Acute Invasive Fungal Sinusitis (AIFS) is an aggressive infection with significant morbidity and mortality. Early and accurate diagnosis is critical, but its nonspecific clinical presentation often complicates timely detection. This study aims to identify clinical, laboratory, and radiological predictors associated with biopsy-confirmed AIFS in patients with suspected disease.
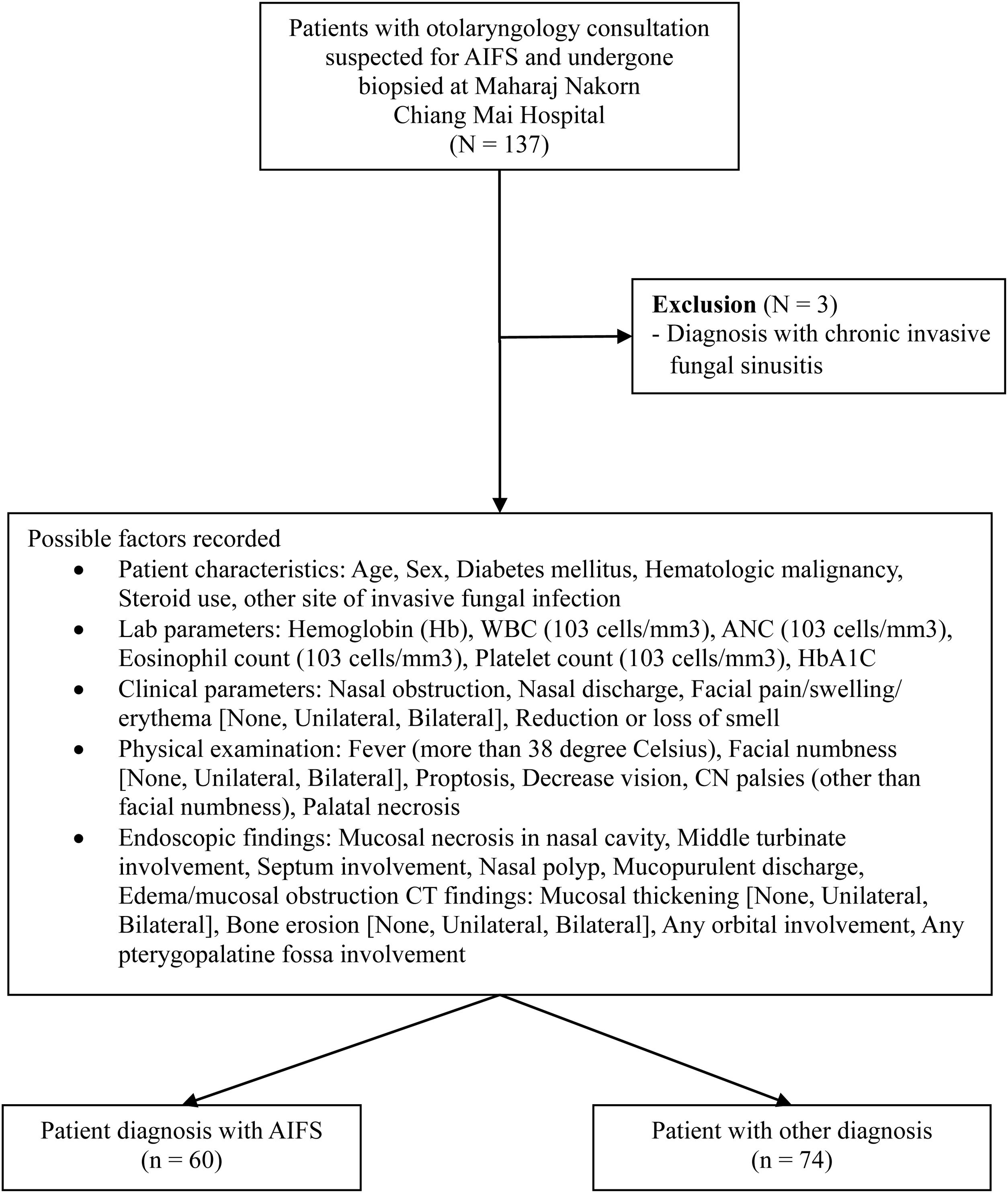
MethodsA retrospective analysis was conducted on 134 adult patients who underwent biopsies for suspected AIFS at a tertiary referral center between January 2009 and January 2024. Patients diagnosed with chronic invasive fungal sinusitis were excluded. Among the patients, 60 cases (44.8%) were biopsy-confirmed AIFS. Key variables analyzed included demographic data, comorbidities, clinical signs, endoscopic findings, laboratory markers, and imaging findings. Backward stepwise and multivariable logistic regression analyses were used to identify independent predictors.
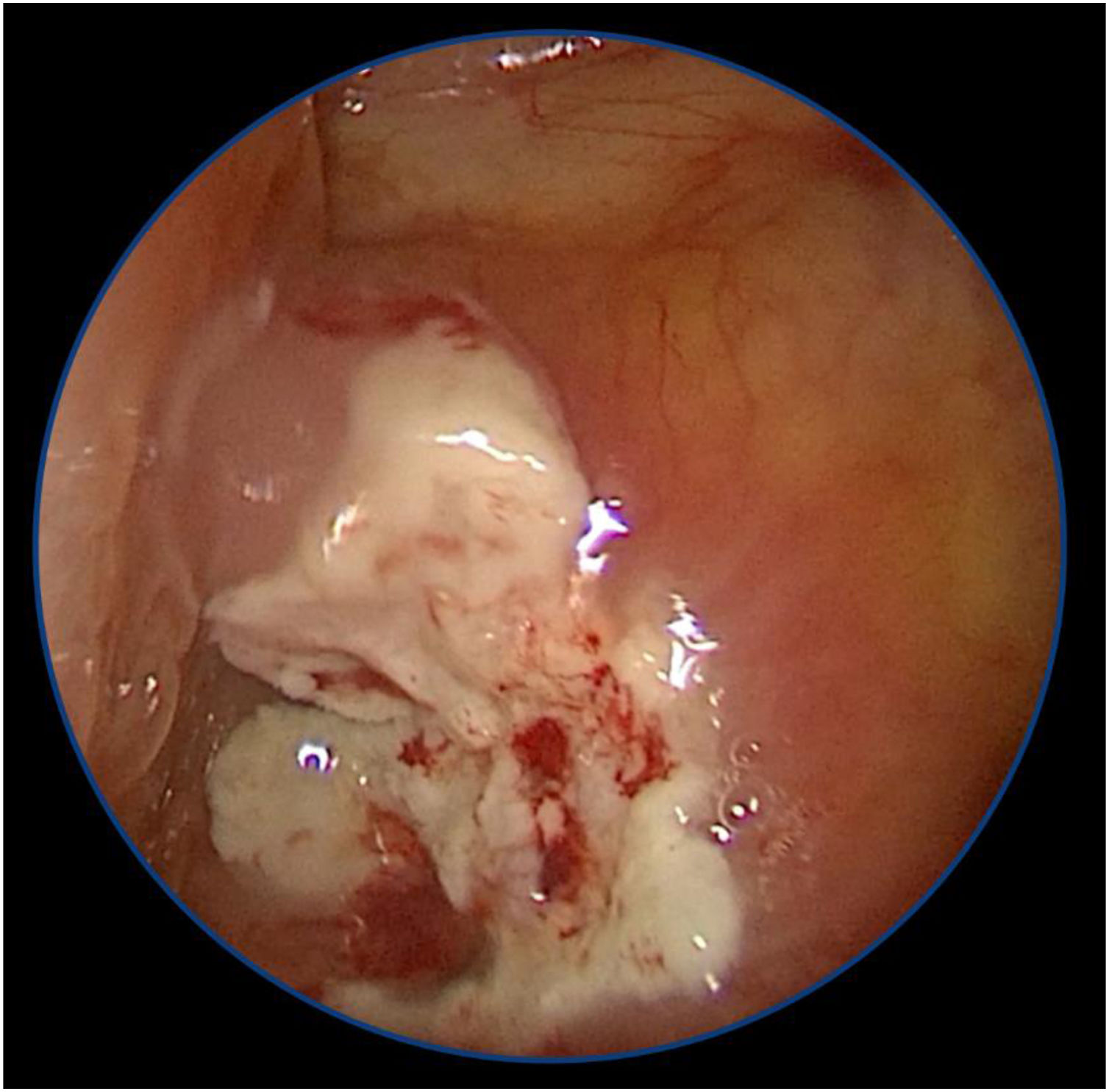
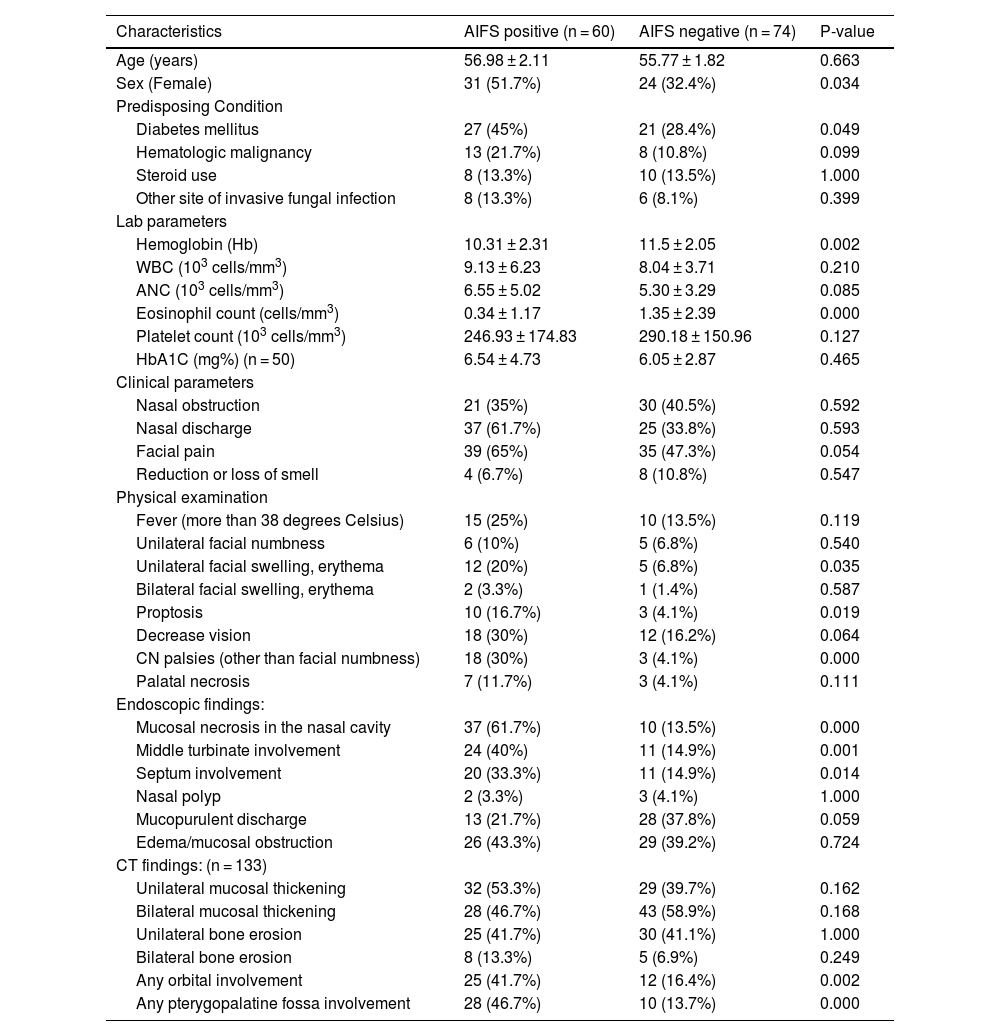
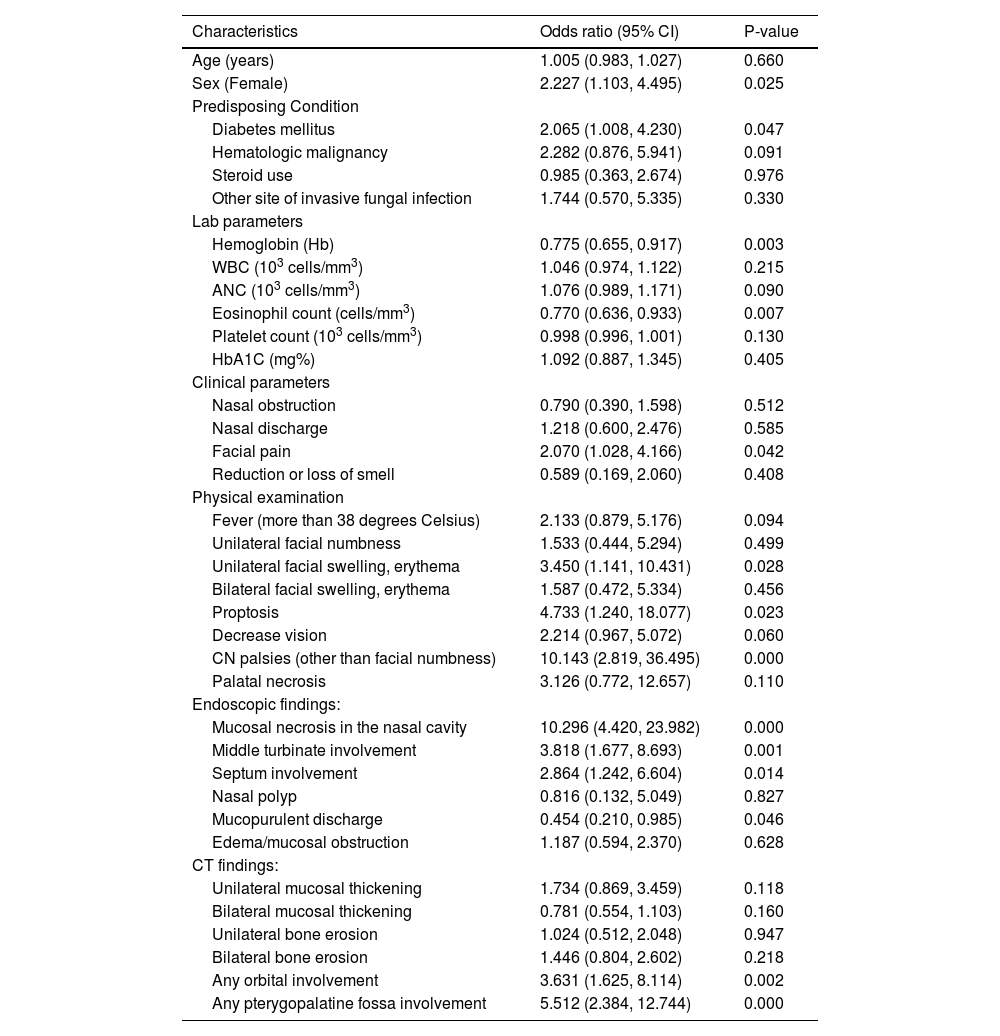
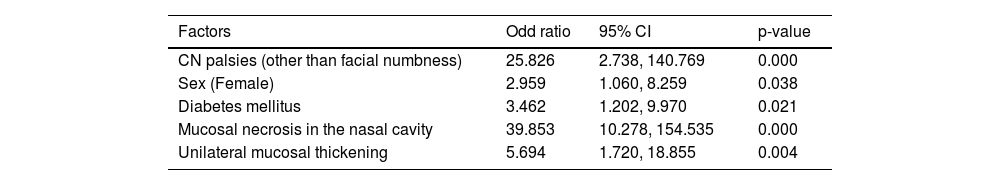
ResultsOf 36 clinical variables initially assessed, stepwise regression identified 5 significant variables for multivariable analysis. Mucosal necrosis in the nasal cavity (OR 39.853; 95% CI 10.278–154.535; p = 0.000) and cranial nerve palsies (OR 25.826; 95% CI 2.738–140.769; p = 0.000) were the strongest predictors. Other significant factors included unilateral mucosal thickening (OR 5.694; 95% CI 1.720–18.855; p = 0.004), diabetes mellitus (OR 3.462; 95% CI 1.202–9.970; p = 0.021), and female sex (OR 2.959; 95% CI 1.060–8.259; p = 0.038).
ConclusionCranial nerve palsies and mucosal necrosis in the nasal cavity are strong predictors of biopsy-confirmed AIFS, highlighting the importance of these clinical signs in early diagnosis.
La Sinusitis Fúngica Invasiva Aguda (SFIA) es una infección agresiva con una morbilidad y mortalidad significativas. El diagnóstico temprano y preciso es crucial, pero su presentación clínica inespecífica a menudo dificulta la detección oportuna. Este estudio busca identificar predictores clínicos, de laboratorio y radiológicos asociados con la SFIA confirmada por biopsia en pacientes con sospecha de la enfermedad.
MétodosSe realizó un análisis retrospectivo de 134 pacientes adultos sometidos a biopsias por sospecha de SFIA en un centro de referencia terciario entre enero de 2009 y enero de 2024. Se excluyó a los pacientes con diagnóstico de sinusitis fúngica invasiva crónica. De estos pacientes, 60 casos (44,8%) fueron SFIA confirmados por biopsia. Las variables clave analizadas incluyeron datos demográficos, comorbilidades, signos clínicos, hallazgos endoscópicos, marcadores de laboratorio y hallazgos de imagen. Se utilizaron análisis de regresión logística escalonada hacia atrás y multivariable para identificar predictores independientes.
ResultadosDe las 36 variables clínicas evaluadas inicialmente, la regresión escalonada identificó 5 variables significativas para el análisis multivariable. La necrosis de la mucosa nasal (OR: 39,853; IC del 95 %: 10,278−154,535; p = 0,000) y las parálisis de pares craneales (OR: 25,826; IC del 95 %: 2,738−140,769; p = 0,000) fueron los predictores más sólidos. Otros factores significativos incluyeron engrosamiento mucoso unilateral (OR: 5,694; IC del 95 %: 1,720−18,855; p = 0,004), diabetes mellitus (OR: 3,462; IC del 95 %: 1,202−9,970; p = 0,021) y sexo femenino (OR: 2,959; IC del 95 %: 1,060−8,259; p = 0,038).
ConclusiónLas parálisis de pares craneales y la necrosis mucosa en la cavidad nasal son fuertes predictores de sinusitis fúngica invasiva aguda confirmada por biopsia, lo que resalta la importancia de estos signos clínicos en el diagnóstico precoz.