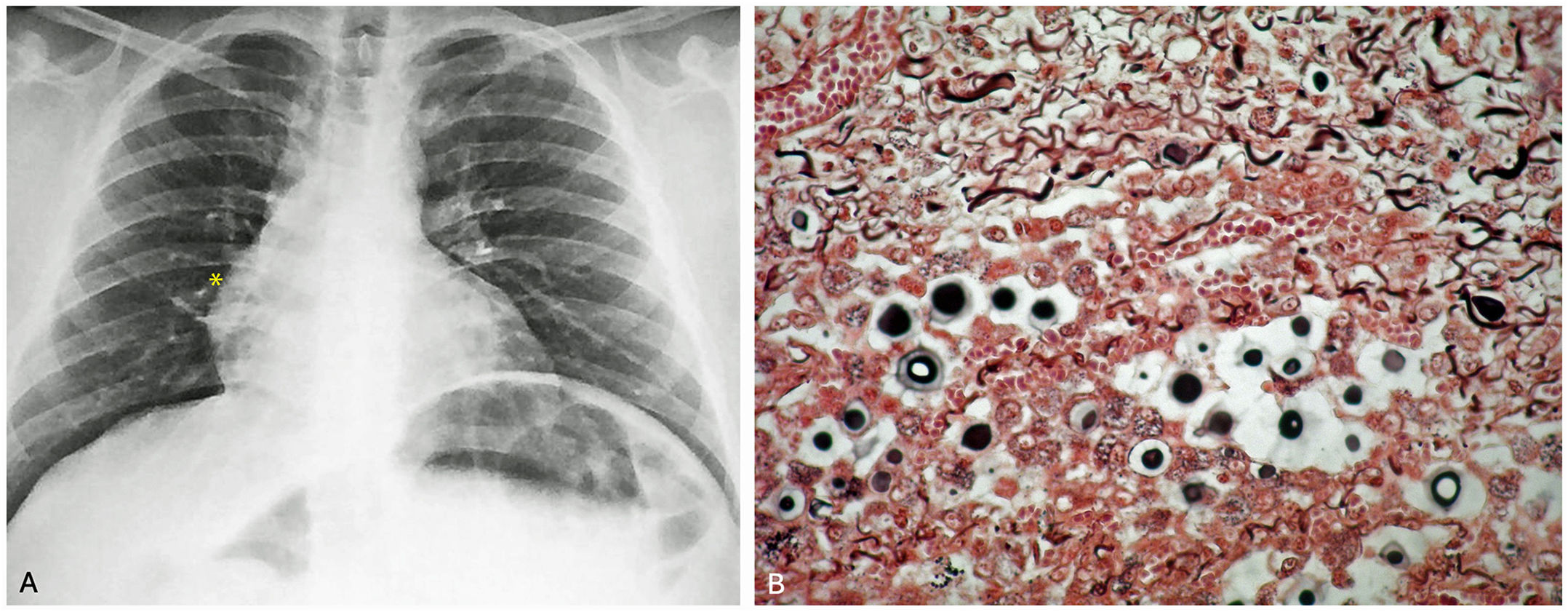
A 35-year-old male presented with a nine-month history of progressively worsening right hemithorax pain, dry cough, and occasional nocturnal diaphoresis. In the fifth month, his symptoms intensified, prompting hospitalization for community-acquired pneumonia, treated with a one-week course of antibiotics. Partial improvement was noted, but symptoms persisted. Physical examination revealed diminished breath sounds in the right lung base. A chest X-ray showed opacities in the perihilar and lower zones of the right lung, consistent with chronic infiltrates (Fig. 1A). Bronchoalveolar lavage via fiberoptic bronchoscopy revealed a predominance of neutrophils (87%), but tests for tuberculosis were negative. A transbronchial biopsy was performed, and the histopathological analysis demonstrated granulomas with extensive necrosis and vacuolated structures, which stained positively with Grocott and Gomori stains (Fig. 1B), confirming a diagnosis of pulmonary cryptococcosis by Cryptococcus neoformans. He was treated with oral fluconazole at 400 mg daily for six months, leading to significant clinical improvement.
A. Initial Chest X-ray: Nodular opacity in the perihilar region and right lung base (yellow asterisk). B. Several encapsulated yeast-like structures were observed (Gomori stain, 40x). (For interpretation of the references to color in this figure legend, the reader is referred to the web version of this article.)
Patient written informed consent was obtained.
Ethical committeeComité de Investigación de la UDEM.
None.
There was no funding or financial support in the creation of this clinical image.