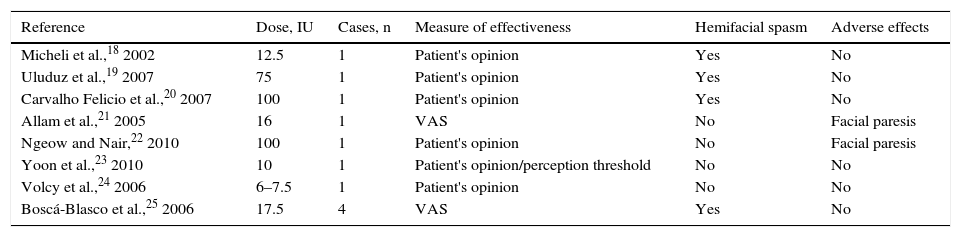
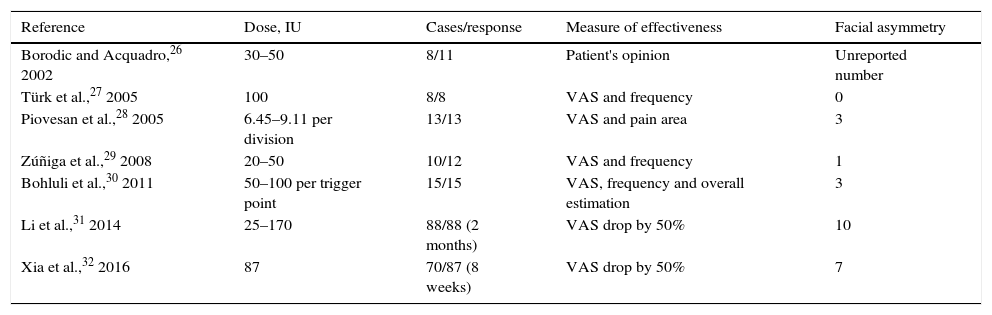
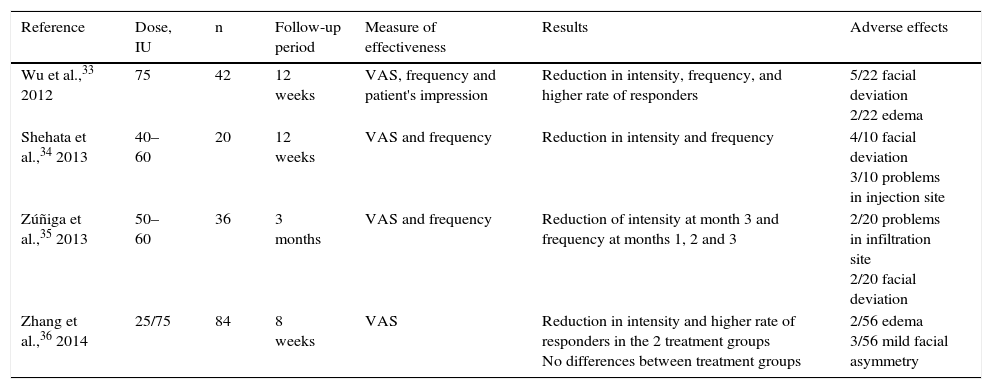
Trigeminal neuralgia is one of the most disabling facial pain syndromes, with a significant impact on patients’ quality of life. Pharmacotherapy is the first choice for treatment but cases of drug resistance often require new strategies, among which various interventional treatments have been used. In recent years a new therapeutic strategy consisting of botulinum toxin has emerged, with promising results.
DevelopmentWe reviewed clinical cases and case series, open-label studies and randomized clinical trials examining the use of botulinum toxin for drug-refractory trigeminal neuralgia published in the literature.
ConclusionsThe administration of botulinum toxin has proven to be a safe and effective therapeutic strategy in patients with drug-refractory idiopathic trigeminal neuralgia, but many questions remain unanswered as to the precise role of botulinum toxin in the treatment of this disease.
La neuralgia del trigémino es uno de los síndromes de dolor facial más incapacitantes, con un importante impacto sobre la calidad de vida. Su tratamiento inicialmente es farmacológico, pero a menudo se presentan casos de farmacorresistencia que obligan a buscar nuevas estrategias, entre las que se han utilizado diversos tratamientos intervencionistas. En los últimos años ha surgido una nueva estrategia terapéutica consistente en el uso de toxina botulínica, con resultados prometedores.
DesarrolloSe han revisado los casos clínicos y las series de casos, los estudios abiertos y los ensayos clínicos aleatorizados publicados sobre el uso de la toxina botulínica en el tratamiento de la neuralgia del trigémino farmacorresistente.
ConclusionesLa administración de toxina botulínica ha mostrado ser una estrategia terapéutica segura y efectiva en pacientes con neuralgia del trigémino farmacorresistente idiopática, pero quedan por responder numerosas cuestiones que terminen de situar su papel dentro de la terapéutica de esta enfermedad.