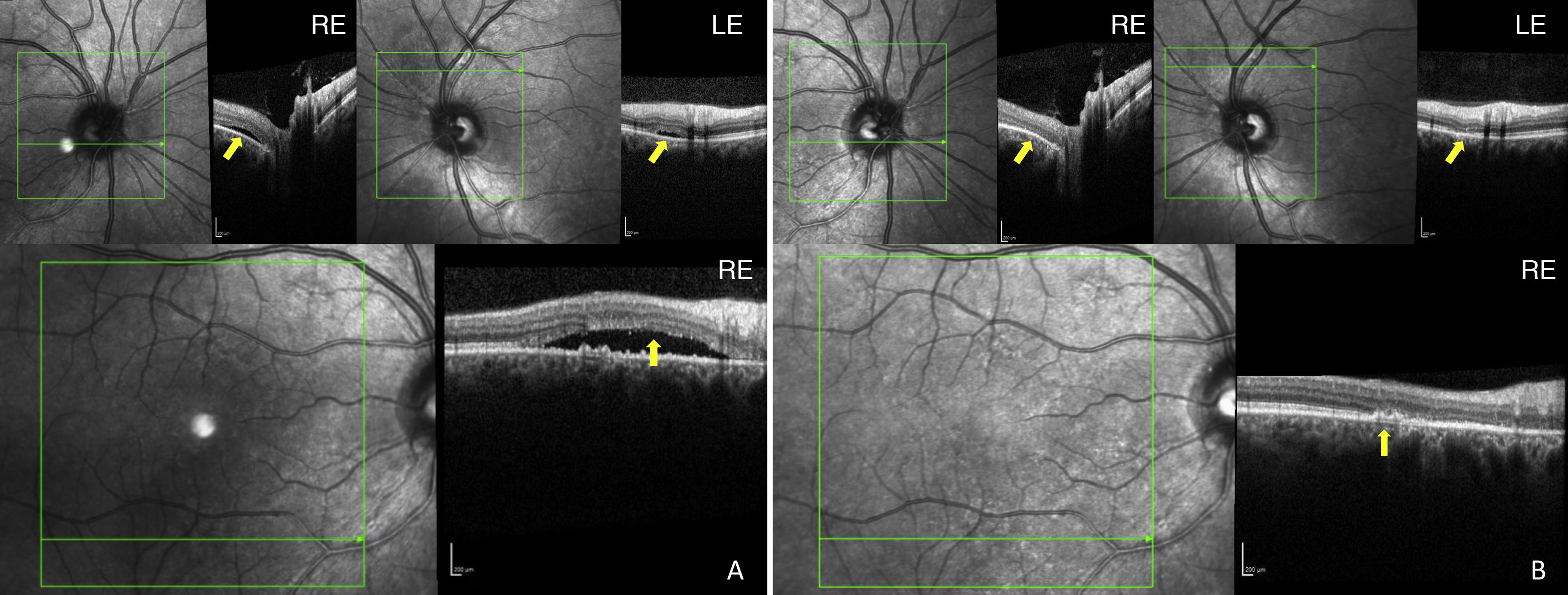
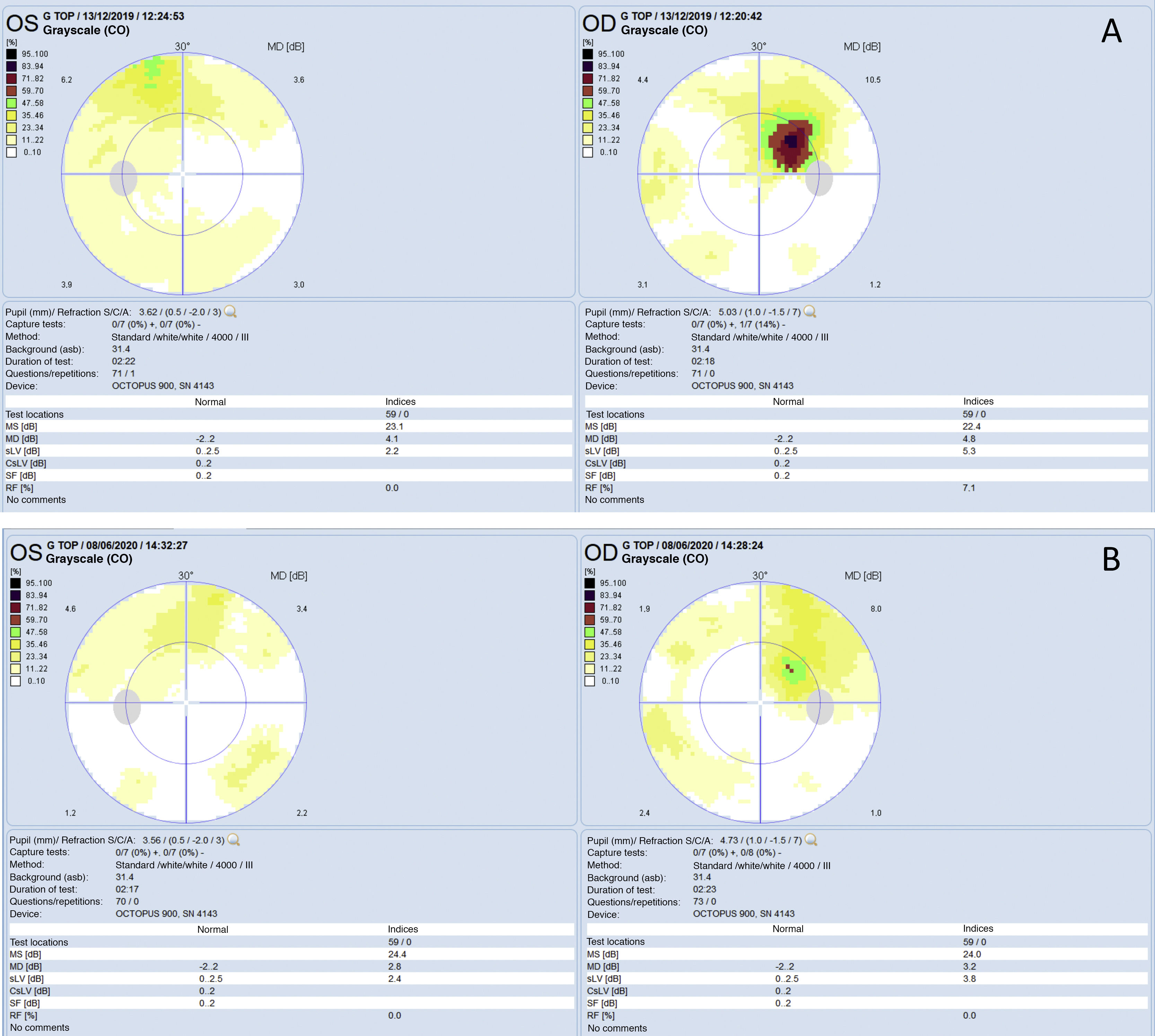
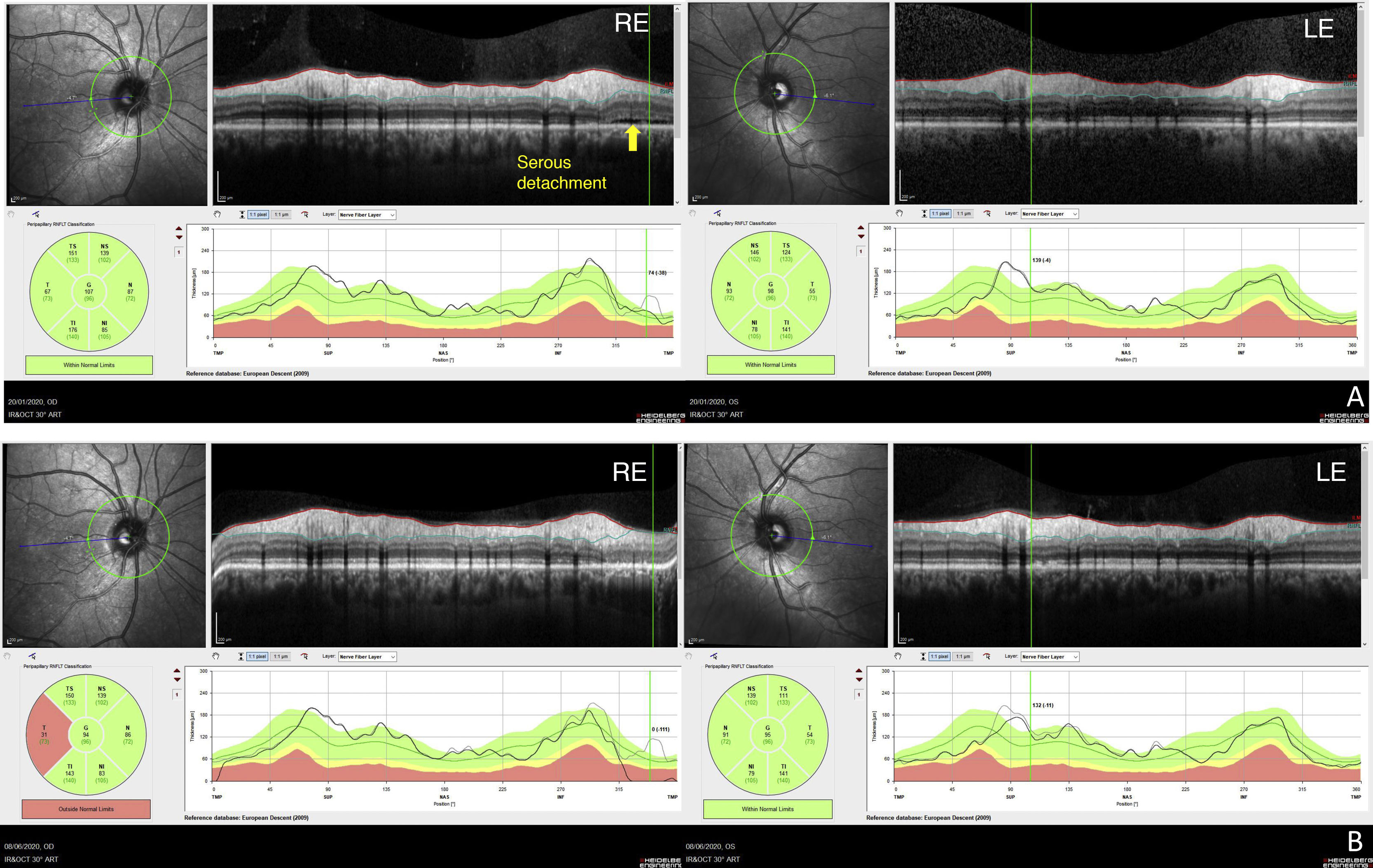
A 53-year-old male with no systemic disorders, other than controlled arterial hypertension, presented with asymptomatic, bilateral neurosensory retinal detachment (NRD) detected during a routine revision. The patient reported the use of tadalafil (a phosphodiesterase-5 inhibitor [PDE5I]) for erectile dysfunction. Following suspension of the drug, subretinal fluid reabsorption was confirmed, with the persistence of chronic alterations in the optical coherence tomography (OCT) and the visual field. PDE5Is have ocular side effects, including exudative retinal detachment. Although no direct causal relationship has been confirmed, PDE5 inhibition at chorioretinal level produces vasodilatation, increased choroid hydrostatic pressure, and exudation into the subretinal space. In cases of NRD, a thorough assessment of the drug treatment history is crucial. Patients who use PDE5I drugs should be alerted to their potential ocular side effects.
Se presenta el caso de un varón de 53 años con desprendimiento retiniano neurosensorial (DNS) bilateral asintomático detectado en una revisión rutinaria. No se encontraron patologías sistémicas subyacentes, salvo hipertensión arterial controlada. En la anamnesis dirigida, el paciente reveló ingesta de tadalafilo, un inhibidor de la fosfodiesterasa 5 (IPDE5) utilizado en el tratamiento de la disfunción eréctil. Tras la retirada del fármaco, se observó una reabsorción del fluido subretiniano con persistencia de alteraciones crónicas y campimétricas en la tomografía de coherencia óptica (OCT). Los IPDE5 presentan efectos secundarios oculares entre los que se ha descrito el desprendimiento seroso retiniano. Aunque no se ha podido comprobar la relación causal directa, la inhibición de la fosfodiesterasa 5 (PDE5) a nivel coriorretiniano produce vasodilatación, aumento de la presión hidrostática coroidea y exudación al espacio subretiniano. En casos de DNS, es fundamental una historia farmacoterapéutica completa. Se debería advertir de los posibles efectos secundarios oculares de los IPDE5 a los pacientes usuarios de este tipo de fármacos.