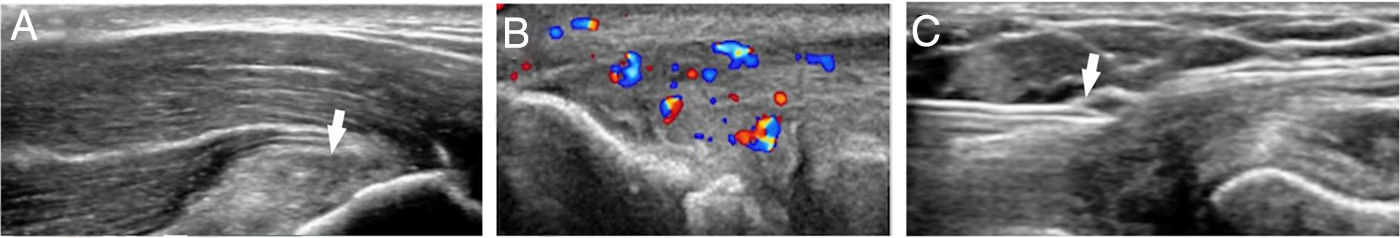
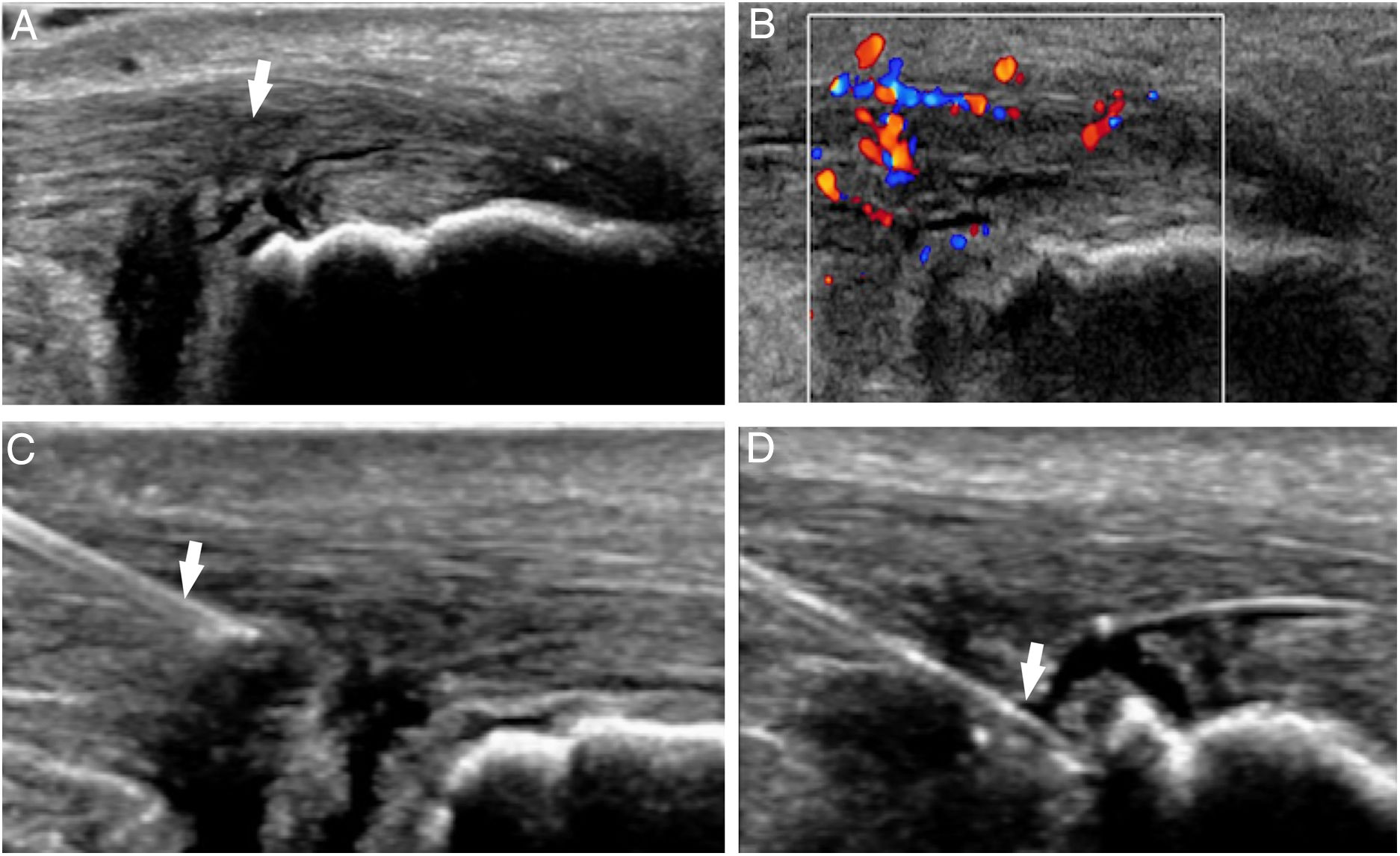
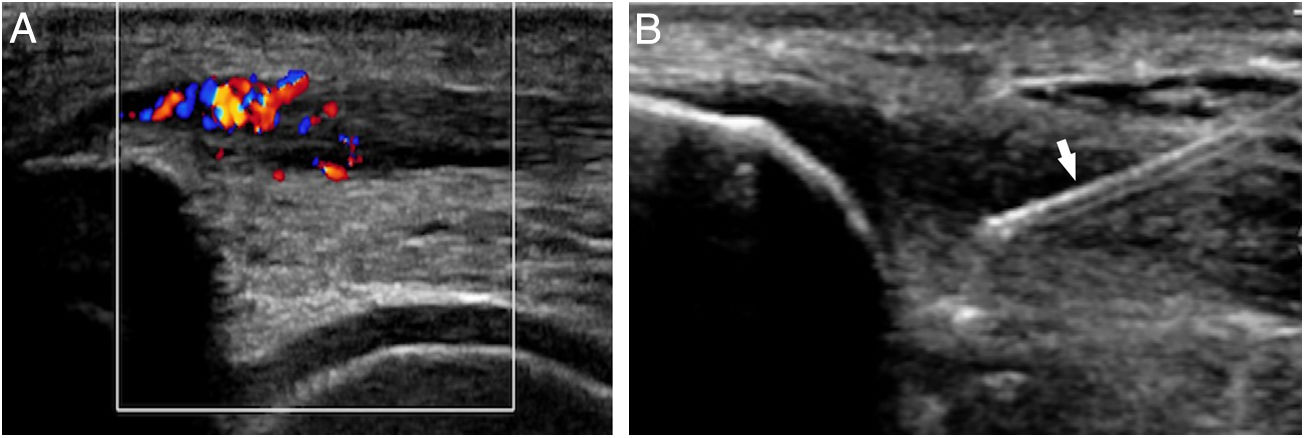
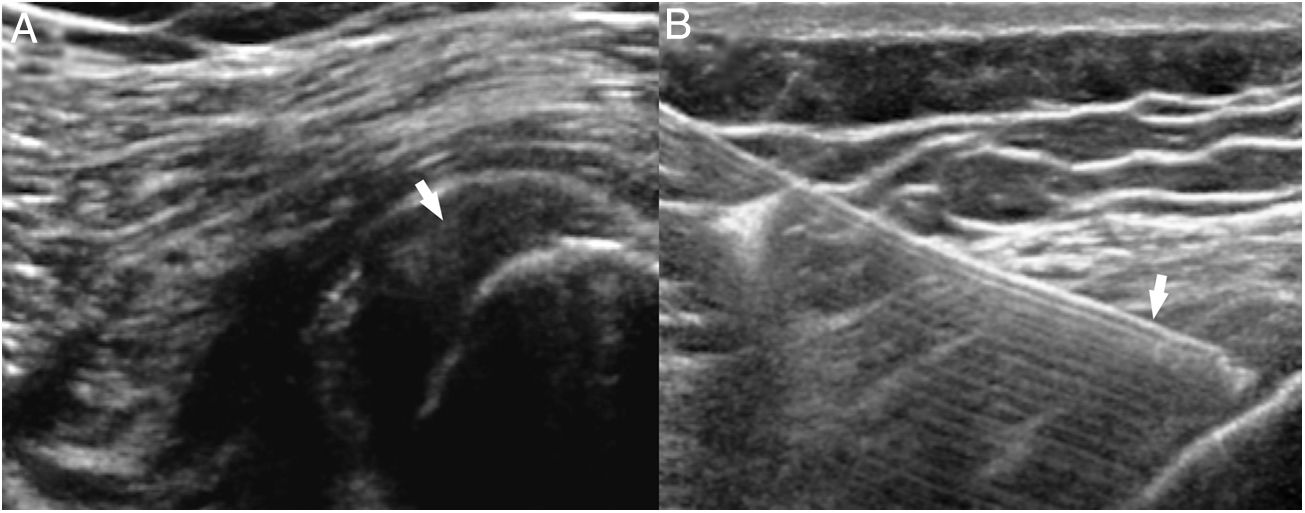
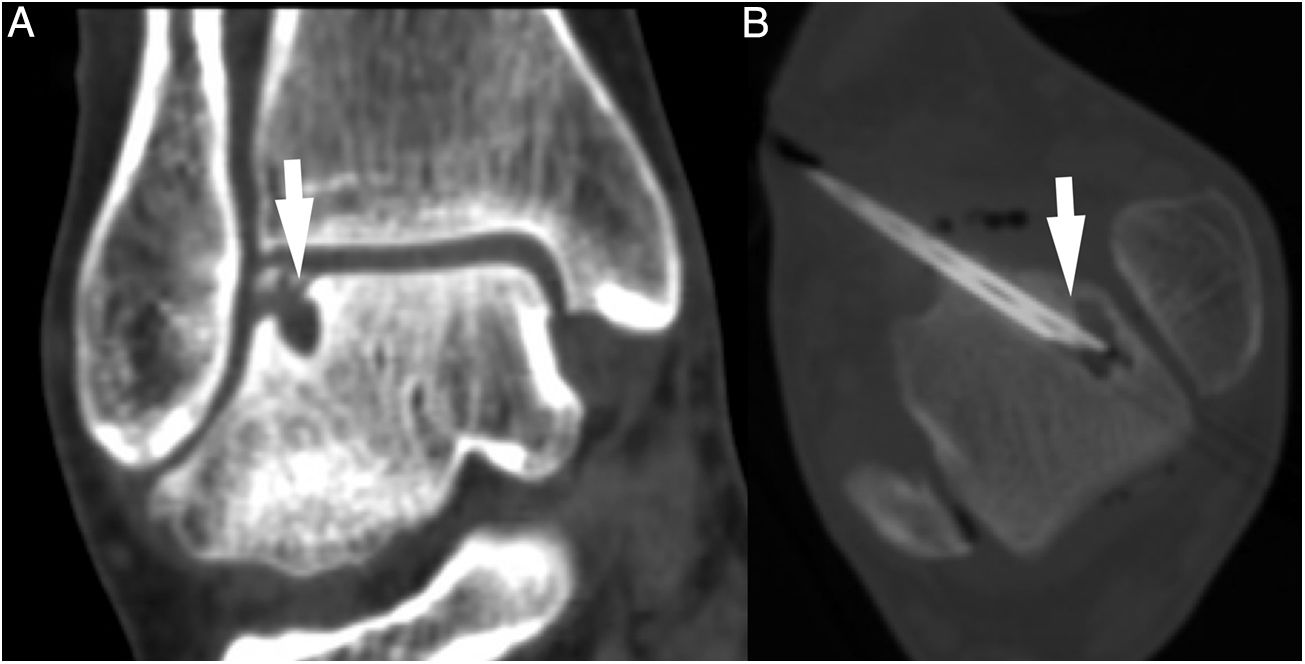
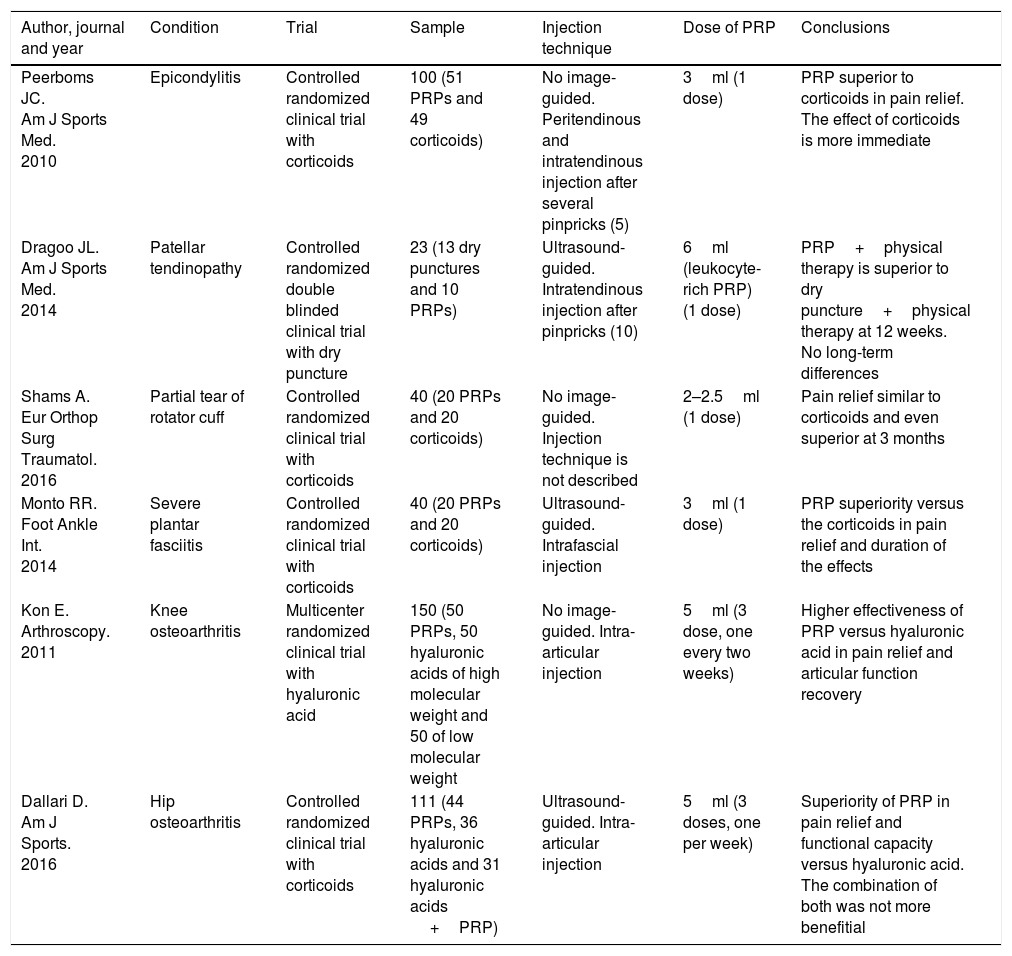
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is a preparation for therapeutic purposes that is increasingly accepted for various musculoskeletal disorders, due to its theoretical potential to repair tissues with poor healing capacity. Several randomized clinical trials have investigated the capacity of PRP to repair tendons, ligaments, muscles and cartilage, and to date there is level 1a evidence to support its use for lateral epicondylitis, osteoarthritis of the knee, plantar fasciitis and rotator cuff tendinopathy; and level 1b for patellar tendinopathy and osteoarthritis of the hip. Retrospective cohort studies and case series describe promising results with PRP for treating other musculoskeletal disorders.
Since its side effects are fewer than those of the control groups, the treatment is considered practically harmless and is being increasingly used. Further randomized clinical trials are necessary to establish future indications, and to confirm effectiveness and safety.
El plasma rico en plaquetas (PRP) es un preparado con fines terapéuticos cada vez más aceptado en diversas patologías musculoesqueléticas, debido a su teórico potencial para reparar tejidos con baja capacidad curativa. Se han realizado diversos ensayos clínicos aleatorizados que investigan la capacidad del PRP para la reparación de tendones, ligamentos, músculos y cartílago. Hasta la fecha existe evidencia 1A que apoya su uso para la epicondilitis lateral, la osteoartritis de rodilla, la fascitis plantar y tendinopatías del manguito rotador, y evidencia 1B en la tendinopatía del tendón rotuliano y la osteoartritis de cadera. Estudios retrospectivos, de cohortes y series de casos describen resultados prometedores del PRP para el tratamiento de otras patologías musculoesqueléticas.
Al ser sus efectos secundarios menores que los de los grupos controles hacen que sea un tratamiento considerado como prácticamente inocuo y cada vez más usado. Son necesarios nuevos ensayos clínicos aleatorizados para establecer futuras indicaciones y confirmar su efectividad y seguridad.