Acute stroke leading to intracranial haemorrhage is a rare complication of infectious endocarditis. Unfortunately, the available scientific evidence is limited to small case series; as a result, treatment decisions and recommendations have a low level of evidence. We present the case of a 49-year-old man who developed an intracranial haemorrhage with a fatal outcome after fibrinolytic treatment for infectious endocarditis.
The patient weighed 105kg and his medical history included allergy to quinolones, dyslipidaemia (under treatment with simvastatin), atrial fibrillation for the past 10 years (treated with ASA 300mg), bicuspid aortic valve stenosis, and moderate aortic insufficiency. The patient had developed a fever with no focus of infection 4 days previously and was prescribed cefuroxime and common antipyretics by his primary care physician. On the day of admission, he came to the emergency department of our hospital due to presyncope and right hemiparesis, leading to activation of code stroke. Upon examination, he showed a blood pressure of 95/67, a heart rate of 82bpm, and a temperature of 37.3°C.
Physical examination, which included cardiac auscultation, revealed a systolic murmur (grade I-II/VI); the pulmonary auscultation, abdominal examination, and the study of the extremities yielded normal results. During the neurological examination, the patient was disoriented and showed global aphasia, dysarthria, right hemiparesis which was more marked in the arm (strength 1/5) than in the leg (strength 3/5), and a NIHSS score of 17.
Following the stroke code protocol, the patient underwent a simple CT scan which showed no pathological findings; CT angiography revealed an occlusion in the distal portion of the M1 segment of the left MCA and perfusion CT, a 40% mismatch.
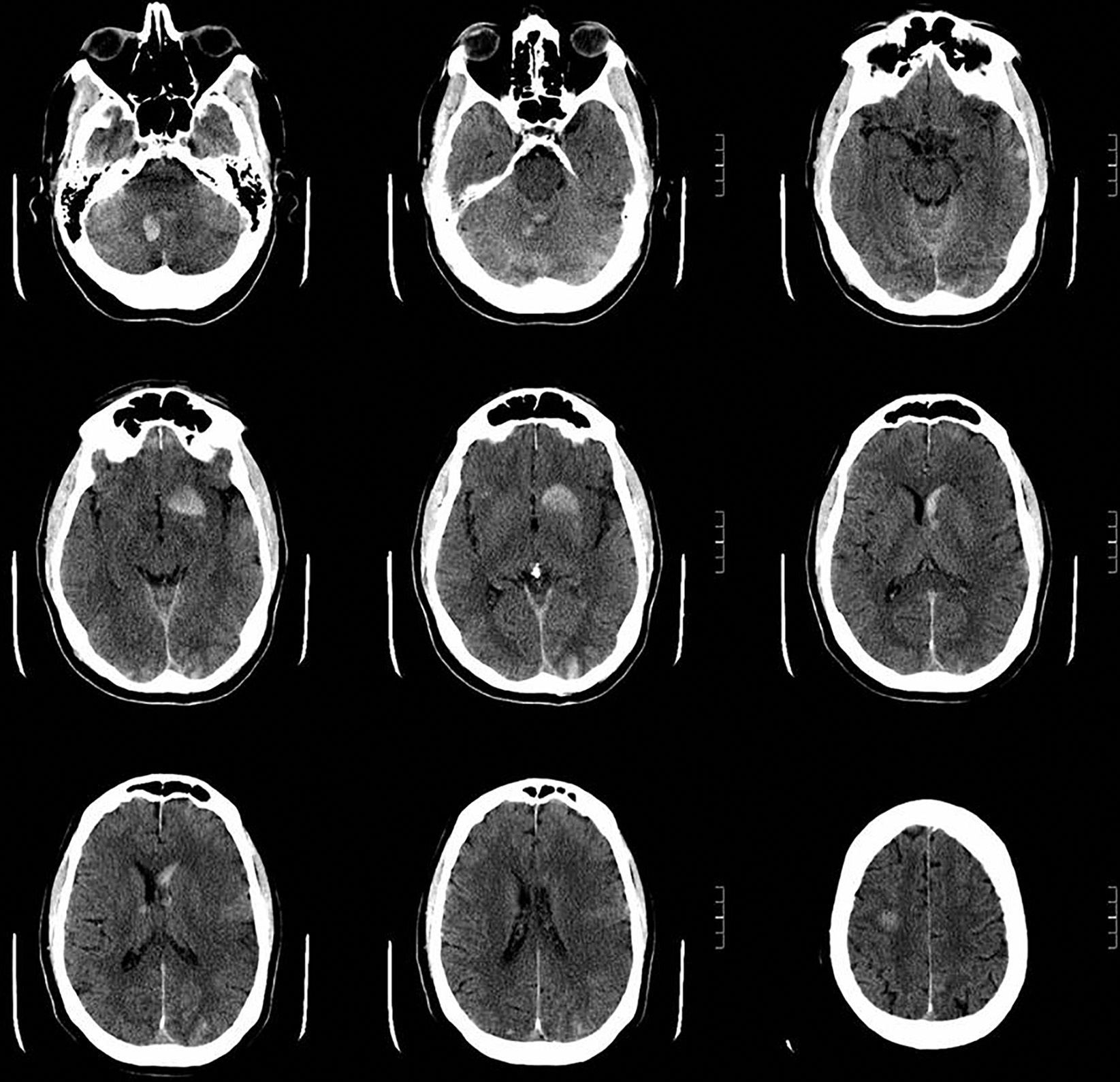
Since our patient met the criteria for thrombolytic treatment, he received a 9mg bolus of rtPA at 2hours and 5minutes followed by an infusion of 81mg. Treatment led to an improvement of paresis in the upper limb at 15minutes and an NIHSS score of 14. During rtPA infusion, our patient began to shiver and his fever peaked at 39.6°C. As a result, 2 blood samples were drawn for culture and he was administered antibiotics. The patient vomited and showed a deterioration in level of consciousness 30minutes after rtPA infusion ended; another CT scan revealed multiple small supra- and infratentorial intraparenchymal haematomas (Fig. 1). Thereafter the patient went into a coma, showing haemodynamic and respiratory instability, at which point he was admitted to the ICU for orotracheal intubation and mechanical ventilation.
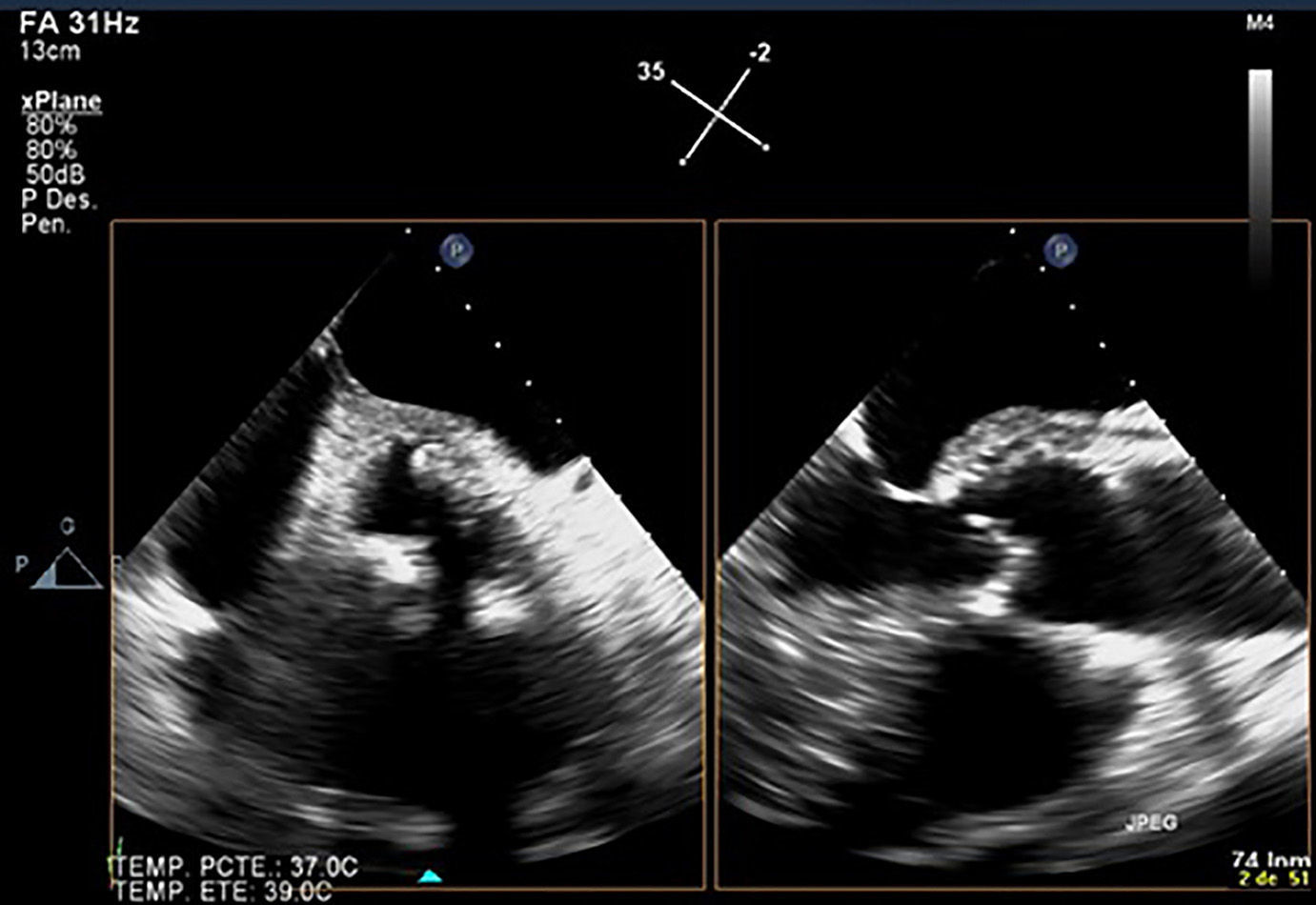
A transoesophageal echocardiography showed a periaortic abscess which affected the junction between the mitral and aortic valves and extended towards the ascending aorta (Fig. 2). The blood cultures were positive solely for meticillin-sensitive Staphylococcus aureus.
Despite support for multiorgan failure secondary to septic shock with vasoactive drugs and renal replacement therapy, the patient died due to refractory hypotension and cardiac arrest 5 days after admission.
Stroke may occur in approximately 4% to 14% of patients with infectious endocarditis,1 21% of whom may develop an intracranial haemorrhage. Our patient received rtPA even though there was no evidence of endocarditis.
Treatment with rtPA improves clinical outcomes in patients with acute stroke. However, the most common cause of intracranial haemorrhage in patients with infectious endocarditis associated with septic emboli is haemorrhagic transformation of ischaemic stroke, most likely secondary to arterial lesions, which may range from a septic erosion of the vessel wall to the presence of mycotic aneurysms.2 In these cases, rtPA administration elevates the risk of haemorrhagic transformation,3 as in our patient. Vegetations are formed by aggregates of inflammatory cells, platelets, microorganisms, and a mesh of fibrin strands, which explains why rtPA is not as effective.4 Reconstructive cardiac surgery was ruled out due to the patient's marked instability during hospitalisation, which led to his death.
Although research into treatment for these patients is scarce, some therapeutic alternatives for this type of disease are being developed, such as intraarterial mechanical thrombectomy, which has shown promising results.5,6 However, the most recent guidelines consider this option to be relatively contraindicated; a risk–benefit analysis should be conducted for each individual case.
The presence of fever, heart murmur, and stroke symptoms at admission should be considered a potential sign of underlying endocarditis. When possible, suspicion should be quickly ruled out with transthoracic echocardiography. If suspicion is high, fibrinolytic treatment should be ruled out and intraarterial mechanical thrombectomy should be considered.
FundingThe authors have received no funding for this study.
Conflicts of interestThe authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Please cite this article as: Fuentes Fernández I, Morales Ortíz A, Sanmartín Monzó J, Jara Rubio R. Evolución fatal tras trombólisis de un ictus secundario a endocarditis infecciosa. Neurología. 2016;31:421–423.