Main treatment options for pharyngoesophageal diverticulum are the surgical excision or diverticulopexy, always associated with a myotomy, and the endoscopic peroral myotomy. The aim of this study was to describe the outcomes of a consecutive surgical series.
MethodsObservational study of patients who underwent open surgery (2004–2024) and who had a 2-years structured follow-up. Main outcome were symptom resolution and postoperative complications. Baseline characteristics, surgical technique, reinterventions, readmission and recurrence were also analyzed. Descriptive statistics was used, including percentages, mean and standard deviations, and medians with complete ranges.
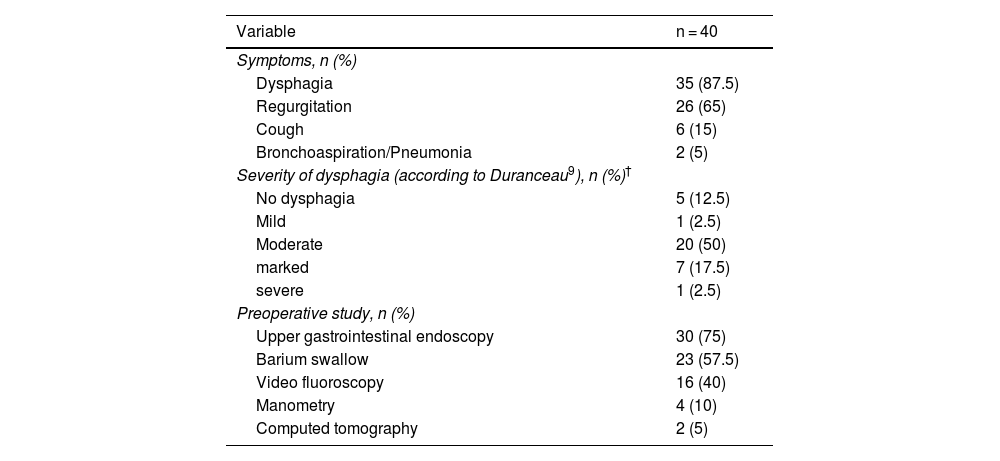
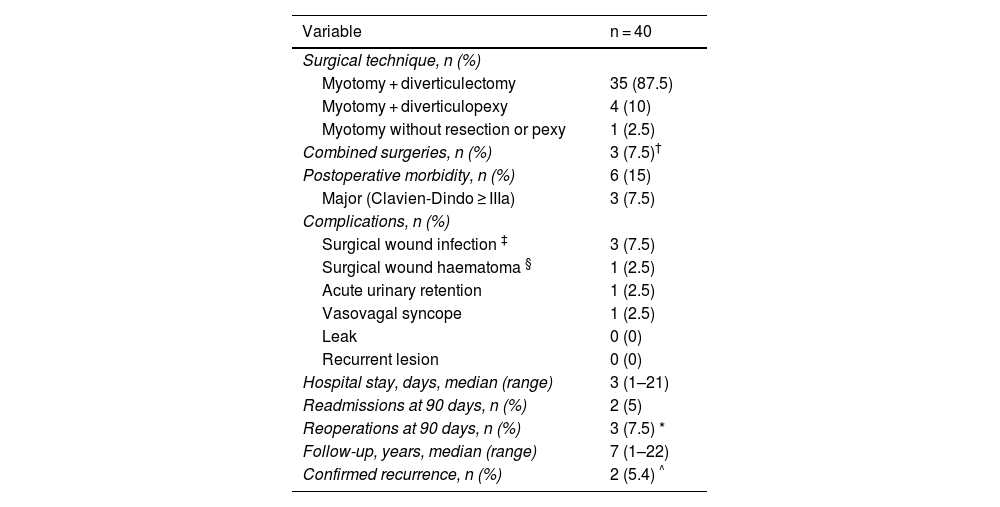
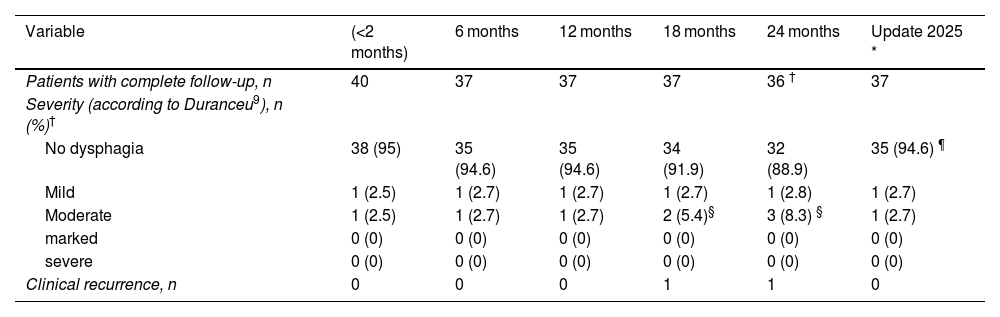
ResultsDuring the study period, 40 patients (73% male) were operated on, with a mean age of 72 ± 11 years. Ninety-five percent presented dysphagia and/or regurgitation, while 2 patients were referred due to a history of pneumonia to bronchoaspiration. The most frequent surgical technique was cricopharyngeal myotomy combined with diverticulectomy. Postoperative morbidity was 15%, with no cases of esophageal fistula. There was no mortality, and the median hospital stay was 3 days. Initial symptom resolution was achieved in 95% of patients. During follow-up (median 7 years [1–20]), 2 recurrences were observed at 18 and 24 months, respectively, both successfully managed endoscopically.
ConclusionsSurgical treatment achieves symptoms resolution in the vast majority of cases, with limited morbidity and recurrence.
Las principales alternativas terapéuticas del divertículo faringoesofágico son la cirugía (miotomía con resección o pexia) y el tratamiento endoscópico (septotomía transoral). El objetivo de este estudio es describir los resultados de una serie consecutiva de pacientes tratados quirúrgicamente.
MétodosEstudio observacional descriptivo de pacientes intervenidos quirúrgicamente (2004–2024), con un seguimiento protocolizado hasta los 24 meses. Las variables principales fueron la resolución de los síntomas y las complicaciones postoperatorias. Se analizaron además las características clínicas basales, la técnica quirúrgica, las readmisiones, las reintervenciones y las recidivas. Se utilizó estadística descriptiva con cálculo de porcentaje, medias y desviaciones estándar y medianas y rangos completos.
ResultadosDurante el período del estudio se intervinieron 40 pacientes (73% hombres), con una media de edad de 72 ± 11 años. El 95% consultó por disfagia y/o regurgitación y 2 pacientes fueron referidos por historia de neumonías secundarias a broncoaspiración. La técnica quirúrgica más frecuente fue la miotomía del cricofaríngeo asociada a una diverticulectomía. La morbilidad postoperatoria fue del 15%, sin demostrarse fístula esofágica en ningún caso. No hubo mortalidad postoperatoria y la estancia mediana fue de 3 días. La resolución inicial de los síntomas fue del 95%. Durante el seguimiento (mediana de 7 años [1–20]), se constataron 2 recidivas (a los 18 y 24 meses, respectivamente), ambas tratadas con éxito por vía endoscópica.
ConclusionesEl tratamiento quirúrgico permite la resolución de los síntomas en la práctica mayoría de casos, con una morbilidad y una recidiva limitadas.