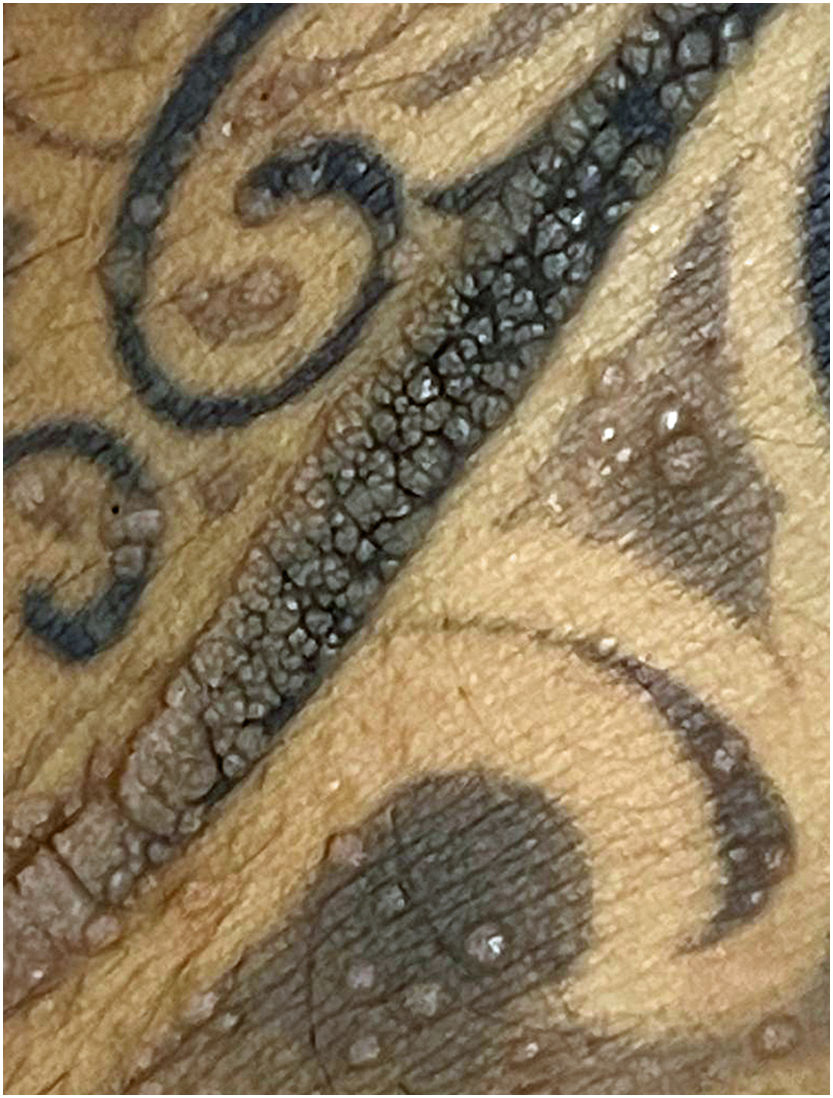
A 23-year-old male came to our clinic with numerous warts on his tattoo. The patient informed us that the lesions had appeared spontaneously 1 month before. He had taken several medications for the clinical condition without effect. The patient was immunocompetent. Physical examination showed abundant verrucae on the tattoo (Fig. 1). The lesions were painless to palpation, soft, of dissimilar diameter, and similar in color to skin affected. The clinical diagnosis was tattoo-associated HPV-induced verrucae, a benign disease caused by human papillomavirus subtype 27. An incisional biopsy was done. Anatomopathological analysis showed hyperparakeratosis, hypergranulosis, and koilocytic cells, which confirmed the diagnosis. The patient was treated with a topical solution of salicylic acid, lactic acid, and elastic collodion with good response. Nevertheless, it is not possible to predict when the warts will recur.
SJR es una prestigiosa métrica basada en la idea de que todas las citaciones no son iguales. SJR usa un algoritmo similar al page rank de Google; es una medida cuantitativa y cualitativa al impacto de una publicación.
Ver másSNIP permite comparar el impacto de revistas de diferentes campos temáticos, corrigiendo las diferencias en la probabilidad de ser citado que existe entre revistas de distintas materias.
Ver másLa tasa de aceptación de las revistas se calcula dividiendo el número total de artículos aceptados (inicialmente y después de la revisión estándar) por el número total de envíos (aceptados y rechazados).
Ver más