Abstracts Asociación Mexicana de Hepatología (AMH) 2024
More infoMASLD is associated with cardiovascular disease due to systemic inflammation and endothelial dysfunction. Carotid intima-media thickness (CIMT) and atherosclerosis are considered markers of generalized atherosclerosis and increased cardiovascular risk (CVR). The objective of this study is to describe the correlation between CVR and changes in CIMT in patients with MASLD.
Materials and PatientsThis observational, cross-sectional, analytical study was conducted at the Instituto de Investigaciones Médico-Biológicas liver clinic from January 2023 to April 2024. Patients who met the eligibility criteria provided informed consent and underwent the following procedures: transitional liver elastography (TE), carotid Doppler ultrasound (USG), somatometric measurements, and biochemical tests. Cardiovascular risk scores (Framingham, ASCVD, SCORE2) and FIB-4 were calculated. Participants were categorized into two groups based on carotid intima-media thickness, altered CIMT (>1.1 mm) and normal CIMT (<1.1 mm). A TE value >8 Kpa indicated a risk of advanced fibrosis. Numerical variables were reported as measures of central tendency and dispersion, while categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages. The Kolmogorov-Smirnov test assessed data distribution and the Levene test evaluated homoscedasticity. For group comparisons, Student's t-test or Wilcoxon test was used for numerical variables, and chi-square or Fisher's exact test for categorical variables. ROC curves were generated to analyze cardiovascular risk and atherosclerosis. Spearman's test was employed to evaluate correlations. Statistical analysis was conducted using SPSS version 26.
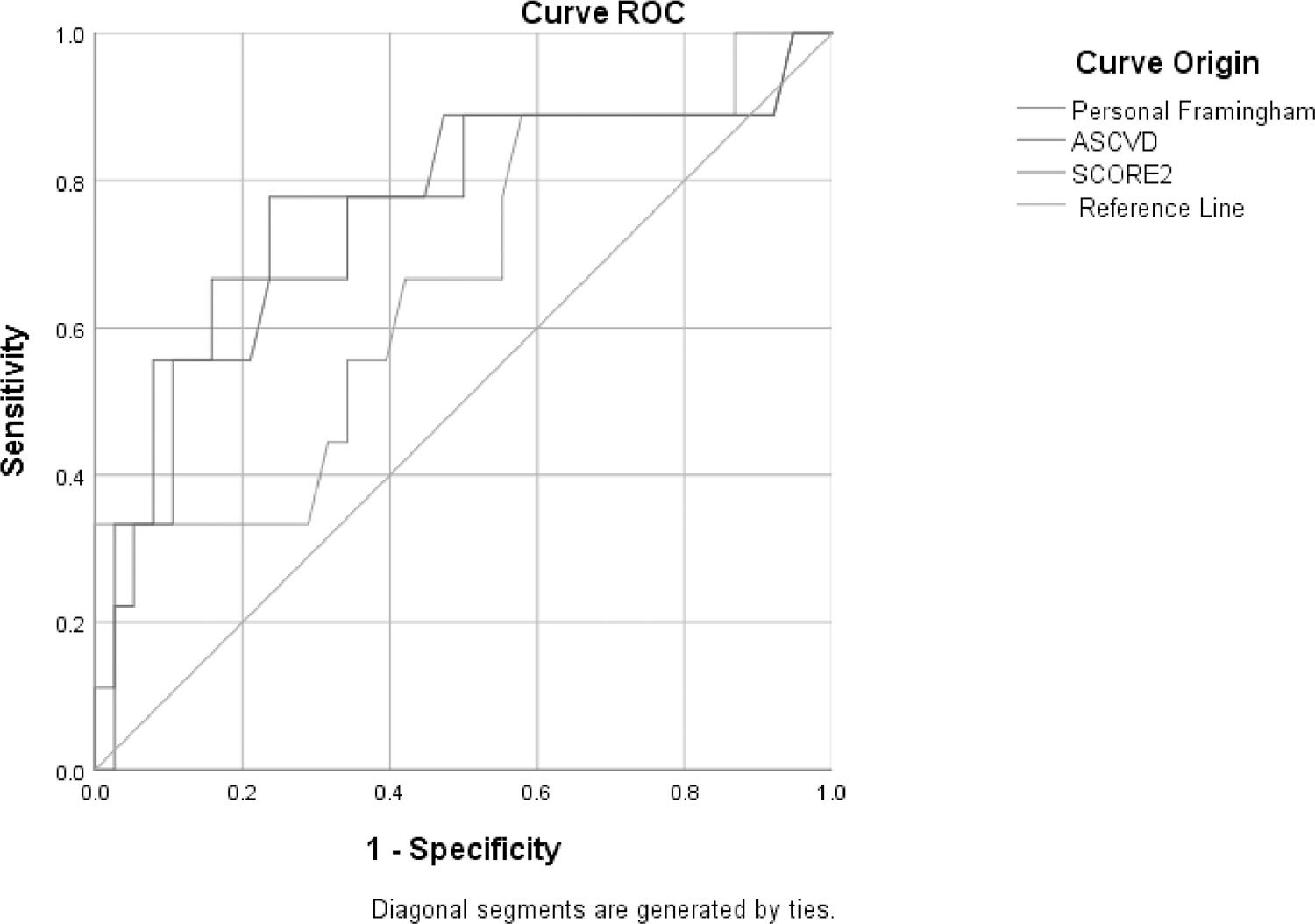
ResultsThis study included 51 patients: 17 (33.33%) with altered CIMT (age 58 [48-72], 58.8% women) and 34 (66.66%) without alterations (age 51.5 [30-68], 79.4% women). Pathological histories, elastography results, biochemical data, and CVR scores are summarized in Table 1. Patients with altered CIMT exhibited a higher age (58 [48-72] vs. 51.5 [30-68], p=0.005), higher LDL concentrations (133.93±37.46 vs. 109.47±41.86 mg/dL, p=0.047), and elevated CVR scores: Framingham (5.8 [3.0-12.3] vs. 1.7 [0.57-5.05], p=0.037), ASCVD (8.4 [5.4-17.25] vs. 3.7 [1.95-10.2], p=0.047), and SCORE2 (8.1 [4.75-12.9] vs. 3.8 [1.7-6.85], p=0.012). Advanced fibrosis (>8 kPa) was more prevalent among patients with altered CIMT (55.6% vs. 21.4%, p=0.037) and was associated with higher CVR scores: ASCVD (15.7 [7.75-24.75] vs. 4.45 [1.97-9.67], p=0.001) and SCORE2 (11.3 [4.85-17.1] vs. 3.95 [2.3-8.12], p=0.004). Sub-analysis showed significant correlations of >8 kPa and high FIB-4 with SCORE2 (r=0.574, p=0.040) and (r=0.564, p=0.045), respectively. Patients with >8 kPa were more likely to have atherosclerosis (OR 4.58, 95% CI: 1.01-20.6, p=0.037) and altered CIMT (OR 4.2, 95% CI: 1.1-16.2, p=0.026). The area under the curve for detecting atherosclerosis was 0.768 (95% CI: 0.570-0.965, p=0.013) for ASCVD, 0.753 (95% CI: 0.552-0.953, p=0.019) for SCORE2, and 0.662 (95% CI: 0.457-0.867, p=0.133) for Framingham.
ConclusionsIn our cohort, MASLD patients with >8 kPa exhibited a significant correlation with SCORE2 and an increased risk of atherosclerosis. These results highlight the importance of assessing cardiovascular risk and carotid alterations in patients with elevated liver stiffness (>8 kPa) and high cardiovascular risk scores.
Ethical statement: All patients have informed consent and personal data protection.
Declaration of interests: None.
Funding: This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-pro-fit sectors.
Characteristics of patients with MASLD according to alterations in carotid intima-media layer thickness.
RIMT: Right Intima-Media Thickness, LIMT: Left Intima-Media Thickness, GGT: Gamma-Glutamyl Transferase, TB: Total Bilirubin, AST: Aspartate Aminotransferase, ALT: Alanine Aminotransferase, ALP: Alkaline Phosphatase, TP: Total Proteins, HDL: High-Density Lipoproteins, LDL: Low-Density Lipoproteins, VLDL: Very Low-Density Lipoproteins, CRP: C-Reactive Protein, HOMA: Homeostatic Model Assessment, SBP: Systolic Blood Pressure, DBP: Diastolic Blood Pressure
Figure 1. ROC curves of cardiovascular risk and atherosclerosis scales.