To determine the state of ocular surface and tear film in college students who are users of inhalants, mainly vapers.
MethodsWe conducted a descriptive, observational, and cross-sectional study with 62 participants whose sociodemographic characteristics, ocular surface status, tear film and variables related to vaping were evaluated. Individuals with a higher (5–7 times per week of consumption) and lower frequency of vaping (1–4 times per week of consumption) were evaluated. Symptom documentation was standardized using the OSDI questionnaire and biomicroscopy to evaluate ocular adnexa and anterior segment structures, blinking frequency and eye protection index (EPI) were also determined.
ResultsA total of 76% of participants were men with a median age of 20.37 years, and an age range between 18 and 28 years. Participants with a higher frequency of vaping exhibited blepharitis (60%) (P-value > .05), meibomian gland obstruction (65.63%) (P-value > .05), tarsal conjunctival hyperemia (52.94%) (P-value < .05), tarsal conjunctival hyperemia (52.94%) (P-value < .05), generalized bulbar hyperemia (72.73%) (P-value > .05), papillary reaction (60%) (P-value > .05), conjunctival staining (75%) (P-value > .05), limbal redness (61.54%) (P-value > .05).
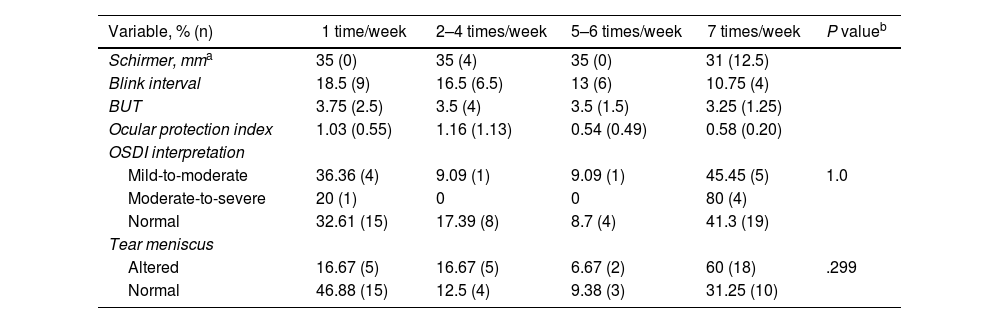
A normal Schirmer I (median 31 mm/5 min), short tear breakup time (median 3.5 s in BUT) and a lower number of blinks per minute (median 10.75) were found, yet the EPI was lower (median 0.58).
ConclusionsVaping could be associated with ocular health alterations, such as blepharitis, meibomian gland obstruction, conjunctival hyperemia, conjunctival staining and altered tear quality. Follow-up studies are recommended to establish causal relationships.
Determinar el estado de superficie ocular y película lagrimal en estudiantes universitarios usuarios de sustancias inhalantes principalmente vapeadores.
MétodosEstudio observacional descriptivo de corte transversal con 62 participantes, dónde se evaluaron características sociodemográficas, estado de superficie ocular, película lagrimal y variables relacionadas con práctica de vapeo, se evaluaron individuos con mayor frecuencia de vapeo (5–7 veces semanales de consumo) y menor (1–4 veces semanales de consumo). Se estandarizó la documentación de síntomas con uso del cuestionario OSDI, biomicroscopía para evaluar los anexos oculares y estructuras del segmento anterior, además se determinó frecuencia de parpadeo e índice de protección ocular (IPO).
ResultadosEl 76% de los participantes fueron hombres con mediana de edad de 20,37 años, con rango de edad de 18 a 28 años. En los participantes con mayor frecuencia de consumo se evidenció blefaritis (60%) (Valor P > ,05), obstrucción de glándulas de Meibomio (65,63%) (Valor P > ,05), hiperemia conjuntiva tarsal (52,94%) (Valor P < ,05), hiperemia bulbar generalizada (72,73%) (Valor P > ,05), reacción papilar (60%) (Valor P > ,05), tinción conjuntival (75%) (Valor P > ,05), enrojecimiento limbal (61,54%) (Valor P > ,05).
Se encontró un Schirmer I normal (mediana 31 mm/5 minutos), tiempo de rotura lagrimal corto (mediana 3,5 segundos en BUT) y menor número de parpadeos por minuto (mediana 10,75). El IPO fue menor (mediana 0,58).
ConclusionesEl vapeo podría asociarse a alteraciones de salud ocular, como blefaritis, obstrucción de glándulas de Meibomio, hiperemia conjuntival, tinción conjuntival y calidad de lagrima alterada. Se recomienda realizar estudios de seguimiento para establecer relaciones causales.