This study aims to analyze the relationship between the role of expert patients and medication adherence among tuberculosis patients.
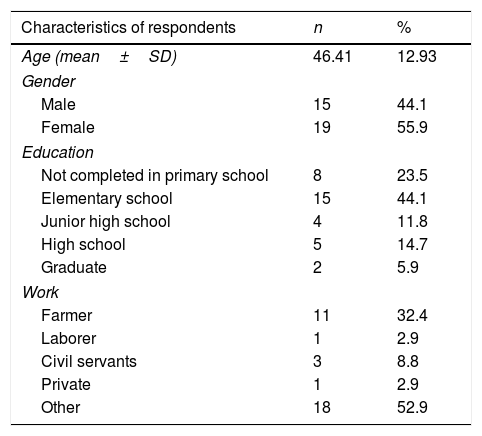
MethodThe research was conducted as a quasi-experiment with control. There were 34 samples selected using the probability sampling technique.
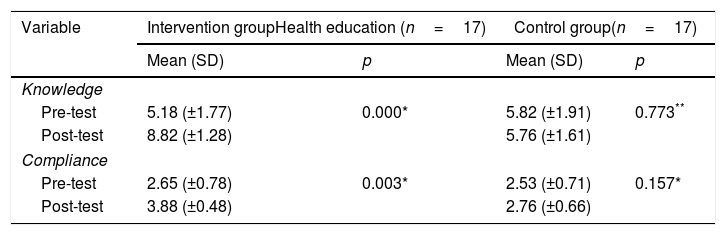
ResultsThe data were analyzed statistically using the Wilcoxon test and paired t-test. The results reveal that there was a change in knowledge and adherence before and after health education in the intervention and control groups. However, only the intervention group experienced a significant change with p<0.05, while in the control group, the change was not significant with p>0.05.
ConclusionThis study showed that there was a significant change in the mean of knowledge and adherence before and after health education by expert patients in the intervention group.