The increase in quality and life expectancy, often leads to many patients asking the glaucoma specialist whether some sports, activities or hobbies would affect their illness. The aim of this article is to establish guidelines for patients, based on the scientific evidence of published papers.
MethodsReview of all published articles on glaucoma and sports or other activities. The papers were classified according to the level of scientific evidence based on the Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine classification.
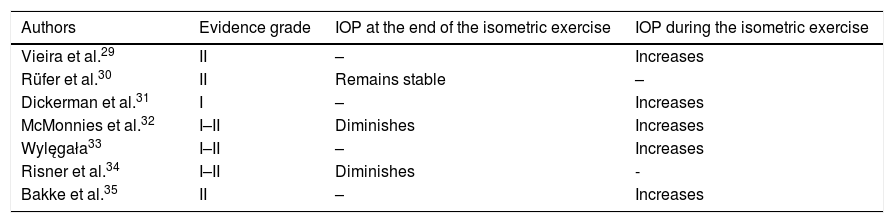
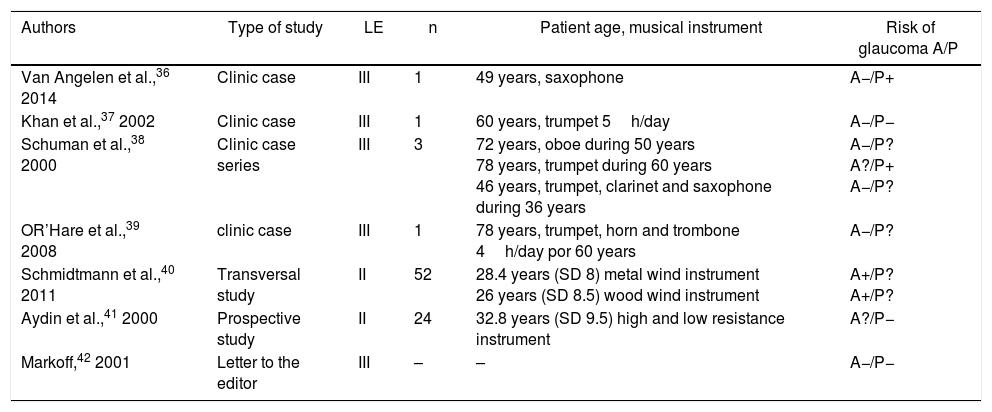
ResultsAerobic sports are beneficial for the patient. Yoga indoor sports or relaxation techniques should be avoided if Valsalva maneuvers are performed or the head is placed very low. Also, the patients must avoid sudden changes in height. Intense heat does not seem to lead to progression of glaucoma, but intense cold can affect patients with vascular dysregulation. Activities using the near vision slightly reduce the intraocular pressure. The use of wind instruments may raise intraocular pressure, depending on the technique used.
ConclusionsCertain sports and activities may have an influence on the onset or progression of glaucoma. Glaucoma specialists should have adequate information about the scientific evidence in the publications, in order to properly advise the patients.
El aumento de la calidad y de la esperanza de vida y el hecho de que el glaucoma se diagnostique cada vez más precozmente hace preguntarse a muchos pacientes si afectan a su enfermedad determinados deportes, actividades o aficiones. El objetivo de este trabajo es establecer unas guías para aconsejar a los pacientes con base en la evidencia científica de los trabajos publicados.
MétodosRevisión de todos los trabajos publicados sobre glaucoma y deportes u otras actividades. Los trabajos fueron clasificados según el nivel de evidencia científica basada en la clasificación del Oxford Centre for Evidence-Based Medicine.
ResultadosLas actividades aeróbicas son beneficiosas para el paciente. Se han de evitar deportes o técnicas de relajación tipo yoga con maniobras de Valsalva o colocación de la cabeza en posición inferior. También se deben evitar los cambios bruscos en altura. El calor intenso no parece influir en el glaucoma, pero el frío intenso puede afectar a pacientes con disregulación vascular. Las actividades de visión próxima disminuyen levemente la presión intraocular. El uso de instrumentos de viento puede elevar la presión intraocular dependiendo de la técnica utilizada.
ConclusionesCiertos deportes y actividades pueden tener una influencia en la aparición o la progresión del glaucoma. Los especialistas en glaucoma deben tener información adecuada sobre la evidencia científica de las publicaciones para poder aconsejar apropiadamente a los pacientes.