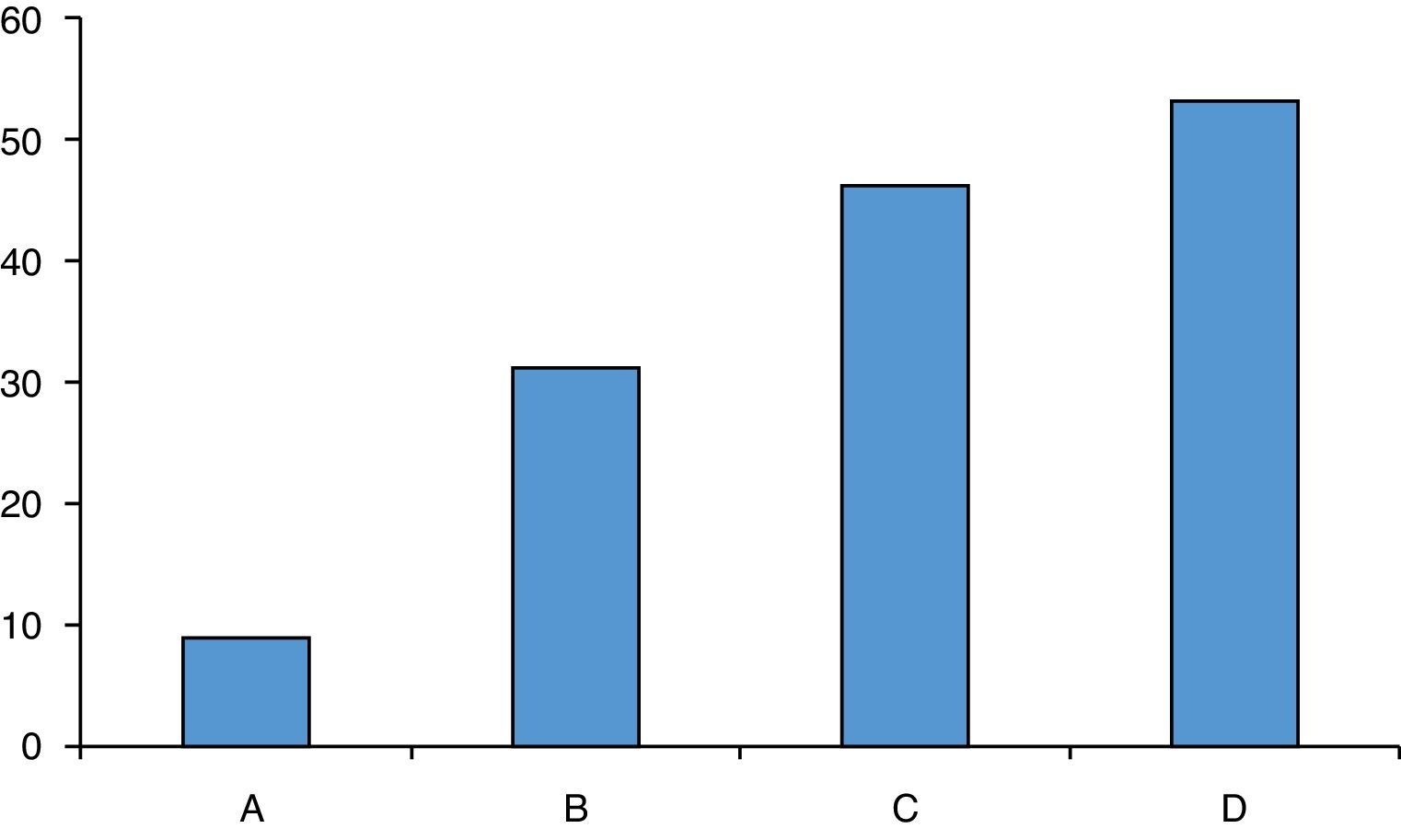
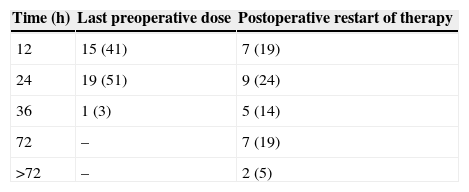
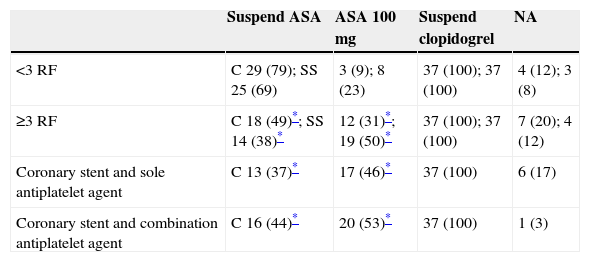
ResultsOf the 73 hospitals included in the National Hospitals Catalogue, a valid response to the online questionnaire was received by 41 anaesthesiologists from 37 sites (response rate 50.7%). Only one response per site was used. A specific protocol was available in 27% of these centres. Mechanical thromboprophylaxis is used, intraoperatively or postoperatively, in 80%, and pharmacological treatment is used by 75% of respondents. Enoxaparin was the most frequent heparin used in craniotomy patients (78%). Craniotomies were performed maintaining acetylsalicylic acid treatment in patients with coronary stents and double anti-platelet treatment in half of the centres.
ConclusionsMechanical thromboprophylaxis is used more frequently than the pharmacological approach in neurosurgical or neurocritical populations in Spanish hospitals. Management of patients under previous anticoagulant treatment was highly heterogeneous among hospitals included in this survey. Previous antiplatelet treatment is modified depending on primary or secondary prescription.
Conocer la práctica clínica de los anestesiólogos españoles en la tromboprofilaxis y el manejo de los anticoagulantes y antiagregantes en pacientes neuroquirúrgicos y neurocríticos.
Material y métodosEncuesta diseñada desde la Sección de Neurociencia de la Sociedad Española de Anestesiología y Reanimación, con 22 preguntas, difundida y contestada en formato electrónico, disponible entre junio y octubre de 2012.
ResultadosDe los 73 centros hospitalarios con servicio de Neurocirugía incluidos en el Catálogo Nacional de Hospitales, se recibió respuesta válida a la encuesta on line por parte de 41 anestesiólogos de 37 centros (tasa de respuesta del 50,7%). Se consideró una respuesta de cada centro. Solo el 27% de los centros respondedores disponían de un protocolo escrito específico para el manejo de estos pacientes. La tromboprofilaxis mecánica se utilizó hasta en un 80%, aunque de forma variable, y la farmacológica en un 75% de los centros. La enoxaparina fue la heparina de bajo peso molecular más utilizada en pacientes sometidos a craneotomía (78%). En la mitad de los centros respondedores se realizaron craneotomías manteniendo el tratamiento con ácido acetilsalicílico en los pacientes con antecedentes de cardiopatía isquémica, stent coronario y antiagregación dual.
ConclusionesLa tromboprofilaxis mecánica es más utilizada que la farmacológica en la población neuroquirúrgica de nuestro país. El manejo de los pacientes tratados previamente con anticoagulantes presenta una marcada variabilidad clínica entre los diferentes hospitales, mientras que el tratamiento con antiagregantes se modifica en función de si se trata de profilaxis primaria o secundaria.