To compare the effectiveness, survival and cost in patients with unresectable hepatic cell carcinoma (HCC) treated with trans-arterial chemoembolization using doxorubicin-eluting beads (DEB-TACE) versus conventional TACE (cTACE) in clinical practice.
Materials and methodsThis single-centered retrospective observational study compared 60 consecutive HCC unresectable patients: 30 were treated with DEB-TACE and 30 used cTACE. Comparisons were with χ2 test, Student t-test, and Kaplan–Meier method.
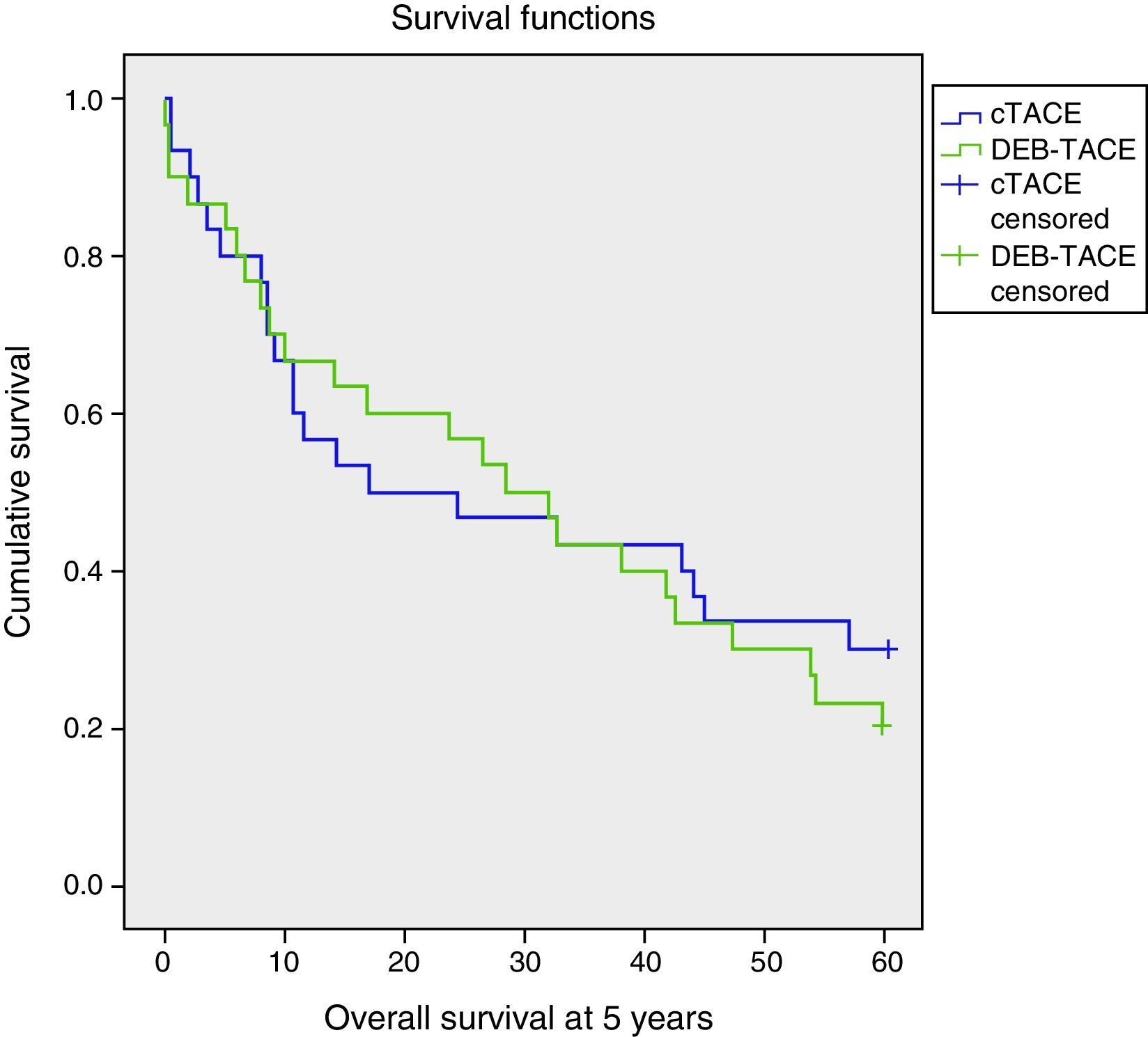
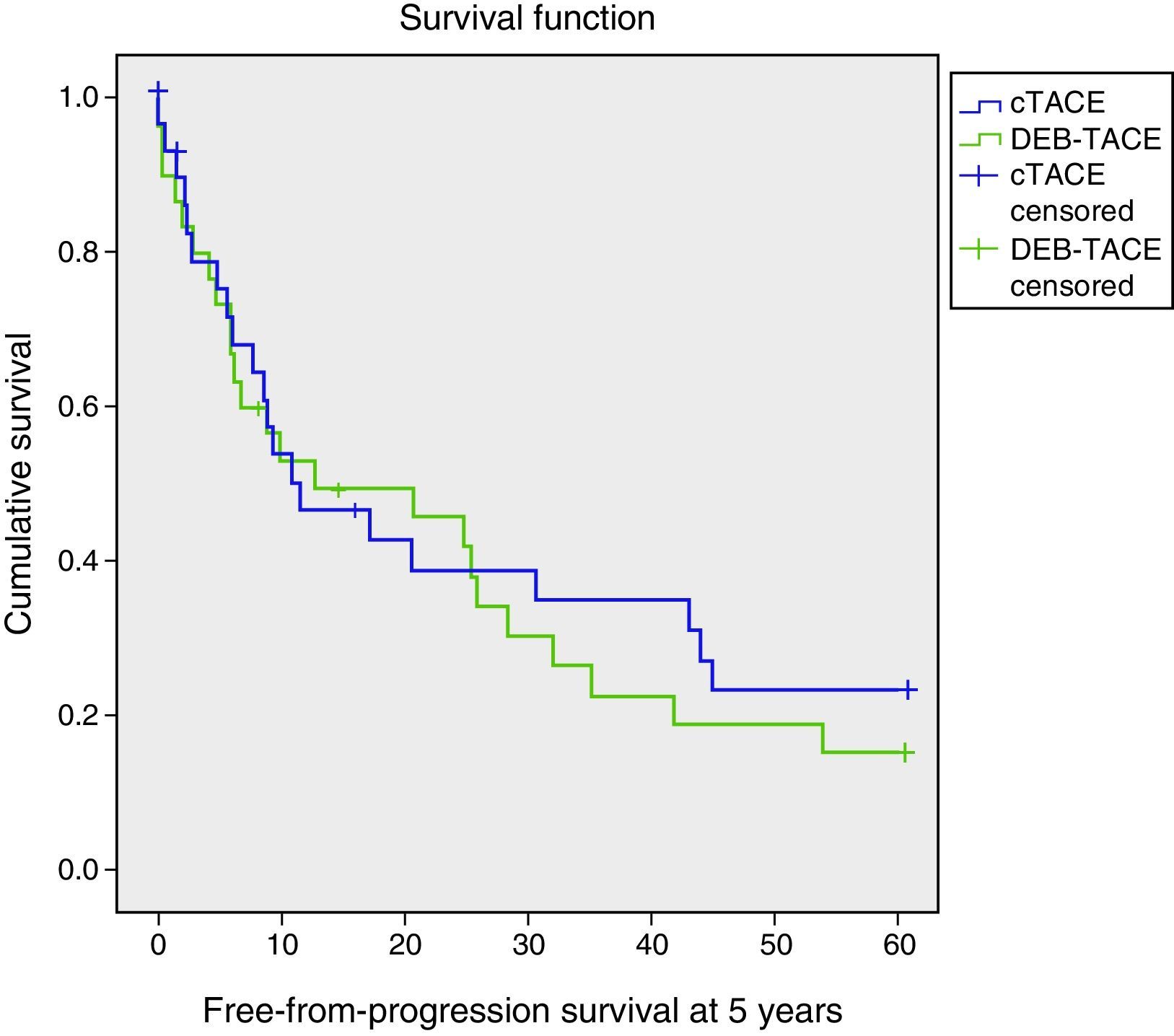
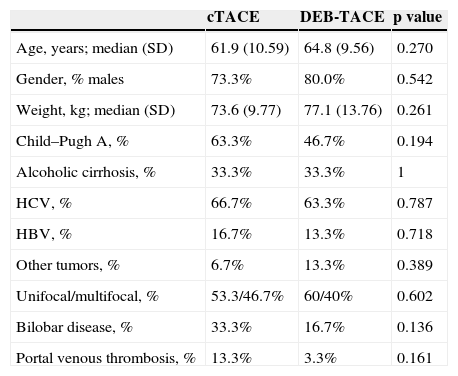
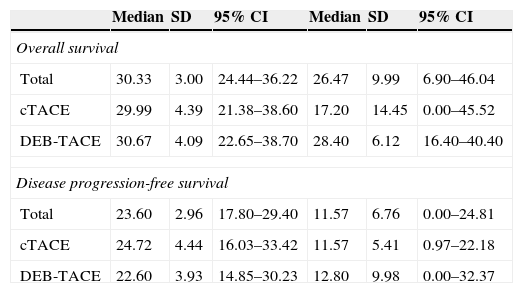
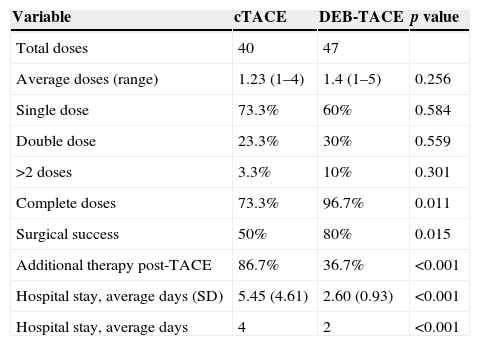
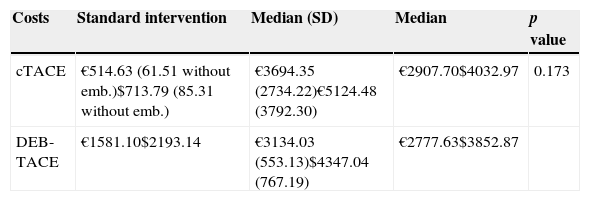
ResultsOf the 60 patients with HCC in non-curative stage, baseline characteristics were similar for both groups of treatment, and of these we observed lower survival in male patients and those who had hepatitis C virus (p=0.014 and p=0.003, respectively). No statistically significant differences were observed as a function of treatment employed with respect to overall survival (OS) at 5 years (29.99 months; 95%CI: 21.38–38.60 versus 30.67 months; 95%CI: 22.65–38.70; p=0.626) and progression free survival (PFS) median of 11.57 months (95%CI: 0.97–22.18) versus 12.80 months (95%CI: 0.00–32.37; p=0.618). The median length of hospital admission was 2.6 and 5.4 days (p<0.001) for DEB-TACE and cTACE, respectively. Toxicities grade 2–4 were higher in cTACE group (54 versus 31; p<0.001). The cost of the treatment was 1581 € for DEB-TACE and 514.63 € for cTACE. The overall mean cost of intervention was 3134 € and 3694.35 €, respectively (p=0.173).
ConclusionsChemoembolization in patients with unresectable HCC achieved OS close to 30 months at 5 years, independent of the technique employed. Similar overall costs but better tolerance of the DEB-TACE justified the higher costs of the procedure.
Comparar la efectividad, supervivencia y coste de la quimioembolización transarterial con partículas liberadoras de doxorrubicina (DEB-TACE) y la quimioembolización convencional (cTACE) en pacientes con carcinoma hepatocelular (CHC) irresecable.
Material y métodosEstudio unicéntrico, observacional y retrospectivo que comparó 60 pacientes con CHC irresecable separados en dos grupos comparables de 30 pacientes tratados con DEB-TACE y otros 30 con cTACE. Se realizaron las pruebas de χ2 y t de Student, y se utilizó el método de Kaplan Meier.
ResultadosLa supervivencia fue menor en hombres y en pacientes con hepatitis C (p=0,014 y p=0,003, respectivamente). No hubo diferencias estadísticamente significativas en la supervivencia global a los 5 años (29,99 meses; IC del 95%: 21,38–38,60 y 30,67 meses; IC del 95%: 22,65–38,70; p=0,626) y la supervivencia libre de progresión (mediana: 11,57 meses; IC del 95%: 0,97–22,18 y 12,80 meses; IC del 95%: 0,00–32,37; p=0,618). El tiempo medio de ingreso fue de 2,6 y 5,4 días (p<0,001) para DEB-TACE y cTACE, respectivamente. La toxicidad grado 2–4 fue superior en el grupo cTACE (54 y 31; p<0,001). El coste del tratamiento fue de 1.581 € con DEB-TACE y de 514,63 € con cTACE. El coste total medio fue de 3.134 € y 3.694,35 €, respectivamente (p=0,173).
ConclusiónLa quimioembolización en pacientes con CHC irresecable tiene una supervivencia global cercana a 30 meses a los 5 años, independientemente de la técnica empleada. Los costes globales son similares, aunque la mejor tolerancia de la DEB-TACE justifica el mayor coste del procedimiento.