Etiological diagnosis of community-acquired pneumonia (CAP) is only reached in 30%–40% of cases, which frequently requires keeping empirical antibiotic regimens. The new nucleic acid amplification techniques (NAAT) in respiratory samples raise the possibility of improving this clinical practice. Our objective was to analyze TAANs contribution estimating both their costs and benefits.
Patients and methodsThe admitted CAPs were analyzed, in which, if the conventional diagnostic tests were negative, a NAAT was performed. If positive results was made, we assessed if antimicrobials were modified, a cost estimate, and isolation measures.
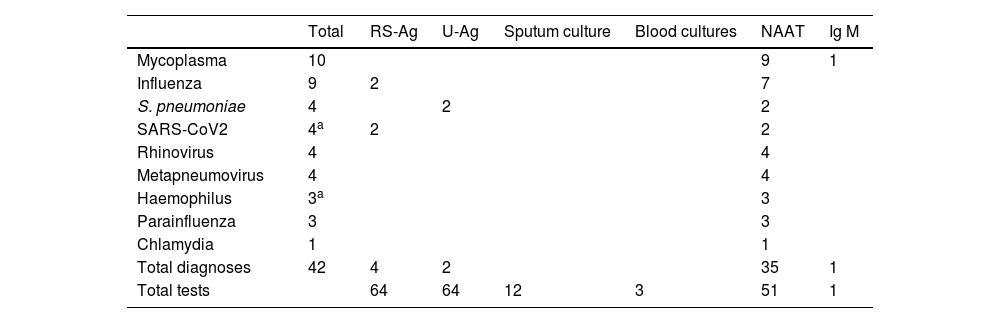
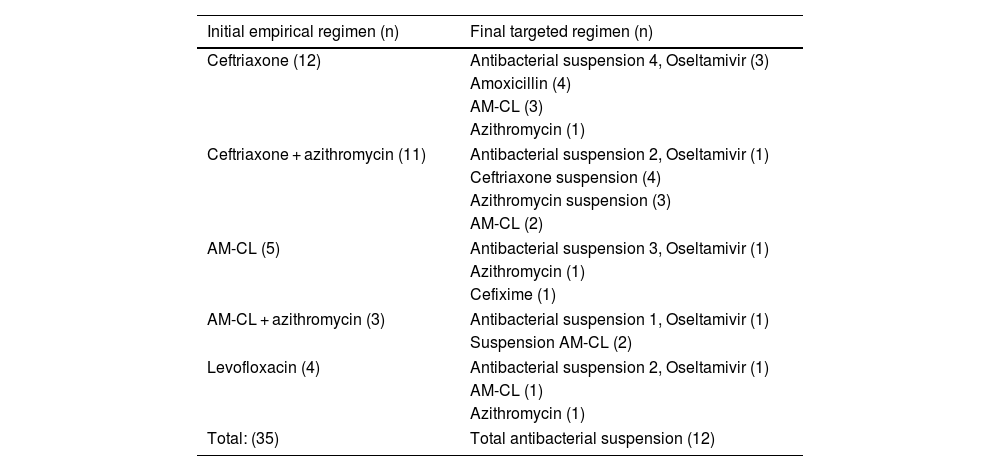
Results64 cases were documented. An etiological diagnosis was made in 65.6%: 10.9% were obtained by conventional techniques and the rest (54.7%) by TAAN. These tests’ results led to antimicrobial regimen’s modification in 88.9% of cases and isolations in 78.5%
ConclusionsCompared to TAAN’s economic cost, it is worth considering its contributions, such as antimicrobials’ reduction, ecological pressure, and isolations’ indications.
En la neumonía adquirida en la comunidad (NAC), tan sólo se alcanza un diagnóstico etiológico en 30%–40% de casos, lo cual supone frecuentemente el mantenimiento de pautas antibióticas empíricas. Las nuevas técnicas de amplificación de ácidos nucleicos (TAAN) en muestras respiratorias, plantean la posibilidad de poder mejorar esta práctica clínica. Nuestro objetivo fue analizar la contribución de las TAAN, estimando tanto sus costes como sus beneficios.
Pacientes y metodosSe analizaron las NAC ingresadas, en las que, si las pruebas diagnósticas convencionales fueron negativas, se realizó una TAAN. En los casos con resultados positivos se valoró; si se modificaron los antimicrobianos, una estimación de costes, y si implicó medidas de aislamiento.
ResultadosSe documentaron 64 casos, en el 65,6% se obtuvo un diagnóstico etiológico; en el 14,2% por técnicas convencionales y el resto (51.4%) por TAAN. El resultado de las pruebas condujo a modificar la pauta antimicrobiana en el 83,3% de casos y a aislamientos en un 78,5%.
ConclusionesFrente al coste económico de las TAAN, cabe considerar sus aportaciones, como la reducción de los antimicrobianos, y por tanto de la presión ecológica, así como la indicación de aislamientos.