Inguinoscrotal hernia (ISH) represents an advanced form of inguinal hernia, with greater technical complexity and higher risk of complications. Despite its significant prevalence, its management remains heterogeneous in Spain. This study evaluates clinical practice and adherence to the recommendations of the European Hernia Society (EHS).
MethodsA cross-sectional observational study was conducted through an online survey distributed among members of the Spanish Association of Surgery (AEC). Demographic variables and specific data on the diagnostic and therapeutic management of ISH were collected. Subgroup analyses were performed based on age and specialization in abdominal wall surgery.
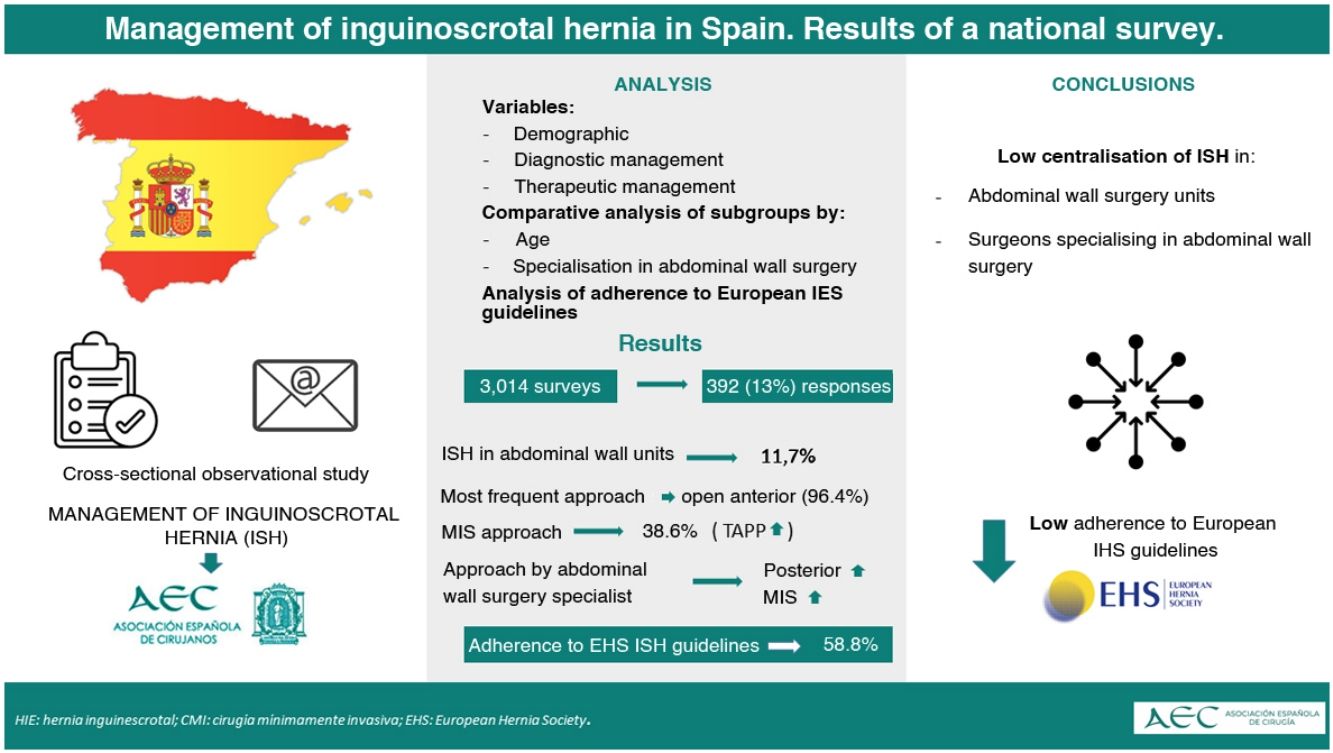
ResultsOut of 3014 surveys distributed, 392 complete responses were obtained (13%). While 60.2% had an Abdominal Wall Unit, only 11.7% centralized all inguinal hernia cases. Open surgery remains the most frequent approach (96.4%). In ISH cases, the use of minimally invasive surgery (MIS) is lower (38.6%), with TAPP being the predominant technique. Surgeons specialized in abdominal wall procedures used more posterior and endoscopic techniques. Adherence to EHS guidelines was partial (58.8%).
ConclusionsThe treatment of ISH in Spain lacks proper centralization in specialized units, which limits the adoption of advanced techniques and adherence to international guidelines. Promoting specific training, European certification, and the creation of specialized units could improve clinical outcomes and the quality of life for these patients.
La hernia inguinoescrotal (HIE) representa una forma avanzada de hernia inguinal, con mayor complejidad técnica y riesgo de complicaciones. A pesar de su prevalencia relevante, su abordaje continúa siendo heterogéneo en España. Este estudio evalúa la práctica clínica y la adherencia a las recomendaciones de la European Hernia Society (EHS).
MétodosEstudio observacional transversal mediante encuesta online distribuida entre los miembros de la Asociación Española de Cirugía (AEC). Se recogieron variables demográficas y datos específicos sobre el manejo diagnóstico y terapéutico de la HIE. Se analizaron subgrupos por edad y especialización en cirugía de pared.
ResultadosDe 3014 encuestas enviadas, se obtuvieron 392 respuestas completas (13%). Un 60,2% disponía de Unidad de Pared Abdominal, pero solo el 11,7% centralizaba todos los casos de hernia inguinal. El abordaje abierto continúa siendo el más frecuente (96,4%). En HIE, el uso de cirugía mínimamente invasiva (CMI) es inferior (38,6%) y predomina el TAPP. Los especialistas en pared emplean más técnicas posteriores y endoscópicas. La adherencia a las guías EHS fue parcial (58,8%).
ConclusionesEl tratamiento de la HIE en España carece de una adecuada centralización en unidades especializadas, lo que limita la adopción de técnicas avanzadas y la adherencia a guías internacionales. Fomentar la formación específica, la certificación europea y la creación de unidades especializadas podría mejorar los resultados clínicos y la calidad de vida de estos pacientes.