Polycystic ovarian syndrome (PCOS) has been treated recently with chromium supplementations. However, it is unknown if this dietary supplement has similar effect to metformin.
AimThe aim of this study was to investigate the efficacy of chromium supplementation in women with PCOS.
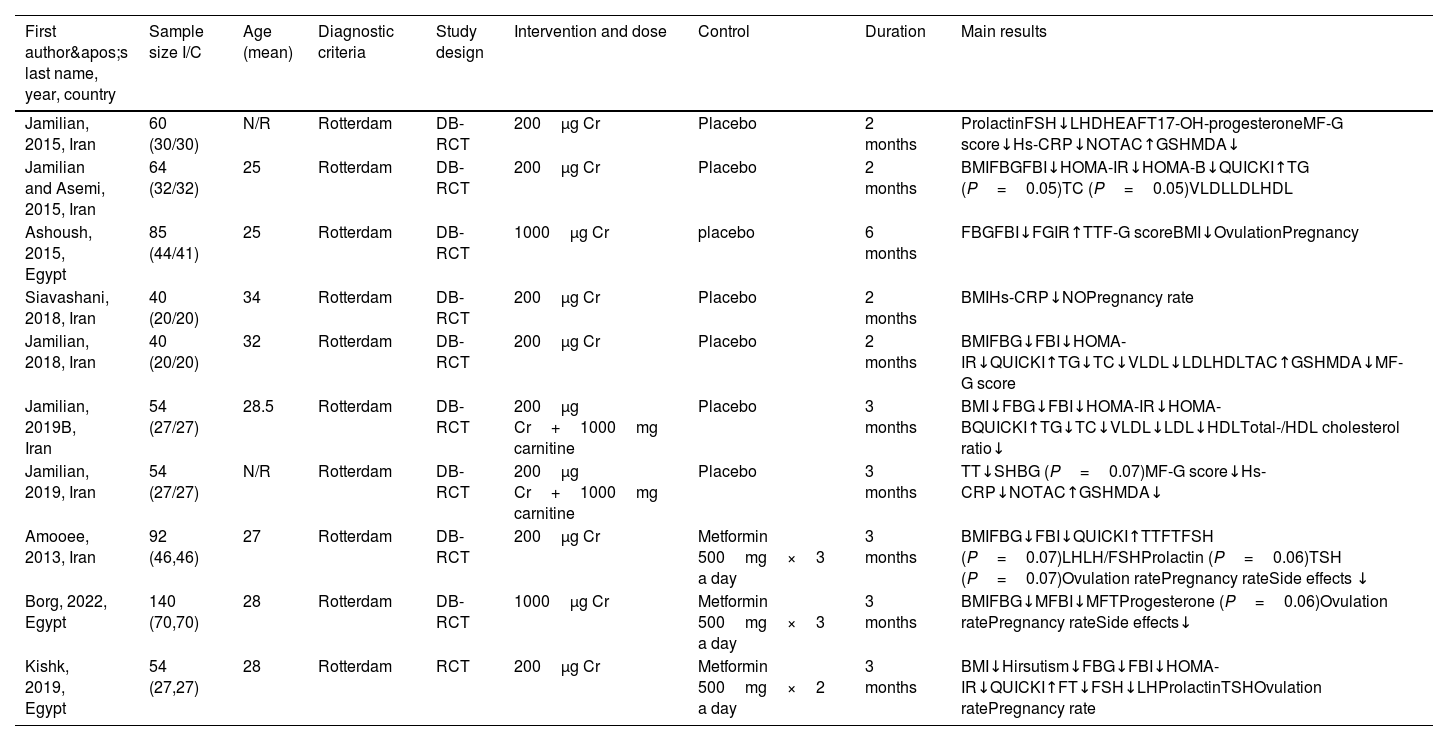
MethodsA meta-analysis was conducted using relevant articles obtained from searches of PubMed, Scopus, Embase, and Google Scholar. The mean difference and standardized mean difference were employed to determine the effect size for biochemical parameters.
ResultsA total of 10 randomized controlled trials involving 683 women were included in the analysis. The results indicated that chromium supplementation, as vs a placebo, significantly decreased fasting blood insulin (P=0.01), triglyceride (P<0.00001), total cholesterol (P<0.00001), very low-density lipoprotein (P<0.00001), low-density lipoprotein (P=0.0003), high sensitivity C-reactive protein (P=0.02), malondialdehyde (P=0.007), follicle stimulating hormone (P=0.0007), and prolactin (P=0.01), and increased the Quantitative Insulin Sensitivity Check Index (P=0.02), total antioxidant capacity (P<0.0001), and ovulation incidence (P=0.001). Chromium supplementation was also found to be more effective than metformin in reducing HOMA-IR (P<0.00001), and luteinizing hormone (P=0.04).
ConclusionChromium picolinate supplementation at a dosage of 200μg may provide benefits similar to metformin with regard to FBG, FBI, ovulation, and pregnancy incidence, with fewer side effects in patients with PCOS. Further experiments are still required to draw effective dietary guidelines related to chromium.
El síndrome de ovario poliquístico (SOP) se ha tratado recientemente con suplementos de cromo. Sin embargo, se desconoce si este suplemento dietético tiene un efecto similar al de la metformina.
ObjetivoEl objetivo de este estudio fue investigar la eficacia de los suplementos de cromo en mujeres con SOP.
MétodosSe realizó un metaanálisis utilizando artículos relevantes obtenidos de búsquedas en PubMed, Scopus, Embase y Google Scholar. Se emplearon la diferencia de medias y la diferencia de medias estandarizada para determinar el tamaño del efecto de los parámetros bioquímicos.
ResultadosSe incluyeron en el análisis un total de 10 ensayos controlados aleatorizados con 683 mujeres. Los resultados indicaron que los suplementos de cromo, en comparación con un placebo, disminuyeron significativamente la insulina en sangre en ayunas (p=0,01), los triglicéridos (p<0,00001), el colesterol total (p<0,00001), las lipoproteínas de muy baja densidad (p<0,00001), las lipoproteínas de baja densidad (p=0,0003), la proteína C reactiva de alta sensibilidad (p=0,02), el malondialdehído (p=0,007), la hormona foliculoestimulante (p=0,0007) y la prolactina (p=0,01), y aumentaron el índice cuantitativo de comprobación de la sensibilidad a la insulina (p=0,02), la capacidad antioxidante total (p<0,0001) y la incidencia de ovulación (p=0,001). Los suplementos de cromo también resultaron más eficaces que la metformina para reducir el HOMA-IR (p<0,00001) y la hormona luteinizante (p=0,04).
ConclusiónLa suplementación con picolinato de cromo a una dosis de 200μg puede proporcionar beneficios similares a la metformina en lo que respecta a la FBG, la FBI, la ovulación y la incidencia de embarazo, con menos efectos secundarios en pacientes con SOP. Aún es necesario realizar más experimentos para elaborar directrices dietéticas eficaces en relación con el cromo.