Suplement “"Advances in Thoracic Radiology”
More infoTo describe the prevalence and characteristics of interstitial lung abnormalities (ILA) in CT scans performed prior to the initiation of antifibrotics in a series of patients with interstitial lung disease (ILD), and to identify characteristics apparent on early CT scans that could help to predict outcomes.
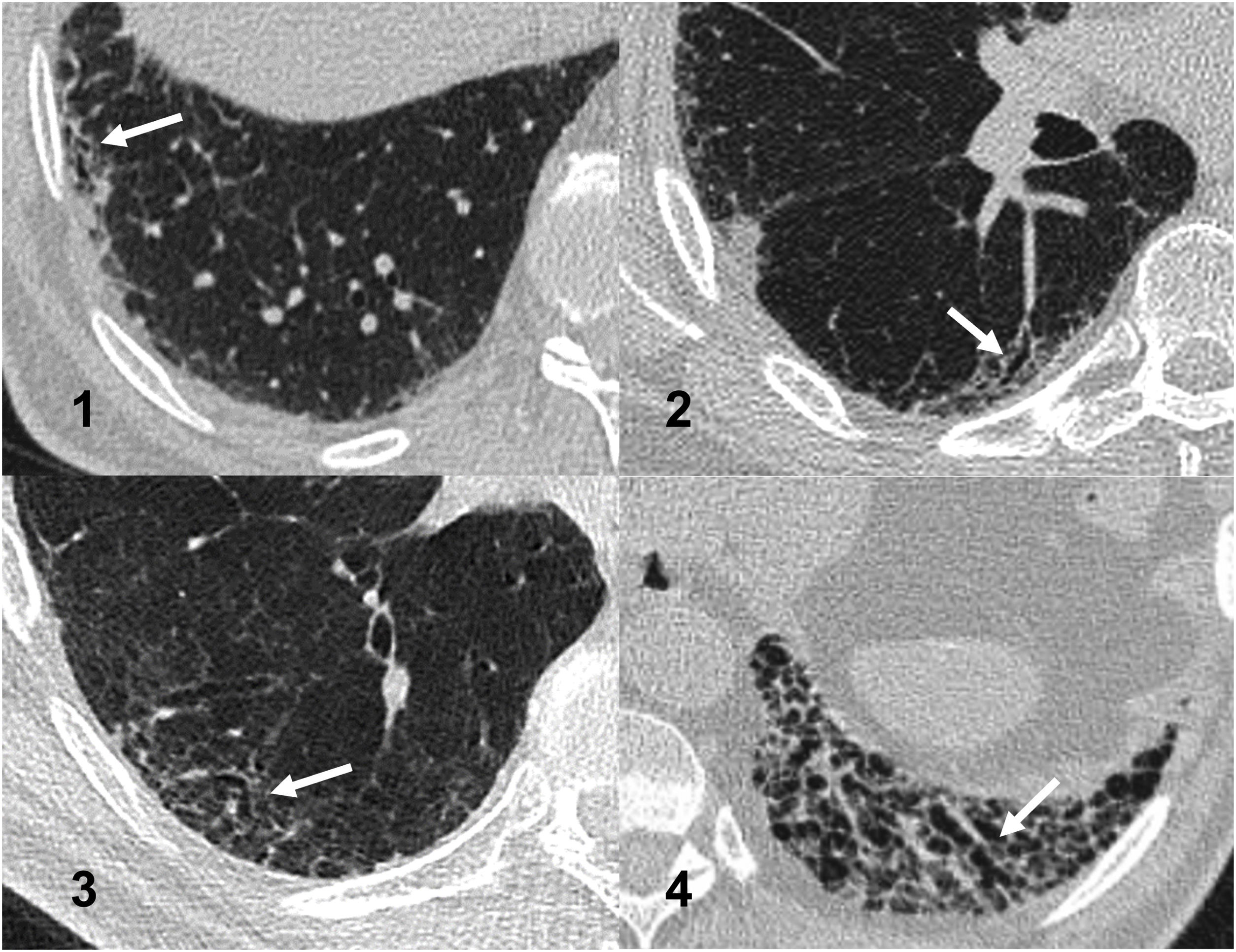
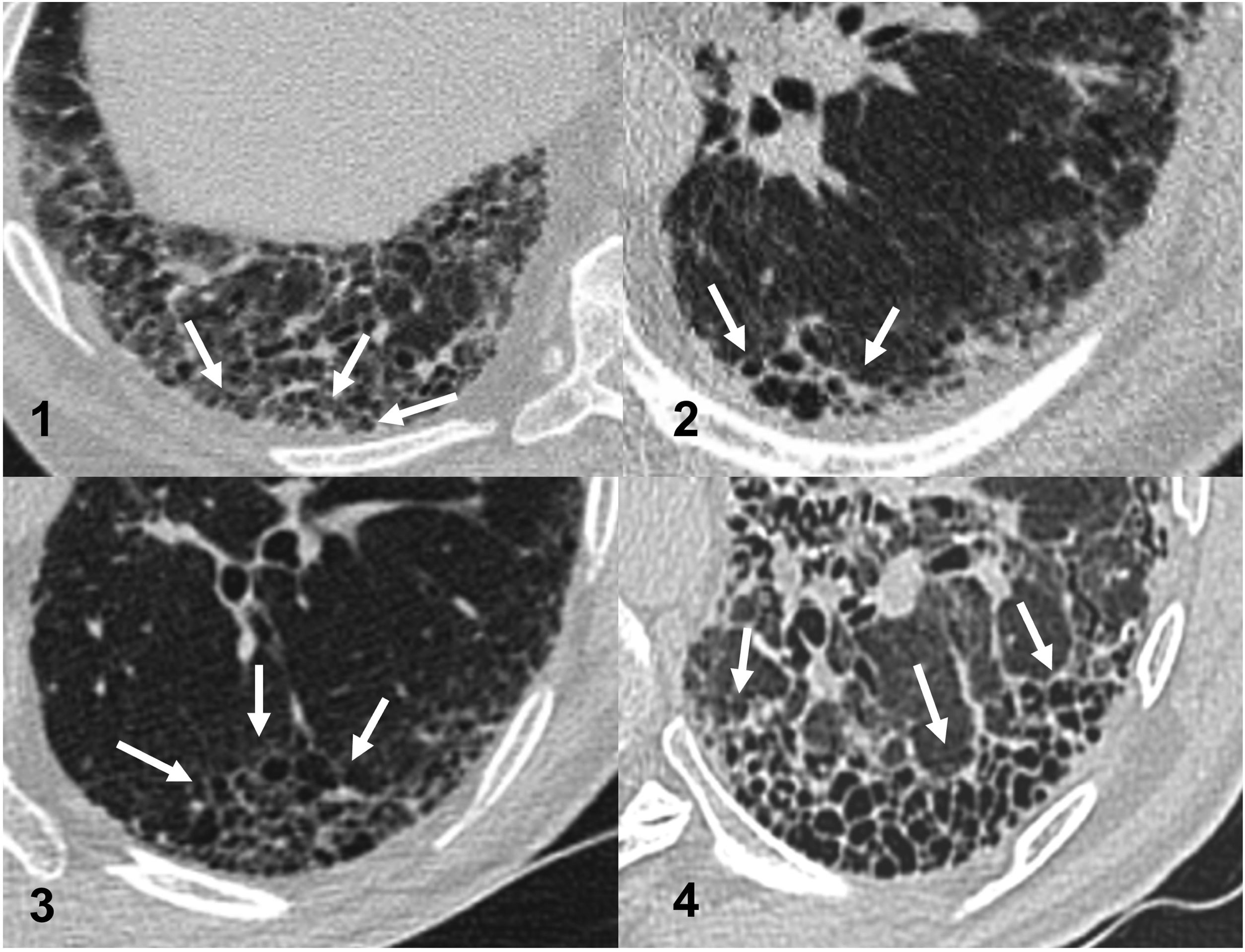
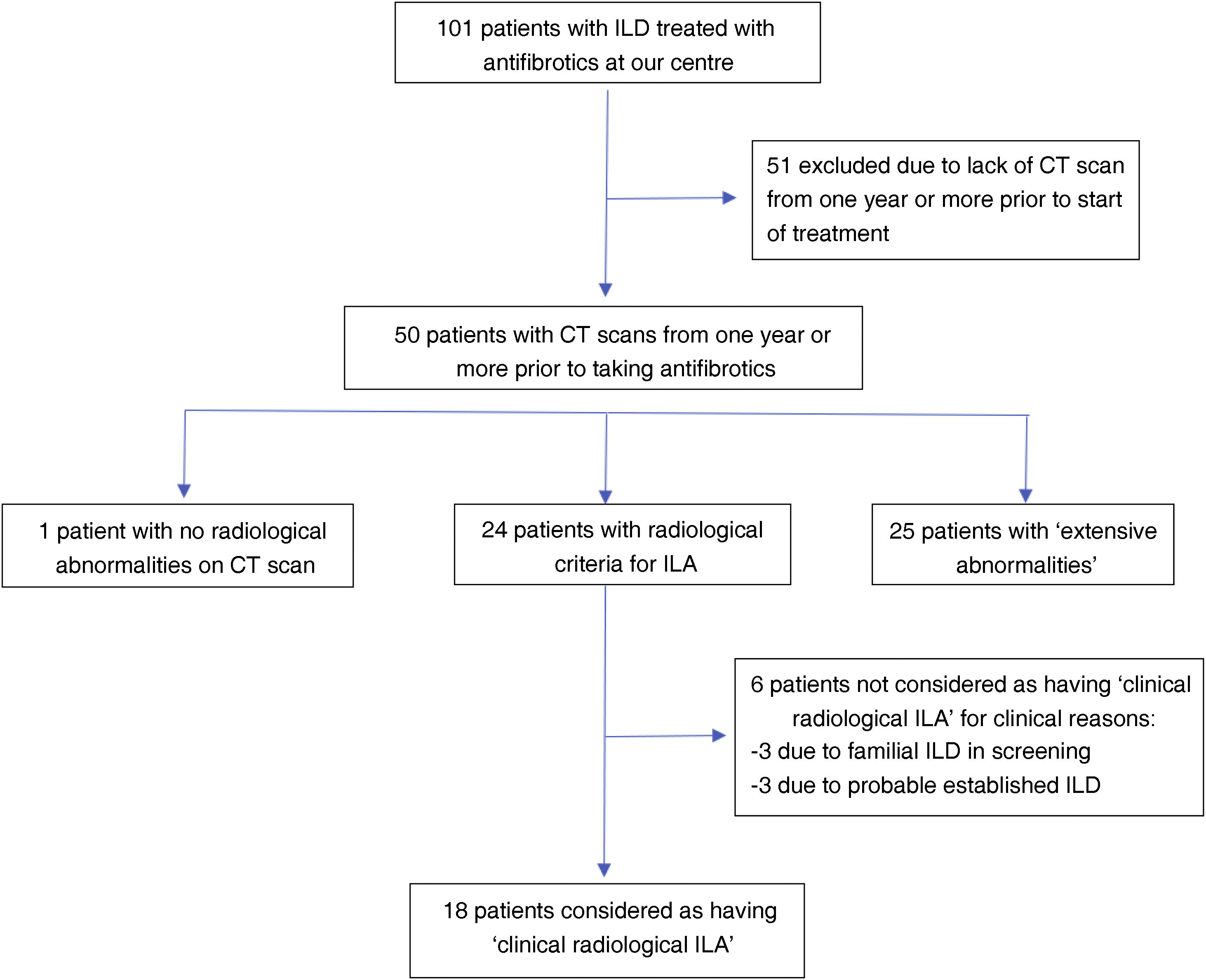
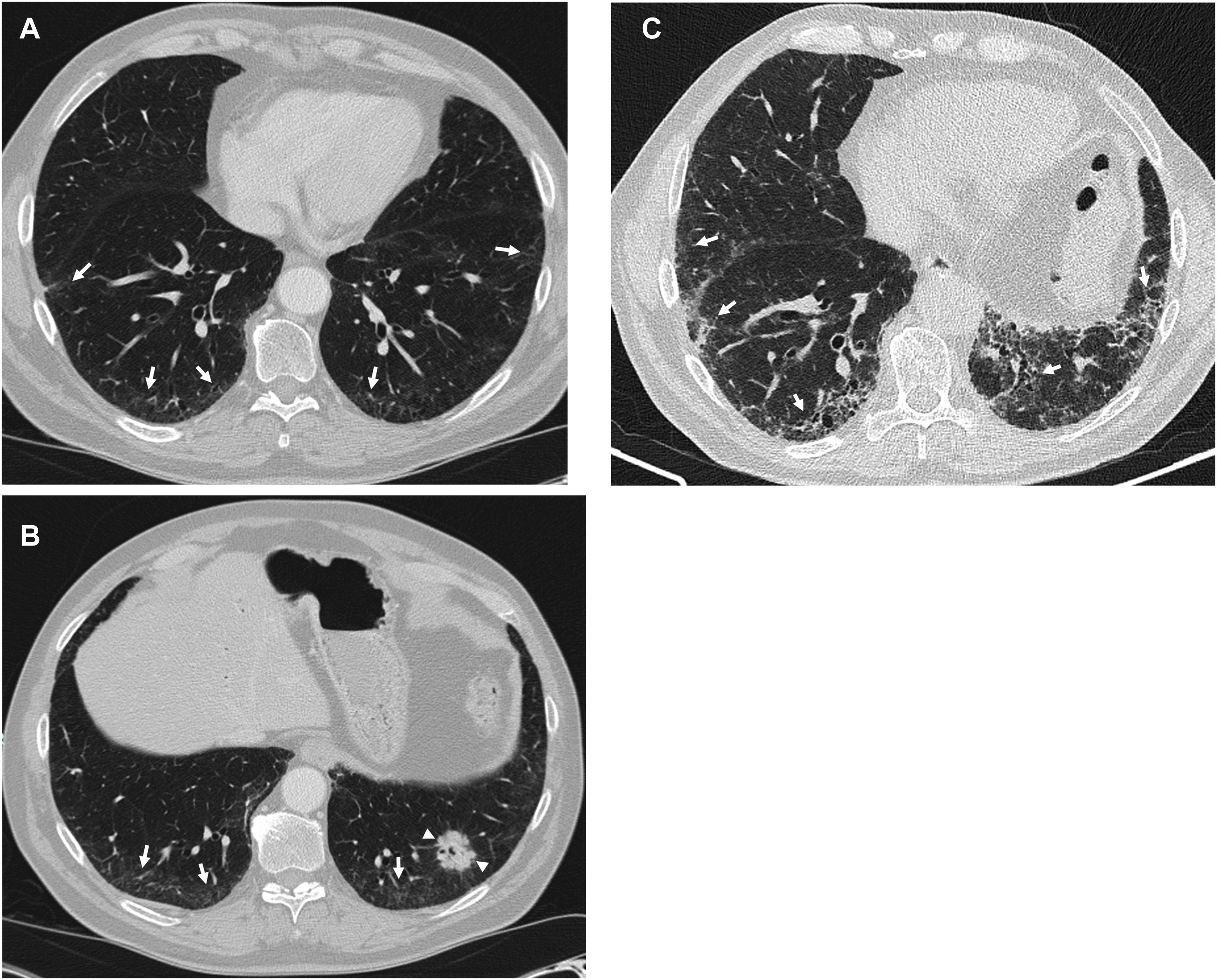
MethodsWe conducted a retrospective observational study. The original cohort consisted of 101 patients diagnosed with ILD and treated with antifibrotics in a tertiary hospital. Patients were included if they had a thoracic CT scan performed at least one year before initiation of therapy. They were classified radiologically in three groups: without ILA, with radiological ILA and extensive abnormalities. ILA were classified as subpleural fibrotic, subpleural non-fibrotic and non-subpleural. The initial scan and the latest CT scan performed before treatment were read for assessing progression. The relationship between CT findings of fibrosis and the radiological progression rate and mortality were analyzed.
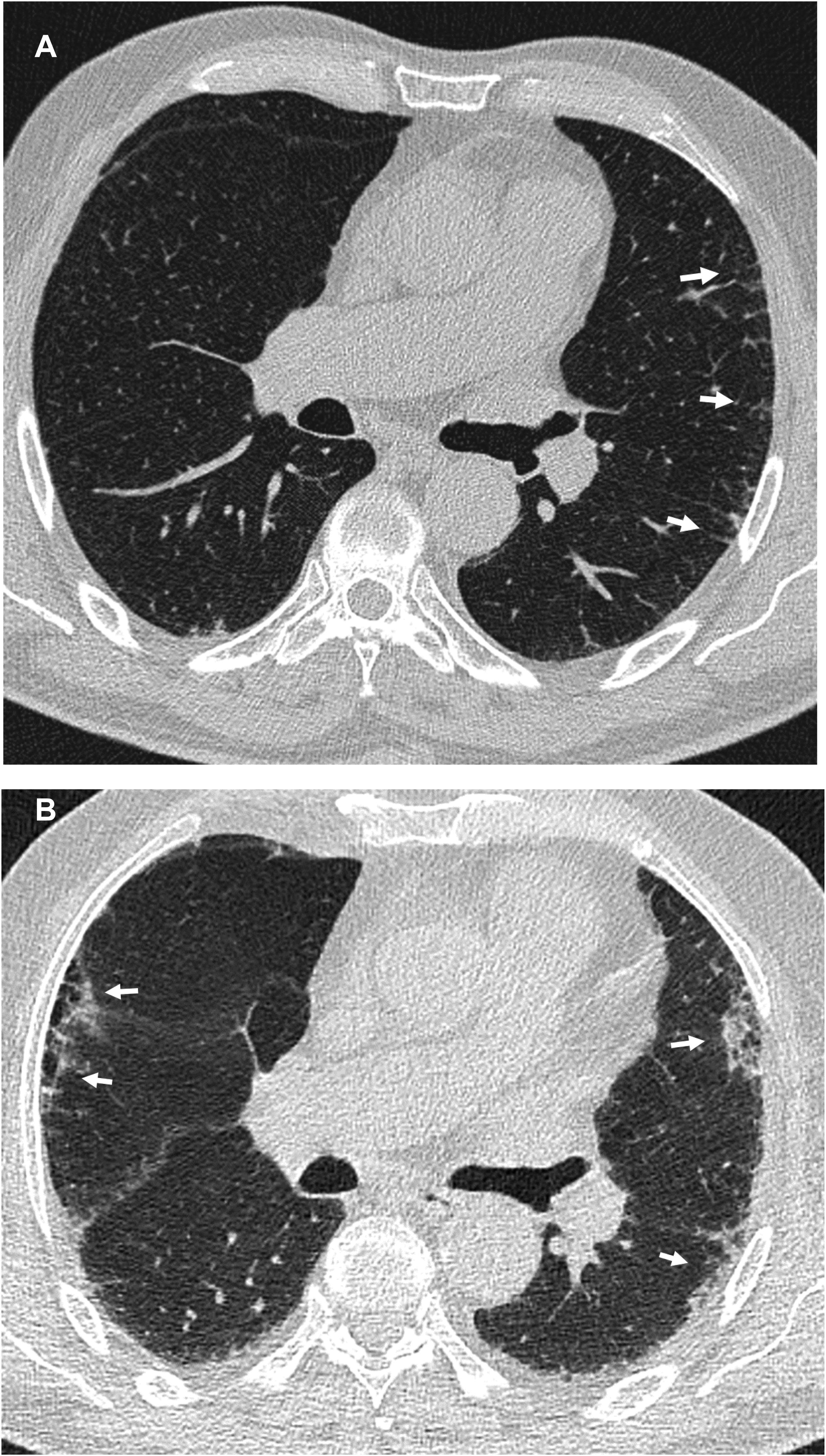
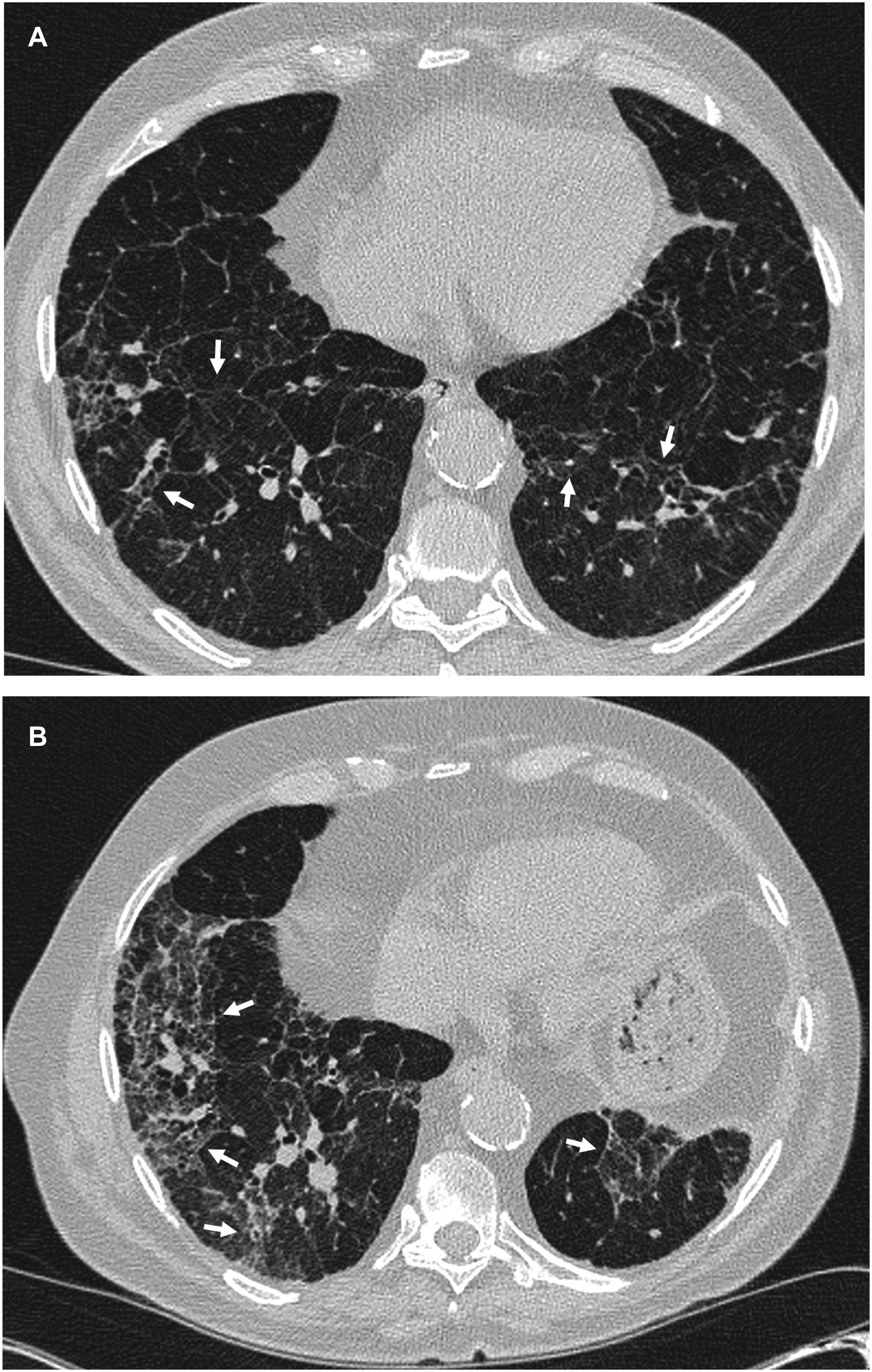
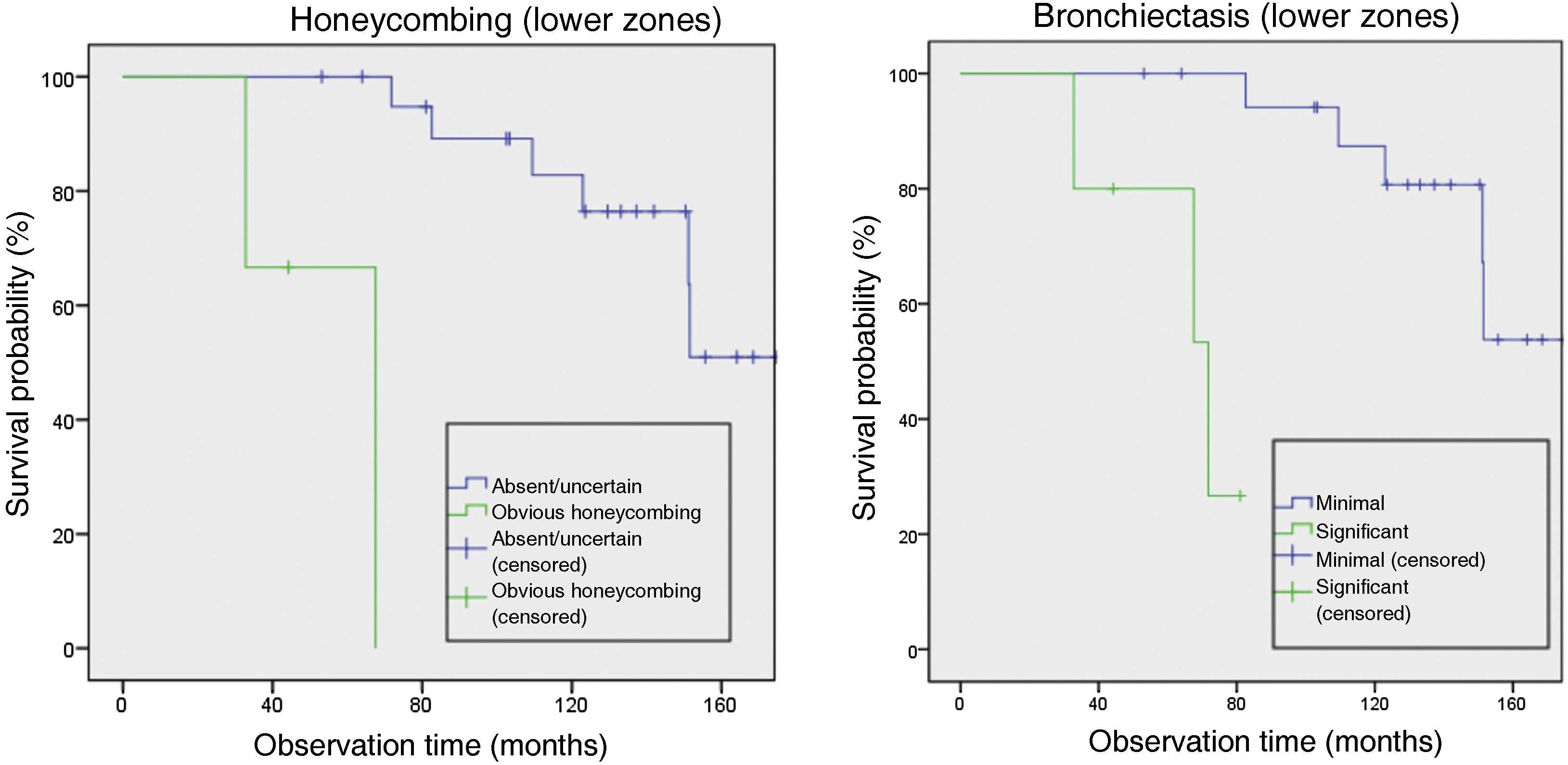
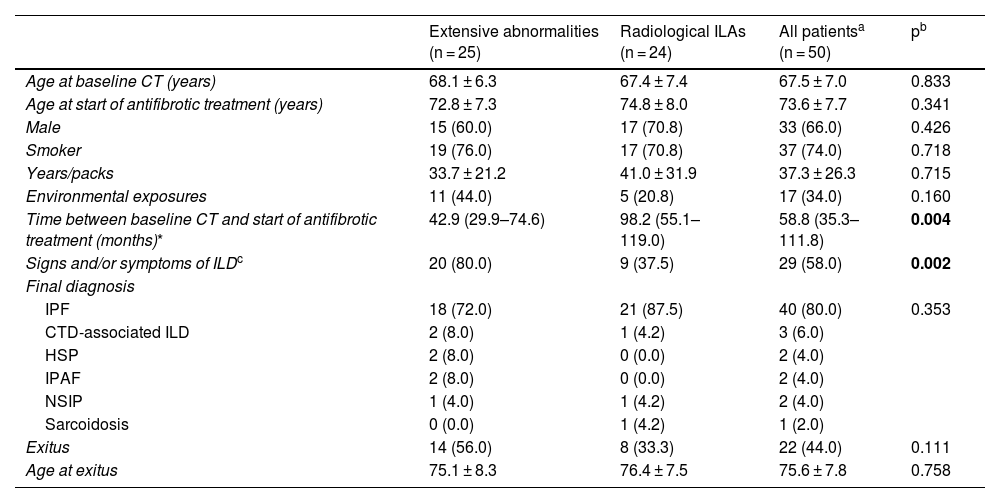
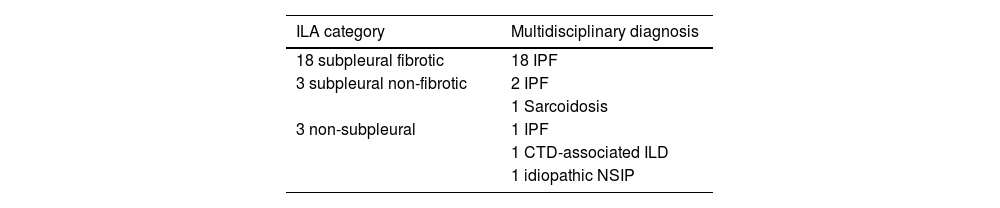
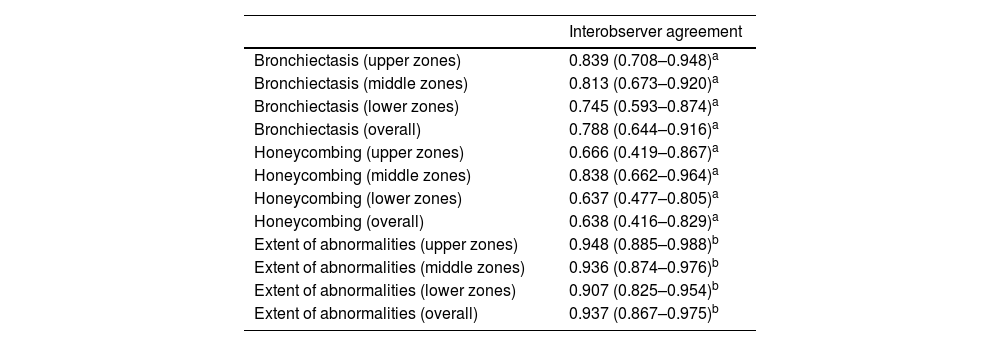
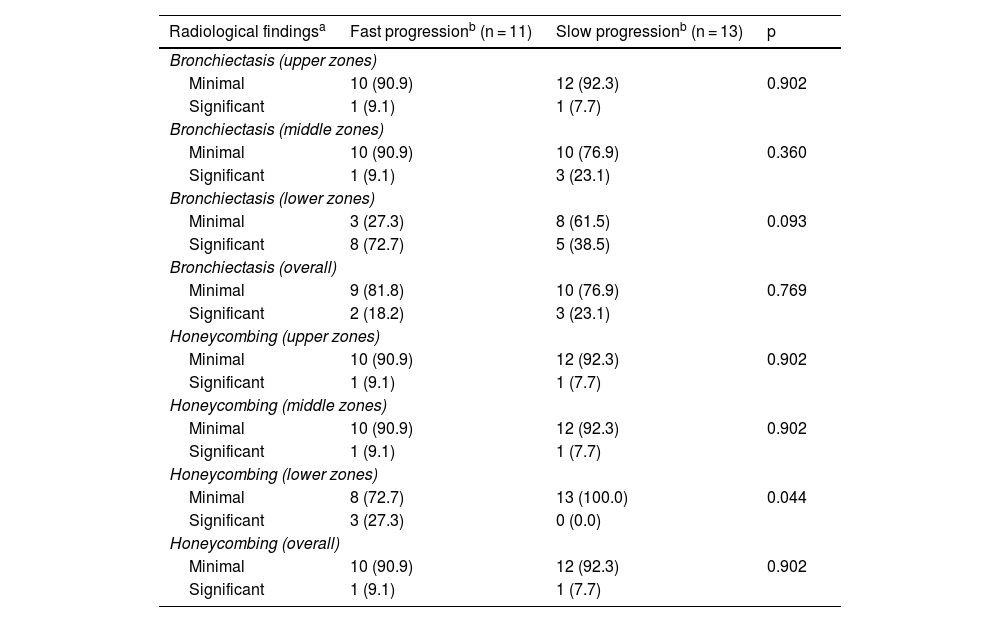
ResultsWe included 50 patients. Only 1 (2%) had a normal CT scan, 25 (50%) had extensive alterations and 24 (48%) had radiological criteria for ILA, a median of 98.2 months before initiation of antifibrotics, of them 18 (75%) had a subpleural fibrotic pattern. Significant bronchiectasis and obvious honeycombing in the lower zones were associated with shorter survival (p = 0.04). Obvious honeycombing in the lower zones was also significantly (p < 0.05) associated with a faster progression rate.
ConclusionsFibrotic ILAs are frequent in remote scans of patients with clinically relevant ILD, long before they require antifibrotics. Findings of traction bronchiectasis and honeycombing in the earliest scans, even in asymptomatic patients, are related to mortality and progression later on.
Describir la prevalencia y características de las alteraciones intersticiales pulmonares (AIP) en tomografías computarizadas (TC) realizadas antes del inicio del tratamiento antifibrótico en una serie de pacientes con enfermedad pulmonar intersticial difusa (EPID), e identificar las características visibles en las TC iniciales que podrían ayudar a predecir el pronóstico.
MétodosEstudio observacional retrospectivo que incluye una cohorte original de 101 pacientes diagnosticados de EPID y tratados con antifibróticos en un hospital terciario. Los pacientes fueron incluidos cuando contaban con una TC torácica realizada al menos un año antes del inicio del tratamiento. Se clasificaron radiológicamente en tres grupos: sin AIP, con AIP y “alteraciones extensas”. Asimismo, las AIP se clasificaron como subpleural fibrótica, subpleural no fibrótica y no subpleural. Se leyeron la TC inicial y la más cercana anterior al tratamiento para evaluar la progresión, y se analizó la relación entre los hallazgos de fibrosis en dicha TC inicial y la tasa de progresión radiológica y mortalidad.
ResultadosSe incluyeron 50 pacientes, solo 1 (2%) tenía una TC inicial normal, 25 (50%) tenían “alteraciones extensas” y 24 (48%) tenían criterios de AIP radiológica una mediana de 98,2 meses antes del inicio del tratamiento. De estas últimas, 18 (75%) tenían un patrón subpleural fibrótico. Las bronquiectasias significativas y el panal evidente en las zonas inferiores se asociaron con una supervivencia más corta (p = 0,04). El panal en las zonas inferiores se asoció significativamente (p < 0,05) con una tasa de progresión más rápida.
ConclusionesLas AIP fibróticas son frecuentes en exploraciones antiguas de pacientes con EPID clínicamente relevante, mucho antes de que requieran tratamiento con antifibróticos. Los hallazgos de bronquiectasias por tracción y panal en las TC iniciales, incluso en pacientes asintomáticos, se relacionan con la mortalidad y progresión más rápida en el futuro.