In December 2019, a novel coronavirus that occurred in Wuhan, China, has spread to all over the world. The disease was named coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) and the virus was designated as severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2) by WHO. Person-to-person transmission has been demonstrated and the main infection source was the patients who with COVID-19. Respiratory droplet transmission is the main route of transmission, and it can also be transmitted through contact.1 SARS-CoV-2 has high pathogenicity and transmissibility, being more infectious than MERS-CoV and SARS-CoV.2 Therefore, the Chinese government has implemented the most stringent control measures, and effectively reduced the spread of the epidemic. The vast majority of patients with COVID-19 presented with fever and cough, but we found that some patients were infected with SARS-CoV-2 without any symptoms. Here, we reported 11 asymptomatic patients were found in Guizhou Province. They were laboratory-confirmed positive for the COVID-19 virus by testing RNA of the pharyngeal swab samples.
One of the 11 patients was a 6-year-old child, and the rest were young or middle-aged (27–56 years old, Table 1). Of 11 patients, 6 were male and 5 female. 2 male had hypertension and 1 female had a history of breast carcinoma (Table 1). 5 patients had a history of exposure in Wuhan, and all of them were isolated at home after return. 2 of the 5 patients were in isolation, and their relatives (without history of exposure to Wuhan) developed symptoms and were diagnosed. They were subsequently diagnosed with COVID-19. The other 3 patients returned to Guizhou province from Wuhan with their relatives and were then isolated at home. Some of their relatives developed fever or cough and were diagnosed with COVID-19. None of these 3 patients showed any symptoms at admission and during admission. Therefore, we cannot determine whether their relatives’ infections originated from them. After returning from Wuhan, 1 of the 5 patients had been solitary isolated without infecting others.
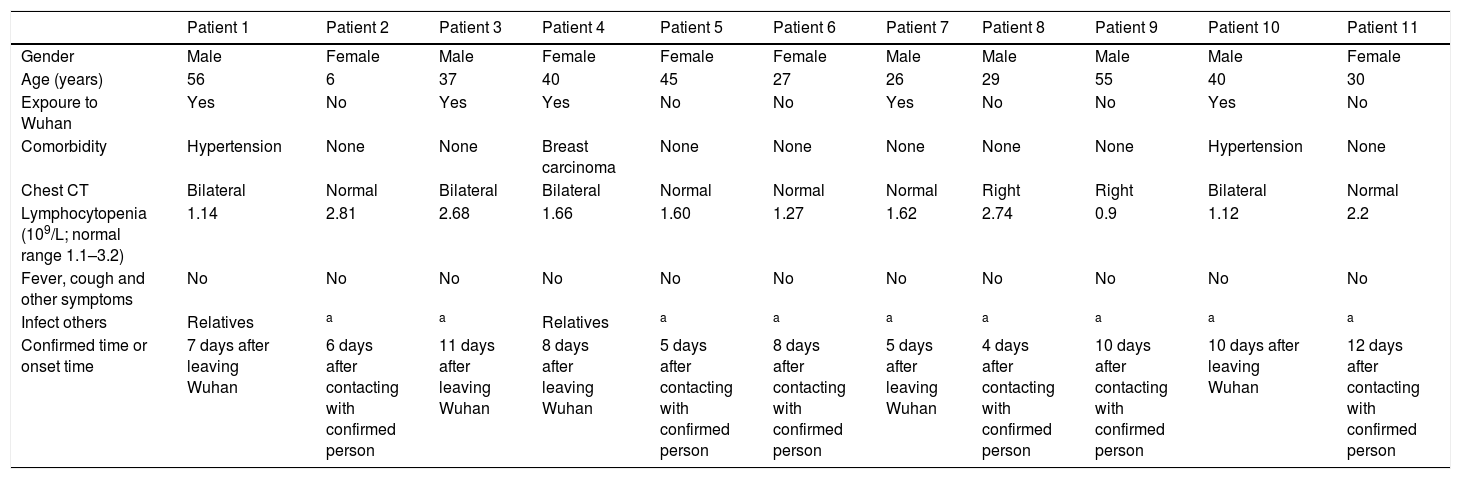
summary of asymptomatic patients.
| Patient 1 | Patient 2 | Patient 3 | Patient 4 | Patient 5 | Patient 6 | Patient 7 | Patient 8 | Patient 9 | Patient 10 | Patient 11 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Gender | Male | Female | Male | Female | Female | Female | Male | Male | Male | Male | Female |
| Age (years) | 56 | 6 | 37 | 40 | 45 | 27 | 26 | 29 | 55 | 40 | 30 |
| Expoure to Wuhan | Yes | No | Yes | Yes | No | No | Yes | No | No | Yes | No |
| Comorbidity | Hypertension | None | None | Breast carcinoma | None | None | None | None | None | Hypertension | None |
| Chest CT | Bilateral | Normal | Bilateral | Bilateral | Normal | Normal | Normal | Right | Right | Bilateral | Normal |
| Lymphocytopenia (109/L; normal range 1.1–3.2) | 1.14 | 2.81 | 2.68 | 1.66 | 1.60 | 1.27 | 1.62 | 2.74 | 0.9 | 1.12 | 2.2 |
| Fever, cough and other symptoms | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No | No |
| Infect others | Relatives | a | a | Relatives | a | a | a | a | a | a | a |
| Confirmed time or onset time | 7 days after leaving Wuhan | 6 days after contacting with confirmed person | 11 days after leaving Wuhan | 8 days after leaving Wuhan | 5 days after contacting with confirmed person | 8 days after contacting with confirmed person | 5 days after leaving Wuhan | 4 days after contacting with confirmed person | 10 days after contacting with confirmed person | 10 days after leaving Wuhan | 12 days after contacting with confirmed person |
6 of the 11 patients had no history of exposure to Wuhan and were all clustered cases. They had a history of close contacts with relatives or colleagues diagnosed with COVID-19, so it is difficult to determine whether they are the index patient. The lymphocytes of 11 patients were not significantly decreased. 6 of the 11 patients had abnormal CT findings, mainly showed ground-glass opacities. The other 5 patients had normal chest CT. All patients’ blood cells, liver function, renal function, coagulation function and high-sensitivity C-reactive protein were in normal range. None of the 11 patients developed severe pneumonia as of March 5, 2020, and 4 patients showed typical symptoms (fever, cough, fatigue, etc.) during hospitalization. Generally, these asymptomatic patients were mildly ill as compared to those reported in Wuhan, Hubei.3
On January 24, The Lancet reported a familial cluster of SARS-CoV-2 infection.4 In this family, there was an asymptomatic child presenting with no fever, respiratory tract or gastrointestinal symptoms, but with ground glass lung opacities on chest CT. Subsequently, asymptomatic patients appeared in many Chinese cities, in which majority having an epidemiological history. A recent report suggested that an asymptomatic carrier was able to transmit the SARS-CoV-2 to another person in Germany.5 In our report, 2 patients were the index patient and transmitted virus to their relatives. Hence, asymptomatic persons have become a potential source of SARS-CoV-2 infection. To prevent and find asymptomatic carriers are the key to prevent the spread of the epidemic. Persons with family members with SARS-CoV-2 infection should be closely monitored and examined to rule out infection, even if they do not have any symptoms. After discharge, patients should be further isolated and received continuous SARS-CoV-2 RNA tests.
Compliance with ethical standardsWritten consent from the patient was waived, because of entirely anonymized images from which the individual cannot be identified.
FundingThis study was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. 81760206).
Author contributionsFC collected clinical data. BF drafted the manuscript. XYF designed the study.
Consent for publicationNot applicable.
Availability of supporting dataThe data sets supporting the results of this article are included within the article.
Conflicts of interestAll authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
We thank all patients included in this study. We are really grateful to all the health workers around the world. Their expertise & humanity are fundamental to stop SARS-COV-2 from spreading further.