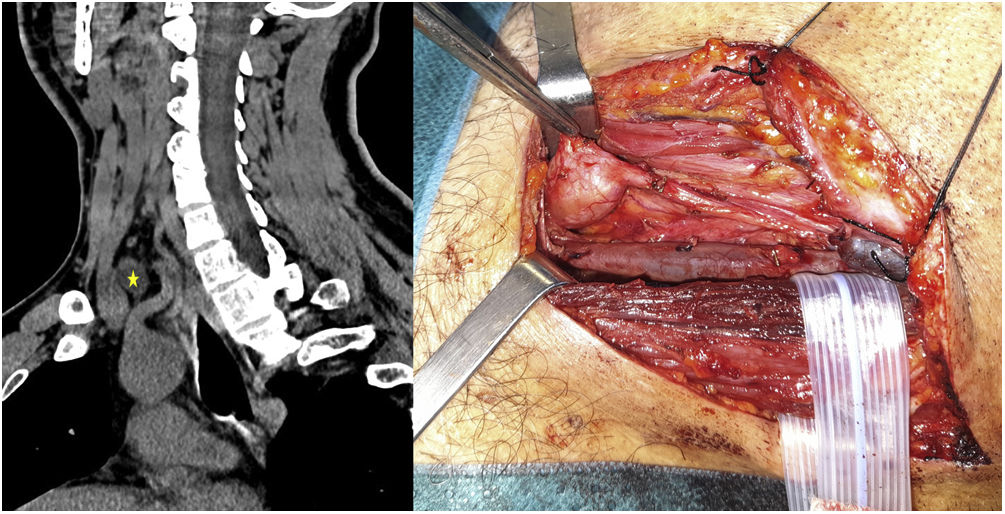
During the course of a left lateral cervical lymphadenectomy for papillary thyroid cancer, it was observed that one of the lymph nodes reported on in the preoperative CT scan as being located between the left carotid and jugular artery (Fig. 1), turned out to be a formation dependent on the vagus nerve. The neurosurgeon identified it intraoperatively as a neurofibroma of the vagus nerve and recommended a wait-and-see attitude since it does not produce clinical symptoms and its resection would imply significant functional deficits.
Neurofibromas are slow-growing tumours originating from the neural sheath which, unlike schwannomas, which grow exophytically in the thickness of the nerve.