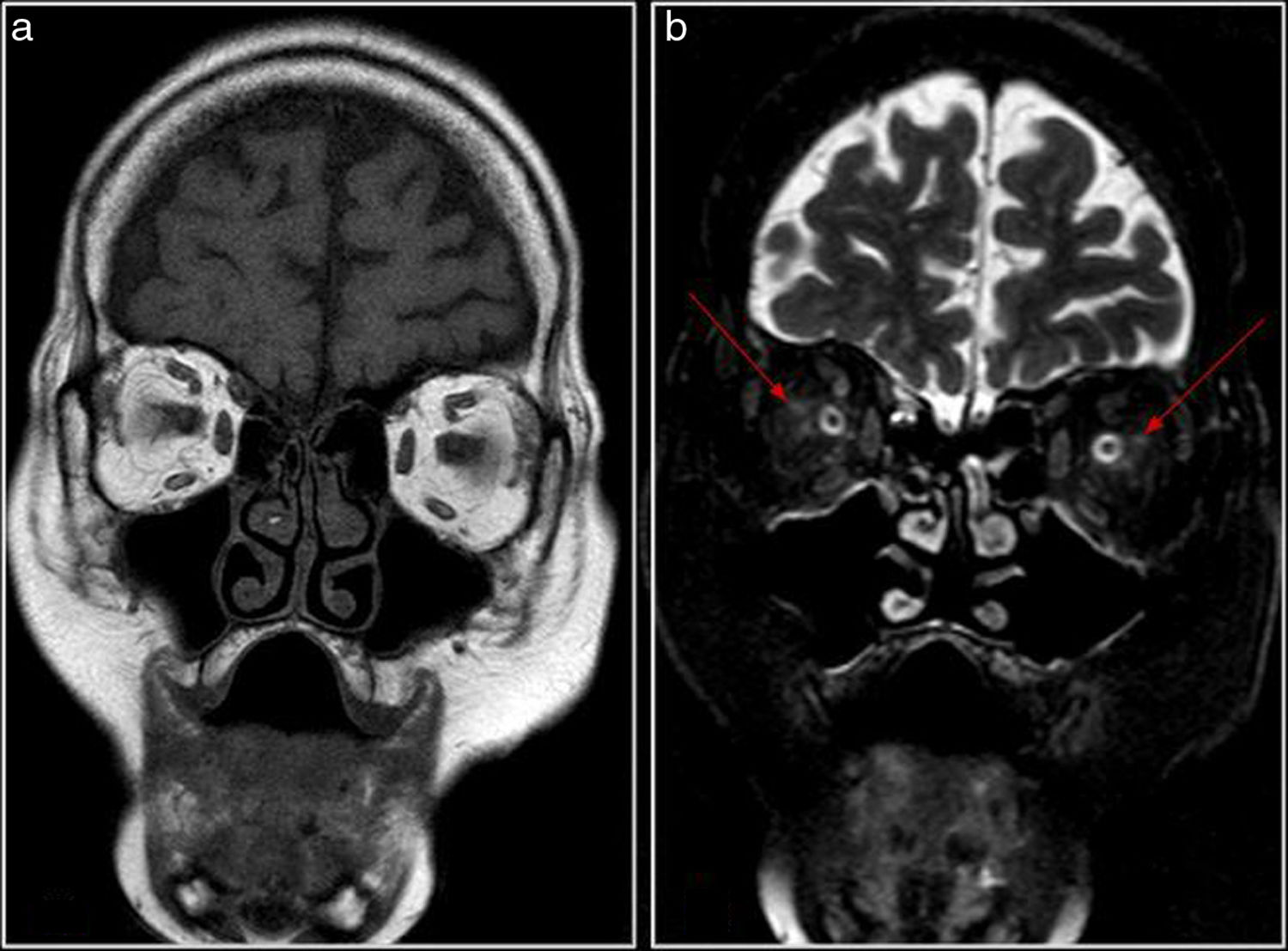
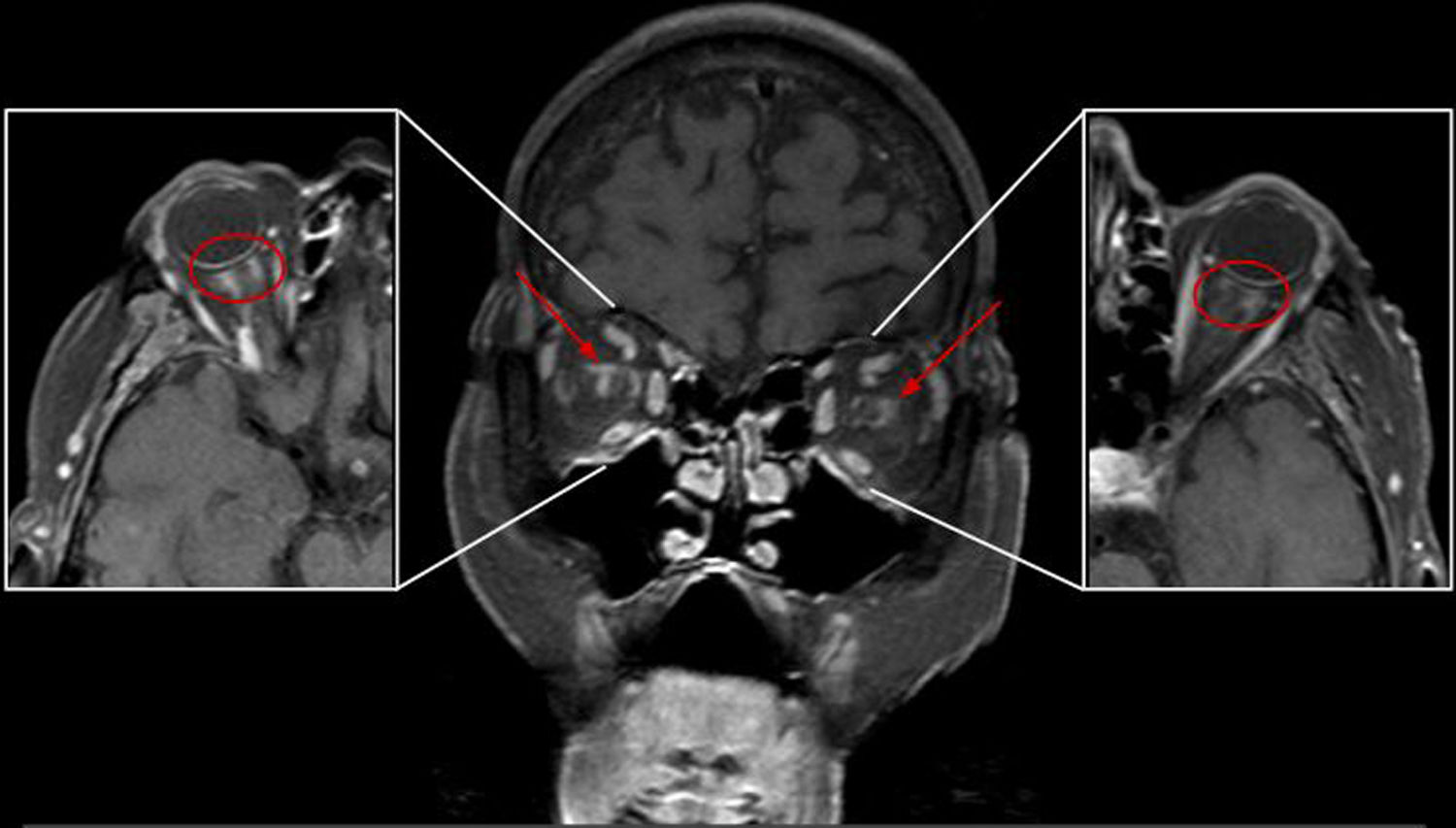
Optic nerve enhancement is a sign seen in different disease states; however, perineural enhancement is less common. This article presents the case of a patient with bilateral amaurosis in whom the diagnosis of giant cell arteritis was suggested by perineural enhancement on orbital magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and confirmed by biopsy of the temporal artery.
The clinical presentation of giant cell arteritis is occasionally nonspecific; patients can have visual symptoms, even blindness if the branches of the ophthalmic artery are affected; in these cases, orbital MRI can be very useful for early diagnosis. Although the MRI findings are uncommon, distinct patterns of enhancement have been reported, the most characteristic of which is perineural enhancement. The pattern of optic nerve involvement is relatively unknown, but important because it orients the diagnosis of a disease that can lead to permanent blindness.
La captación del nervio óptico es un signo visualizado en diferentes patologías; sin embargo, el realce perineural es menos frecuente. Se presenta el caso de una paciente con clínica de amaurosis bilateral en la que se sugirió el diagnóstico de arteritis de células gigantes por la captación perineural detectada en una resonancia magnética (RM) orbitaria, que se confirmó por biopsia de la arteria temporal.
La clínica es, en ocasiones, inespecífica y puede presentarse con síntomas visuales, incluso ceguera si afecta a ramas de la arteria oftálmica; en estos casos, la RM orbitaria puede ser de gran utilidad para un diagnóstico precoz. Si bien los hallazgos por RM son poco frecuentes, se han descrito distintos patrones de captación de contraste, entre los que el realce perineural es el más característico. Este patrón de afectación del nervio óptico es poco conocido pero relevante, pues orienta al diagnóstico de una patología que puede conducir a la ceguera permanente.