To evaluate by ultrasonography the effect of chondroitin sulfate (CS) on synovitis in patients with knee osteoarthritis (KOA). To collaborate in the understanding of the biochemical mechanisms involved in the synovial inflammation process.
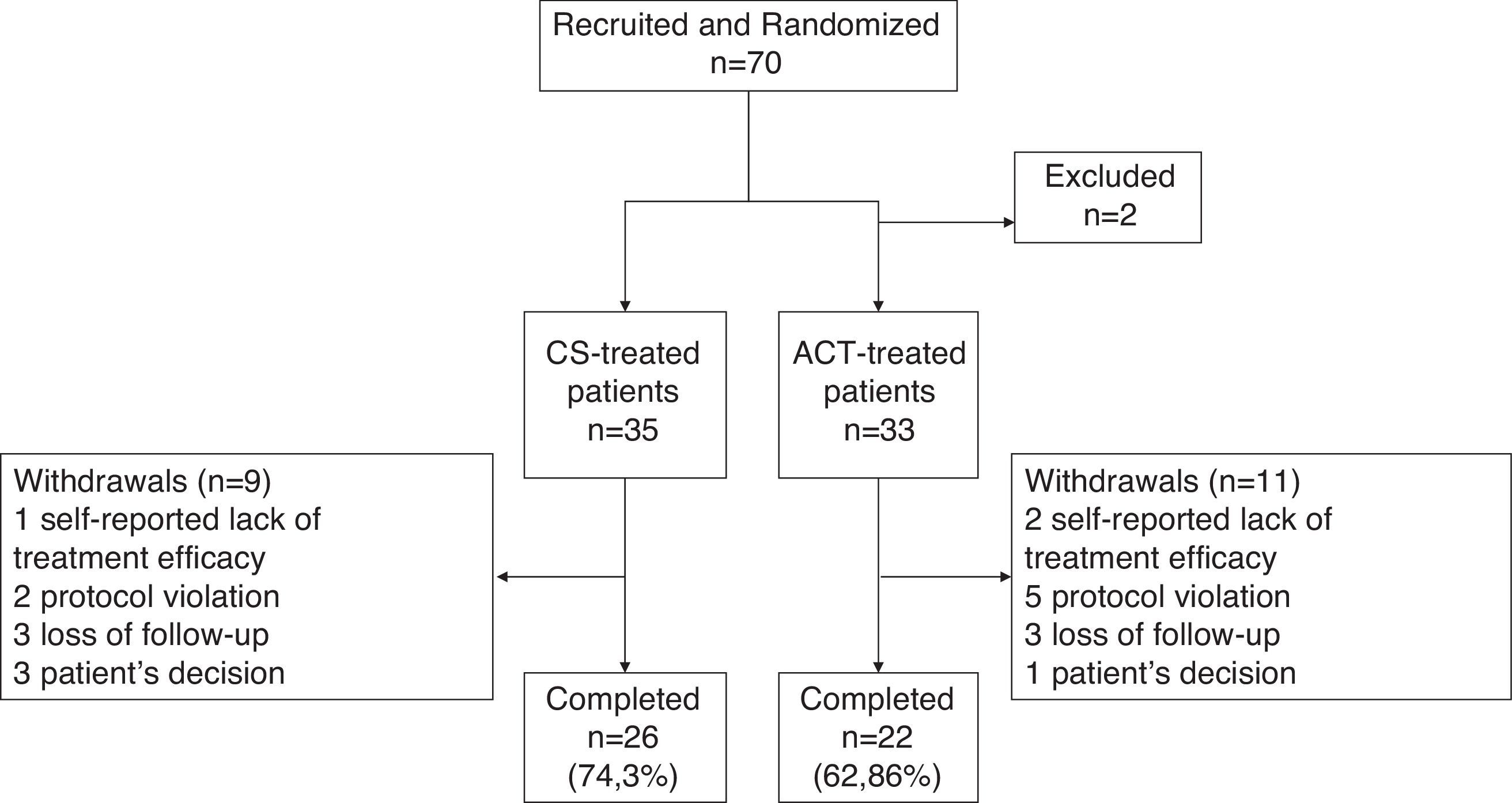
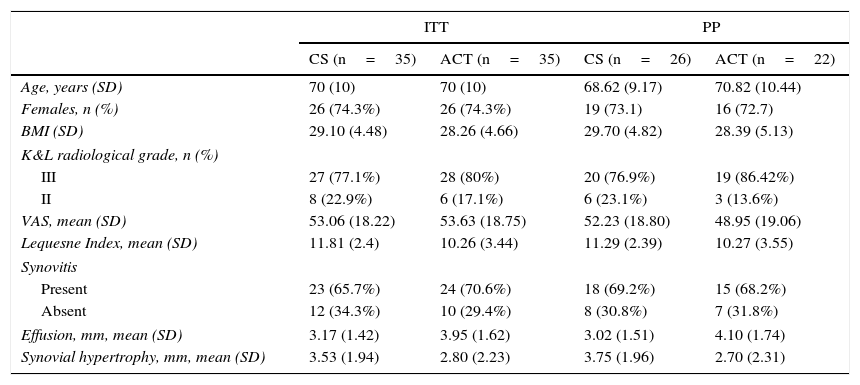
MethodsRandomized, single-blind, controlled trial involving 70 patients with primary KOA treated for 6 months with CS or acetaminophen (ACT). Evaluation of KOA status at baseline, 6 weeks, 3 and 6 months included: ultrasonography to assess synovitis (following the OMERACT expertise group definition), visual analogue scale and Lequesne index to measure pain and function, and ELISA to quantify inflammatory mediators in serum and synovial fluid.
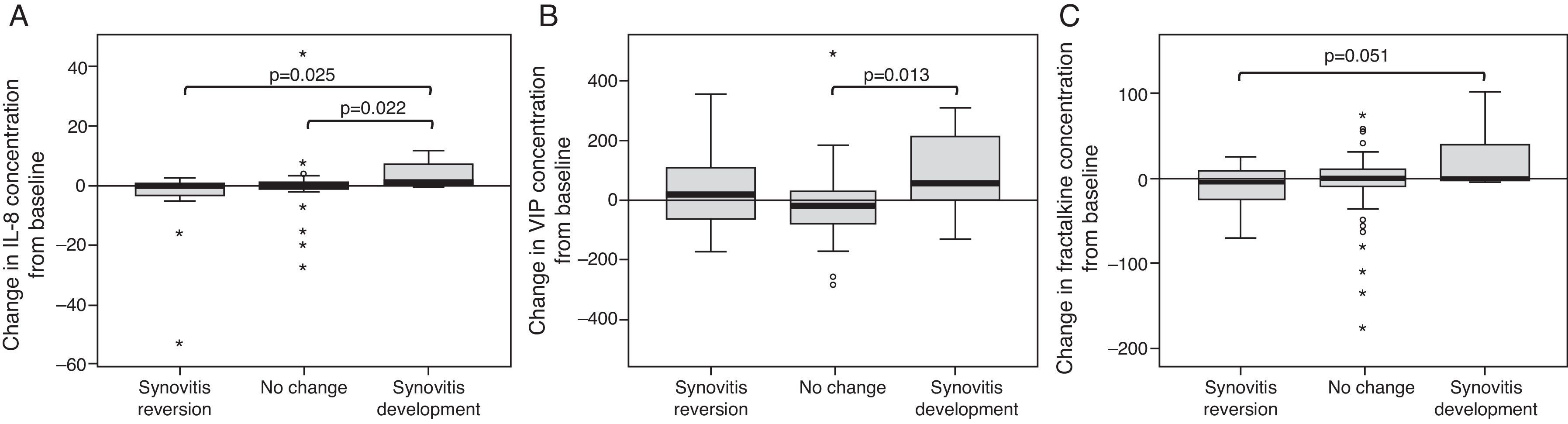
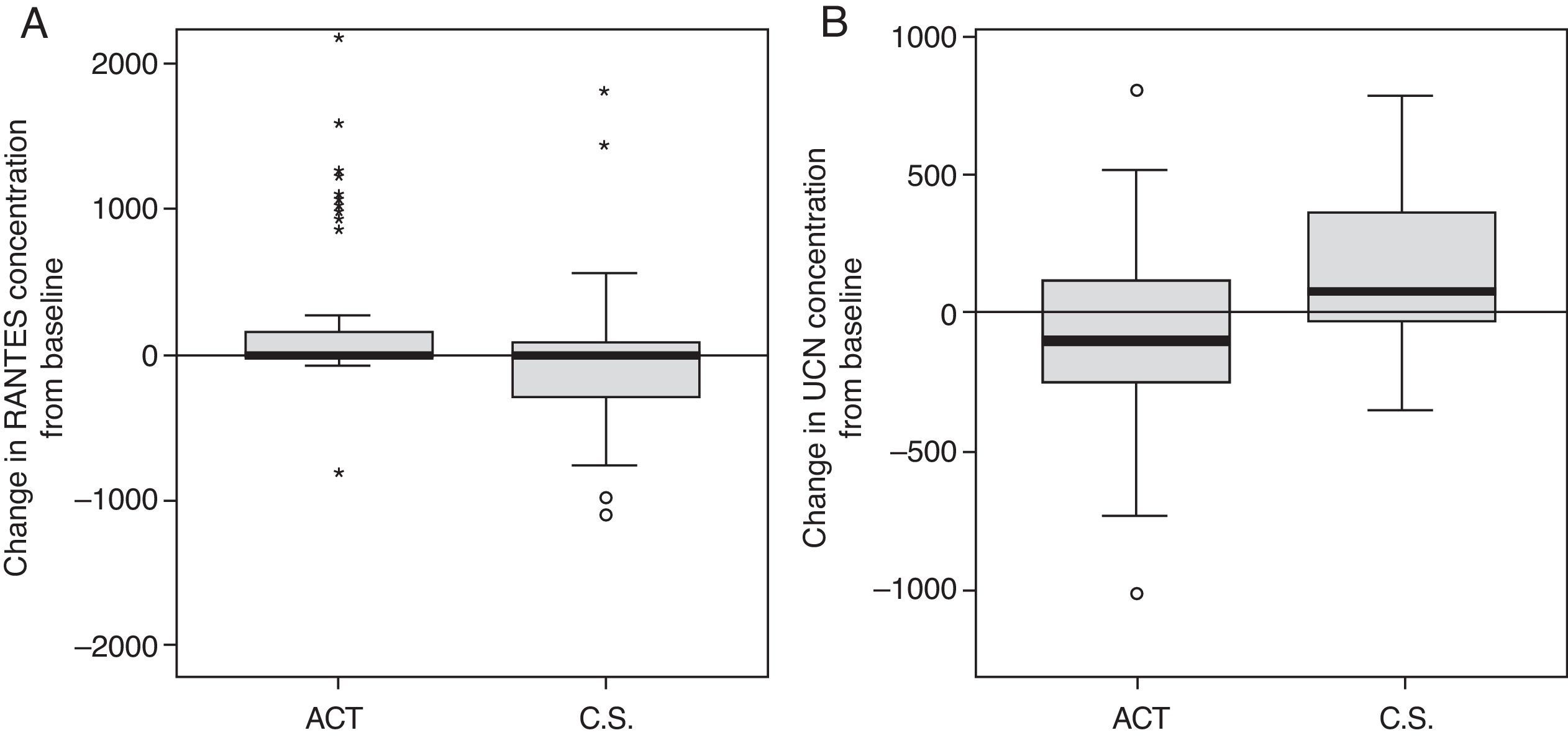
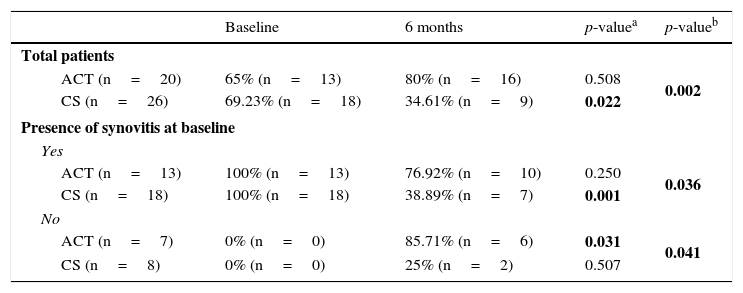
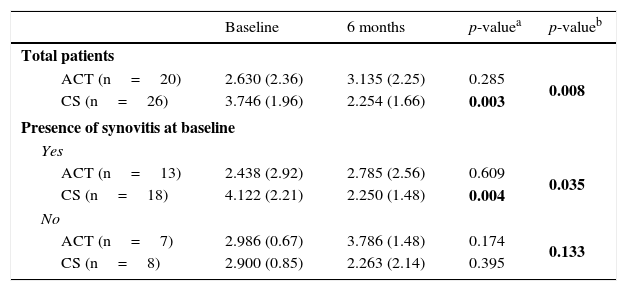
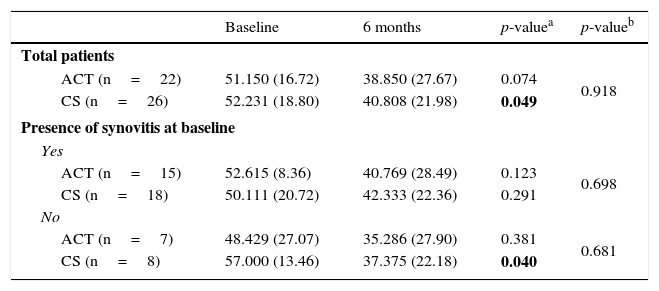
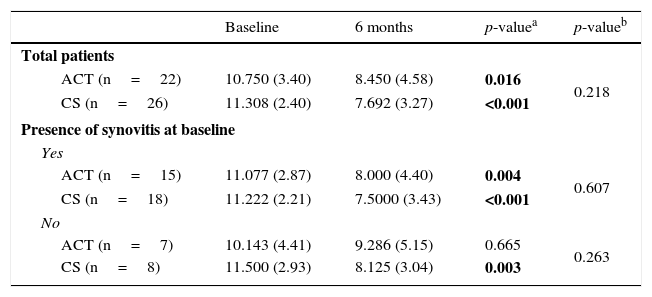
ResultsSynovitis presence was reduced by 50% in the CS group while a 123% increase was observed in ACT group. Conversely, patients without initial synovitis and treated with ACT reached 85.71% synovitis onset, but only 25% in CS group. Both therapies improved articular function, but only CS resulted in significant pain improvement at the end of the treatment. Changes in RANTES and UCN synovial fluid concentration were associated with CS treatment.
ConclusionsTreatment with CS had a sustained beneficial effect, preventing synovitis onset or reducing its presence as well as reducing KOA symptoms. ACT ameliorated clinical symptoms but had no effect on inflammation. The CS anti-inflammatory effect could be related to the observed changes in RANTES and UCN concentration.
Evaluar mediante ecografía el efecto del condroitín sulfato (CS) en la sinovitis de pacientes con artrosis (OA) de rodilla, y colaborar en el conocimiento de los mecanismos bioquímicos involucrados en la inflamación sinovial.
MétodosEstudio controlado, aleatorizado, ciego simple de 70 pacientes con OA de rodilla tratados durante 6 meses con CS o paracetamol (PCT). Los pacientes fueron visitados a tiempo basal, a las 6 semanas, y a los 3 y 6 meses para valorar el estado de su OA según los siguientes parámetros: sinovitis evaluada mediante ecografía (según definición de expertos OMERACT); dolor y función, mediante la escala visual analógica y el índice de Lequesne; y concentración de mediadores inflamatorios en suero y líquido sinovial, mediante ELISA.
ResultadosEl tratamiento con CS redujo en un 50% el número de individuos que presentaban sinovitis; sin embargo, se observó un incremento de un 123% en el grupo tratado con PCT. En los pacientes sin sinovitis inicial, se observó el establecimiento de esta en un 85,71 y 25% de los casos tratados con PCT y CS, respectivamente. Ambas terapias mejoraron la función articular, pero únicamente el tratamiento con CS produjo una mejora significativa del dolor al final del tratamiento. Se observó una asociación entre el tratamiento con CS y los cambios en la concentración de RANTES y UCN en el líquido sinovial.
ConclusionesEl tratamiento con CS tiene un efecto mantenido beneficioso, previniendo la aparición de sinovitis o disminuyendo su presencia, así como reduciendo los síntomas de la artrosis. El PCT también mejora los síntomas clínicos, pero no tiene ningún efecto sobre la inflamación. Las variaciones observadas en la concentración de RANTES y UCN podrían estar relacionadas con el efecto antiinflamatorio asociado al tratamiento con CS.