In liver transplantation (LT), anemia and transfusion of blood products have a negative impact on morbidity and mortality.
MethodsMulticenter, prospective observational study. The main objective was to assess whether correction of iron deficiency anemia with intravenous iron was feasible in LT candidates. Its efficacy and adverse effects were evaluated. Patients with Hb value <115 g/L and ferritin values <800 ng/mL were included. Based on the increase in Hb >10 g/L compared to its baseline level, the analysis of 76 patients was considered.
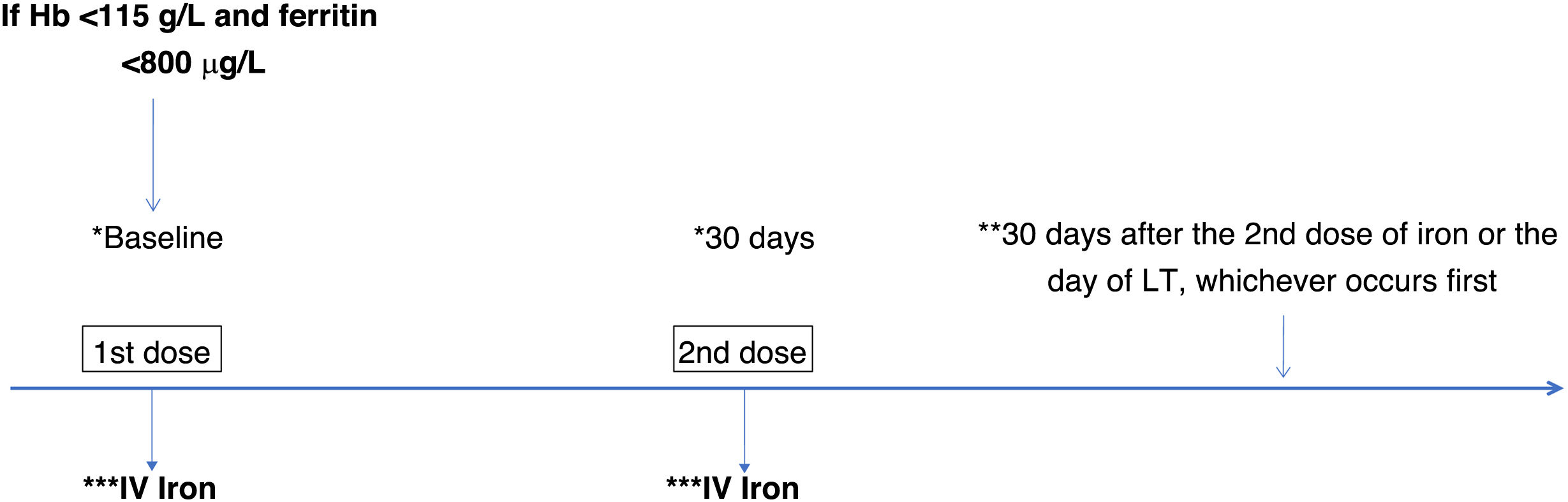
An anemia study was carried out, assigning to the study group those who met the criteria for iron deficiency anemia, which followed a protocol of administration of up to two doses of iron before LT.
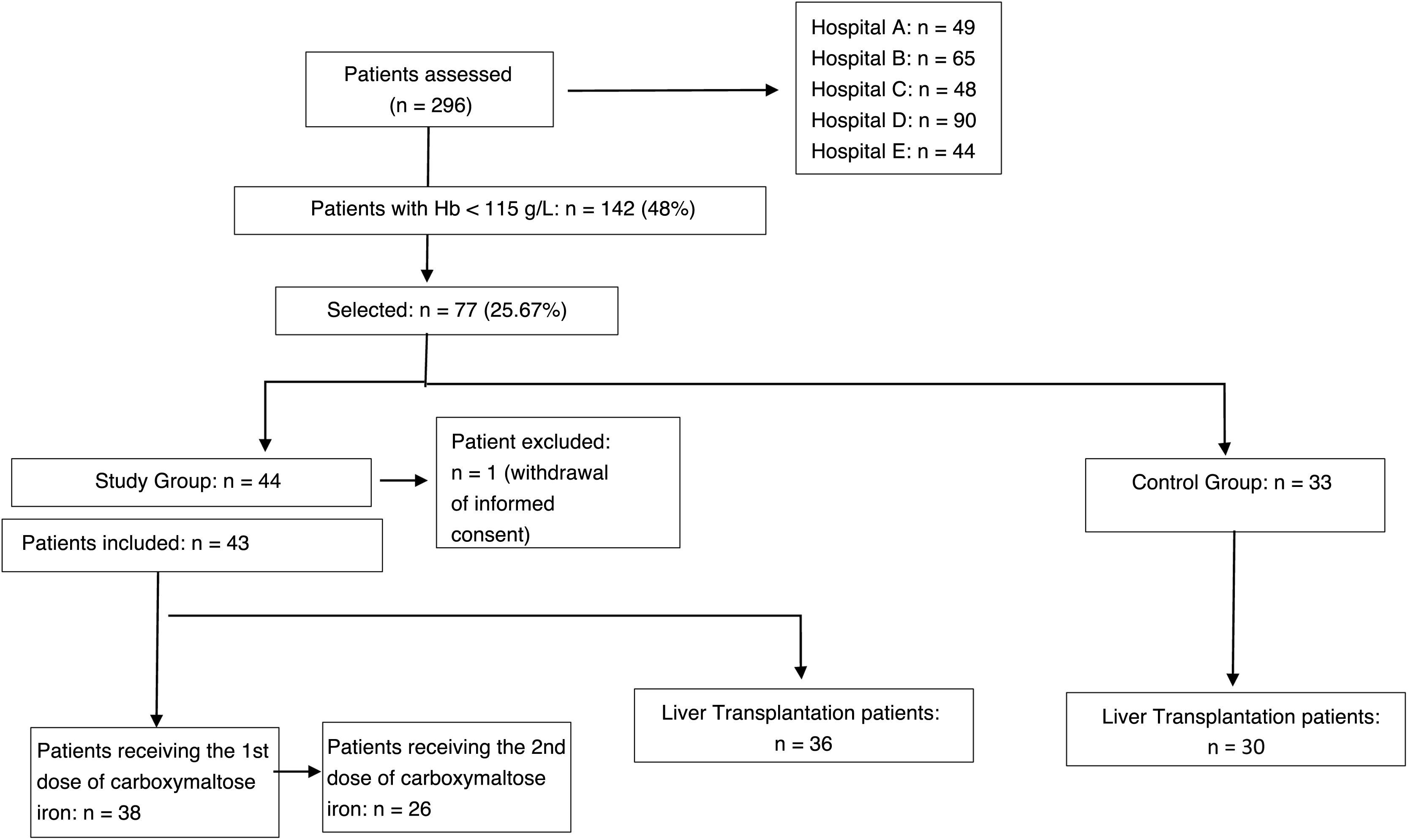
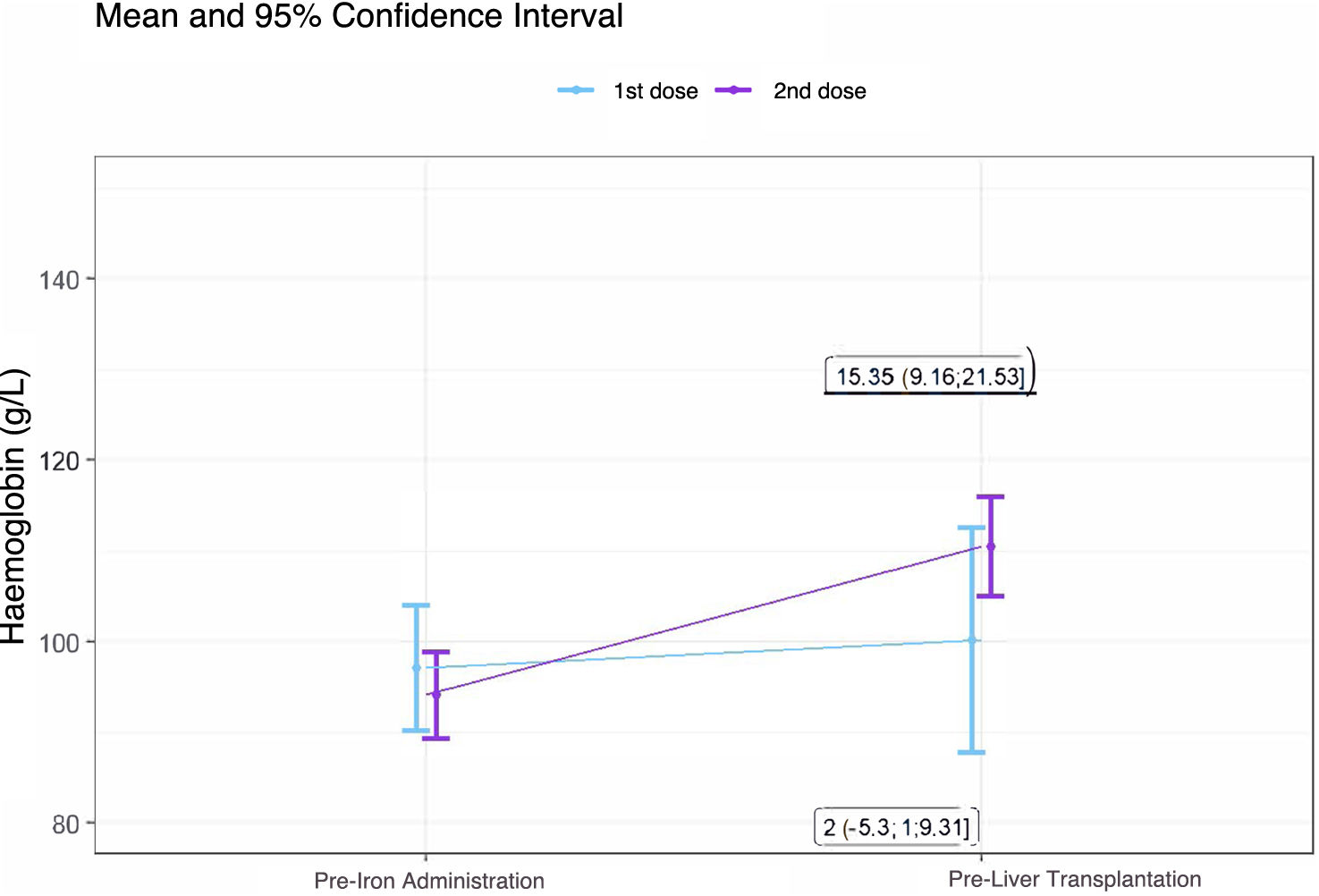
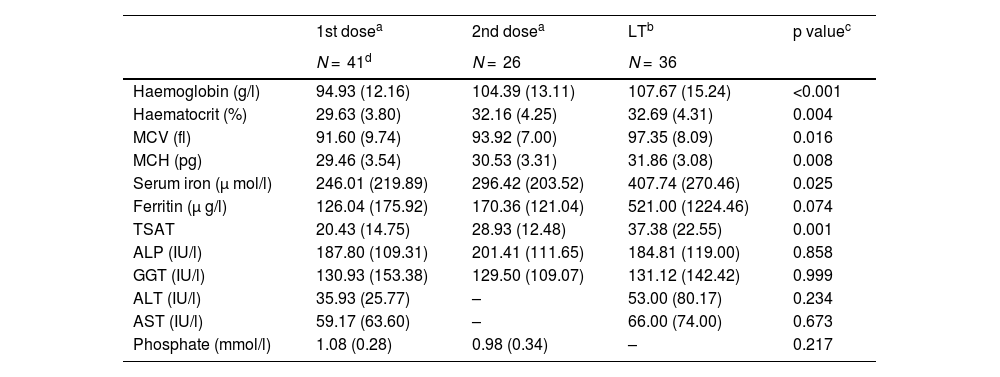
Results296 LT were performed during the study period, 48% of patients had an Hb value <115 g/L. 43 patients made up the study group, in 5 patients the first dose was not administered. The second dose was administered to 55% of patients. No patient presented serious adverse effects or alterations in liver function. Hemoglobin increased compared to baseline by a median of 11.22 g/L (6.47–15.97) after the first administration and 11.64 g/L (6.49–16.78) after the second.
ConclusionsThe implementation of patient blood management in liver transplantation through the administration of intravenous iron is effective and safe. It is necessary to routinely characterize and treat the presence of iron deficiency anemia in these patients.
En el trasplante hepático (TH) la anemia y la transfusión de hemoderivados tienen un impacto negativo en la morbimortalidad.
MétodosEstudio multicéntrico, prospectivo observacional. El objetivo principal fue valorar si la corrección de la anemia ferropénica con hierro endovenoso era factible en los candidatos a TH. Se evaluó su eficacia y efectos adversos. Se incluyeron los pacientes con valor de Hb <115 g/L y valores de ferritina <800 ng/mL. En base al incremento de la Hb >10 g/L respecto a su nivel basal se consideró el análisis de 76 pacientes.
Se realizó un estudio de anemia, asignando al grupo estudio los que cumplieron criterios de anemia ferropénica, que siguió un protocolo de administración de hasta dos dosis de hierro antes del TH.
ResultadosSe realizaron 296 TH en el periodo del estudio, 48 % de los pacientes tenían un valor de Hb <115 g/L. 43 pacientes conformaron el grupo estudio, en 5 pacientes no se llegó a administrar la primera dosis. La segunda dosis se administró en el 55% de los pacientes. Ningún paciente presentó efectos adversos graves ni alteración de la función hepática. La hemoglobina se incrementó respecto a la basal una mediana de 11,22 g/L (6,47−15,97) tras la primera administración y de 11,64 g/L (6,49−16,78) tras la segunda.
ConclusionesLa puesta en marcha de un programa de gestión de la sangre en trasplante hepático mediante la administración de hierro endovenoso es eficaz y segura. Es necesario caracterizar y tratar de forma rutinaria la presencia de anemia ferropénica en estos pacientes.