Abstracts of the 2025 Annual Meeting of the ALEH
More infoEvidence regarding the utility of artificial intelligences (AI) for the diagnosis of clinical cases in gastroenterology is limited, and is even scarcer in hepatology.
Determine the concordance between the responses of various AI models and those of specialist physicians in the resolution of hepatology clinical cases.
Materials and MethodsThis was a clinical, observational, analytical, and prospective study. The assessment instrument comprised six hepatology clinical cases, each featuring five questions. A panel of eight experts from different institutions was convened; and their individual responses were subjected to calculation of the kappa coefficient (κ) and Cronbach’s alpha. Items that failed to meet the validation threshold (≥ 80 % agreement and κ ≥ 0.6) were reviewed through iterative rounds of a modified Delphi method. Finally, κ was calculated to evaluate concordance between responses generated by the AI models and the expert consensus.
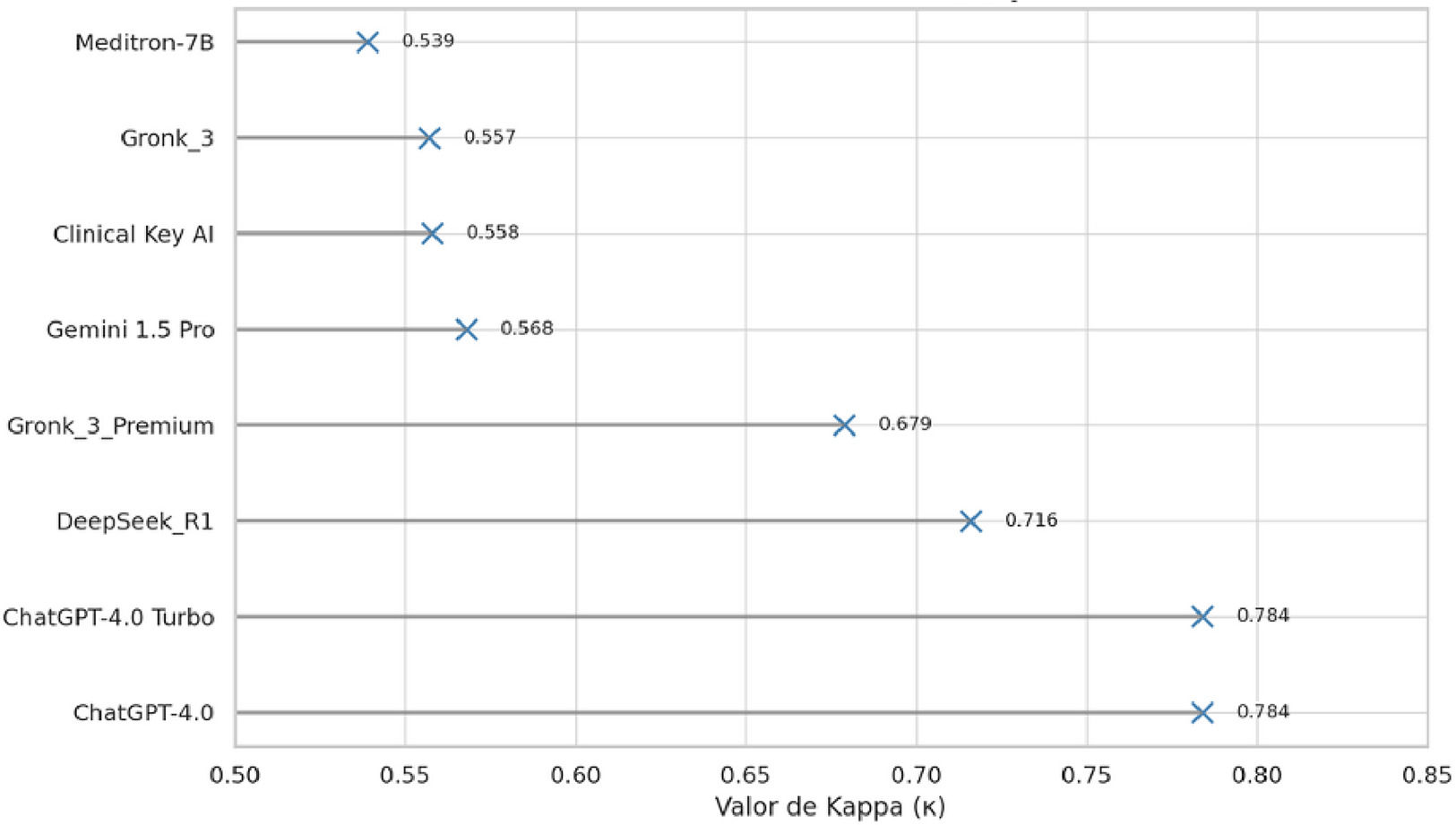
ResultsThe expert consensus demonstrated a high overall concordance (κ = 0.901; 95 % CI [0.860, 0.943]; z = 61.57; p < 0.001). Individual model concordance ranged from moderate to substantial, with κ values between 0.539 (Meditron-7B) and 0.784 (ChatGPT-4.0 and ChatGPT-4.0 Turbo), all statistically significant. In terms of the percentage of correct responses, the highest performing models were ChatGPT-4.0, ChatGPT-4.0 Turbo, and Deepseek-R1 (figure 1).
ConclusionsA moderate to substantial concordance was observed between diagnoses generated by different AI models and expert judgment in hepatology clinical cases, although variations were noted among the evaluated systems.