Antifungal resistance has emerged over the last few decades, is continuously increasing and represents a serious concern regarding the treatment of patients with invasive fungal infections, especially those caused by Candida species. Studying and monitoring the antifungal resistance profile by using reference techniques is essential to detect emerging drug-resistant strains. Currently, the broth microdilution methods are the most recommended for the determination of antifungal susceptibility, which are regarded as the gold standard for detecting isolates resistant to a vast range of antifungal agents. However, these procedures are time-consuming and difficult to implement in clinical microbiology laboratories,1 which has made agar-based methods, such as the disk diffusion method and gradient diffusion methods, topics of interest for researchers.
Vaginal candidiasis has become an important public health problem due to the resistance of its causative fungi to antifungal agents, requiring susceptibility testing to guide therapeutic choices.2,3
In this study we compared three antifungal susceptibility methods: gradient diffusion (Etest®), broth microdilution4 and disk diffusion5 in order to detect resistance of Candida isolates obtained from the vaginal mucosa against amphotericin B, fluconazole, and itraconazole.
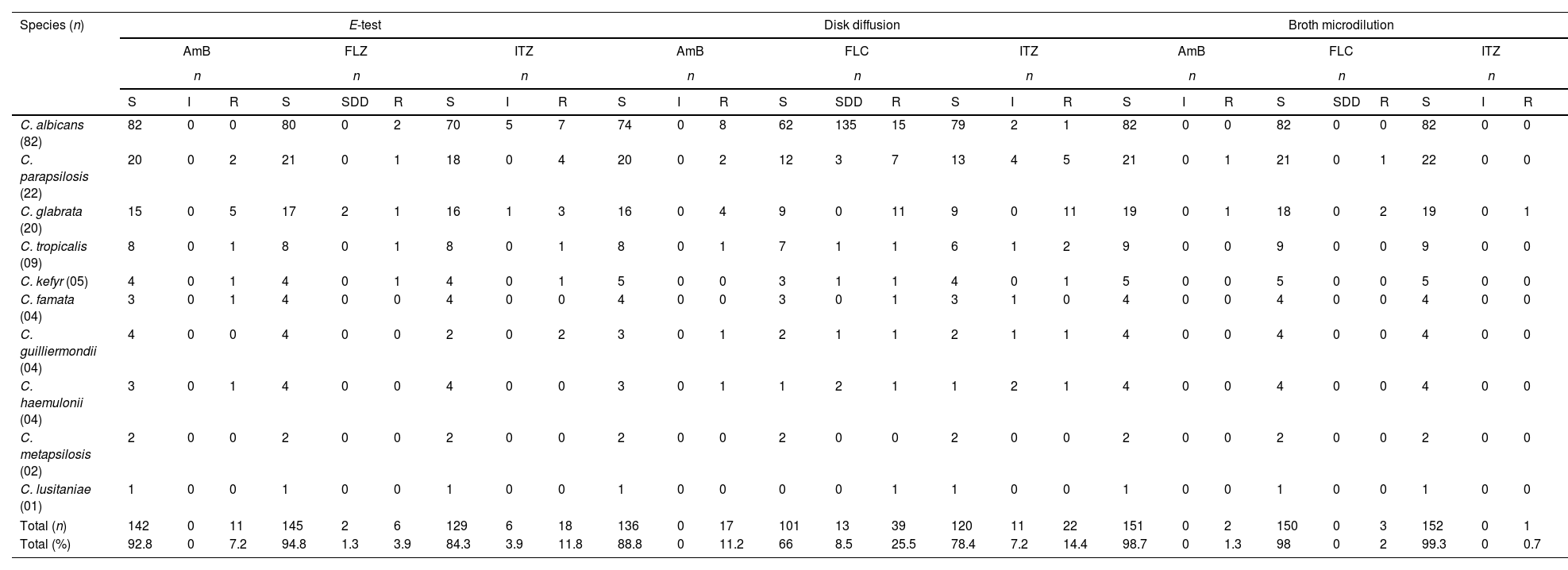
The strains were isolated from November 2008 to May 2010. Vaginal exudates were collected from 258 women, and a total of 153 yeast isolates were studied (Table 1). Among the yeast positive vaginal samples, 51 (33.1%) corresponded to asymptomatic women, 51 (33.1%) to women with primary candidiasis, and 52 (33.8%) to women with recurrent candidiasis. In general, to be considered reliable, the method evaluated should present ≥90% categorical agreement with the standard method. In our study, there was a good agreement between the well-established broth microdilution method and the Etest® method for amphotericin B and fluconazole. The categorical agreement was 94.1% for amphotericin B, and 96.7% for fluconazole. For itraconazole, the categorical agreement was 84.9%. When comparing the disk diffusion method with the broth microdilution, the best categorical agreement was obtained for amphotericin B (90.2%), and was lower for fluconazole (67.9%) and for itraconazole (79.1%). Higher rates of resistance were obtained when the isolates were tested by disk diffusion. Similar results were found for itraconazole by Pedroso et al.6 and Demitto et al.,7 who mentioned that the difficult diffusion of itraconazole molecules in the agar was responsible for such discrepancy and recommended further in vitro studies. Dota et al.8 observed 71% concordance between microdilution and disk diffusion for fluconazole, and one third of the isolates showed resistance when tested by disk diffusion.
In vitro susceptibility of Candida isolates to amphotericin B, fluconazole and itraconazole, by the Etest®, disk diffusion, and broth microdilution methods.
| Species (n) | E-test | Disk diffusion | Broth microdilution | ||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| AmB | FLZ | ITZ | AmB | FLC | ITZ | AmB | FLC | ITZ | |||||||||||||||||||
| n | n | n | n | n | n | n | n | n | |||||||||||||||||||
| S | I | R | S | SDD | R | S | I | R | S | I | R | S | SDD | R | S | I | R | S | I | R | S | SDD | R | S | I | R | |
| C. albicans (82) | 82 | 0 | 0 | 80 | 0 | 2 | 70 | 5 | 7 | 74 | 0 | 8 | 62 | 135 | 15 | 79 | 2 | 1 | 82 | 0 | 0 | 82 | 0 | 0 | 82 | 0 | 0 |
| C. parapsilosis (22) | 20 | 0 | 2 | 21 | 0 | 1 | 18 | 0 | 4 | 20 | 0 | 2 | 12 | 3 | 7 | 13 | 4 | 5 | 21 | 0 | 1 | 21 | 0 | 1 | 22 | 0 | 0 |
| C. glabrata (20) | 15 | 0 | 5 | 17 | 2 | 1 | 16 | 1 | 3 | 16 | 0 | 4 | 9 | 0 | 11 | 9 | 0 | 11 | 19 | 0 | 1 | 18 | 0 | 2 | 19 | 0 | 1 |
| C. tropicalis (09) | 8 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 1 | 8 | 0 | 1 | 7 | 1 | 1 | 6 | 1 | 2 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 | 9 | 0 | 0 |
| C. kefyr (05) | 4 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 | 5 | 0 | 0 |
| C. famata (04) | 3 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 3 | 1 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| C. guilliermondii (04) | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 2 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| C. haemulonii (04) | 3 | 0 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 1 | 2 | 1 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
| C. metapsilosis (02) | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 | 2 | 0 | 0 |
| C. lusitaniae (01) | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 0 |
| Total (n) | 142 | 0 | 11 | 145 | 2 | 6 | 129 | 6 | 18 | 136 | 0 | 17 | 101 | 13 | 39 | 120 | 11 | 22 | 151 | 0 | 2 | 150 | 0 | 3 | 152 | 0 | 1 |
| Total (%) | 92.8 | 0 | 7.2 | 94.8 | 1.3 | 3.9 | 84.3 | 3.9 | 11.8 | 88.8 | 0 | 11.2 | 66 | 8.5 | 25.5 | 78.4 | 7.2 | 14.4 | 98.7 | 0 | 1.3 | 98 | 0 | 2 | 99.3 | 0 | 0.7 |
AmB: amphotericin B; FLC: fluconazole; ITZ|: itraconazole; n: number of isolates; S: susceptible; SDD: susceptible dose dependent; I: intermediate; R: resistant.
Isolates obtained from the group of patients with recurrent vulvovaginal candidiasis showed lower percentages of susceptibility to the antifungals, as well as isolates from the group of asymptomatic women, as detected by all the methods evaluated.
The level of agreement between the disk diffusion method and the broth microdilution method depended to the antifungal tested. The highest concordance was obtained for amphotericin B when susceptibility testing was performed by E-test® and by disk diffusion. Our findings are in agreement with those obtained in some studies9 but differed from others in which the agreement of the Etest® and disk diffusion with the broth microdilution were 65.2% and 67.4%, respectively.6 Thus, we suggest caution when interpreting susceptibility results when an agar-based method (Etest®, disk diffusion) is used for amphotericin B. In our study, the disk diffusion method showed the highest detection rate of true resistant isolates, susceptible-dose-dependent or intermediate. The microdilution method did not underestimate resistance to azoles despite the trailing effect showed when determining resistance to these group of antifungals. Thus, our study suggests that isolates that seem to be resistant by the disk diffusion method, especially to azoles, must be carefully reviewed by repeating the test and/or by determining the susceptibility by a different method.
FundingThis study was supported by the “Conselho Nacional de Desenvolvimento Científico e Tecnológico” (CNPq), “Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior” (CAPES) and by “Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado de São Paulo” (FAPESP).