Hasta época reciente sólo disponíamos del test calórico y del test cinético como pruebas fundamentales para el conocimiento de la función vestibular, los cuales sólo aportan información sobre el canal semicircular externo y el nervio vestibular superior. En los últimos años, ha comenzado a desarrollarse el estudio del potencial vestibular miogénico evocado, que permite valorar el sáculo y el nervio vestibular inferior. Nuestro objetivo es, a partir del estudio de los resultados del test calórico y del potencial vestibular miogénico evocado en pacientes con neuritis vestibular, diferenciar si la afectación es del nervio vestibular superior, inferior o de ambos.
Material y métodosEstudio retrospectivo de 9 pacientes ingresados en un hospital terciario, con diagnóstico de neuritis vestibular. Les practicamos estudio con anamnesis, exploración clínica otoneurológica, test calórico y potencial vestibular miogénico evocado. También se estudió la evolución clínica después del ingreso y la inestabilidad residual.
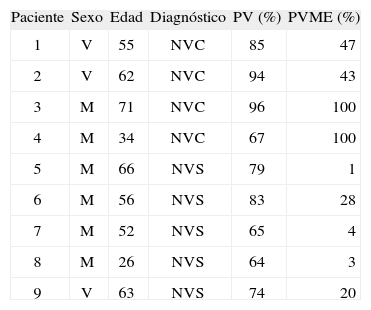
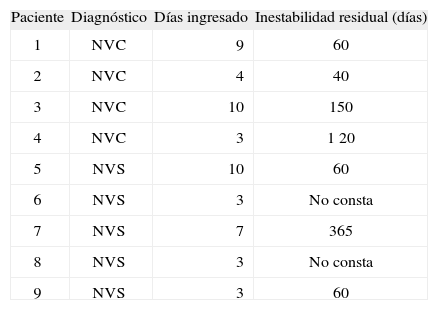
ResultadosHubo una afectación mayor de mujeres (66,6 %). La edad media ± desviación estándar de presentación de la enfermedad fue de 53,8 ± 14 años. El tiempo de estancia hospitalaria ha sido de 5,7 ± 3,2 días. Después de la crisis, presentaron inestabilidad durante 122 ± 114 días. Se diagnosticaron 4 casos de neuritis vestibular completa y 5 de neuritis vestibular superior. La latencia de la onda p13 fue normal en todos los casos. No hay diferencias en el tiempo de estancia hospitalaria, ni en la inestabilidad residual entre los grupos.
ConclusionesActualmente, con el potencial vestibular miogénico evocado, es posible profundizar en el estudio de la neuritis vestibular. Es mucho más frecuente la neuritis vestibular completa y la neuritis vestibular superior que la neuritis vestibular inferior. El comportamiento clínico es similar en los subtipos encontrados.
Until recently, the only tests available to provide information about vestibular function were caloric and kinetic tests, which only give us information about the external semicircular canal and the superior vestibular nerve. In recent years the development of vestibular evoked myogenic potentials has allowed us to assess the saccule and the inferior vestibular nerve.
Our aim is, by studying the caloric test results as well as the vestibular evoked myogenic potentials in patients with Vestibular Neuritis, to determine whether they have involvement of the superior, inferior or both vestibular nerves.
Material and methodsRetrospective study of 9 patients with Vestibular Neuritis admitted to a tertiary care hospital. We studied them by means of anamnesis, otoneurological clinical examination, caloric test and vestibular evoked myogenic potentials. Their clinical progress after admission and any residual instability were also studied.
ResultsWomen were more affected (66.6 %) than males. The mean age for presentation of the disease was 53.8 ± 14.0 years. Hospital stays lasted for 5.7 ± 3.2 days. After their crises, they suffered from instability for 122 ± 114 days. Four cases were diagnosed as Complete Vestibular Neuritis and five as Superior Vestibular Neuritis. P13 wave latency was normal in all cases. There were no differences between the groups in terms of the length of hospital stay nor residual instability.
ConclusionsNowadays, vestibular evoked myogenic potentials make it possible to advance further in the study of Vestibular Neuritis. Complete and superior vestibular neuritis are much more frequent than inferior vestibular neuritis. Clinical behaviour is similar in the sub-types found.