The development of sexual dysfunction (SD) in dialysis patients is multifactorial. We aimed to evaluate whether adequate dialysis had an effect on the development of SD in male and female patients undergoing dialysis due to end stage renal disease. Anxiety, depression, health-related quality of life and the other risk factors related to dialysis were also evaluated in terms of SD.
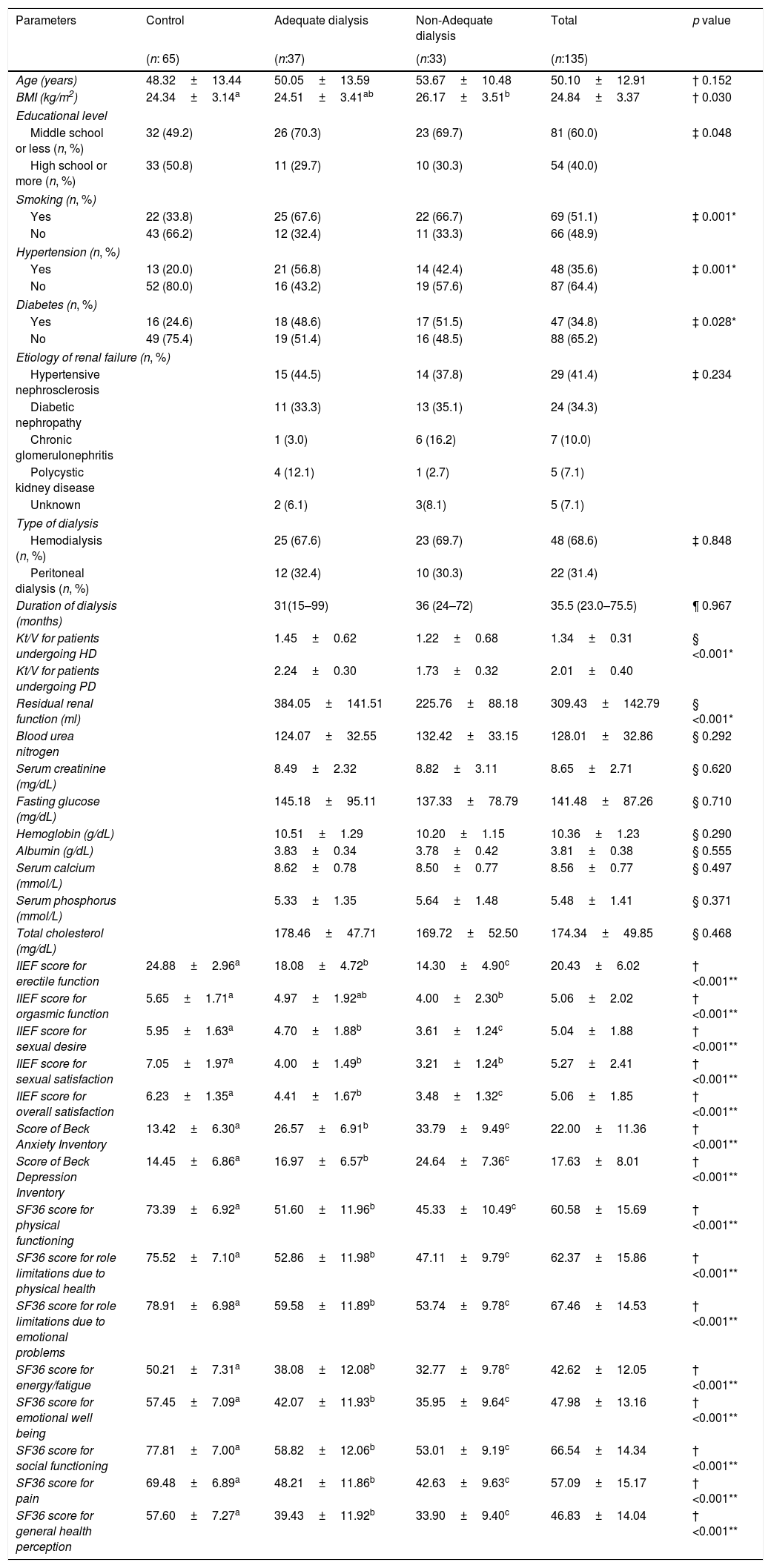
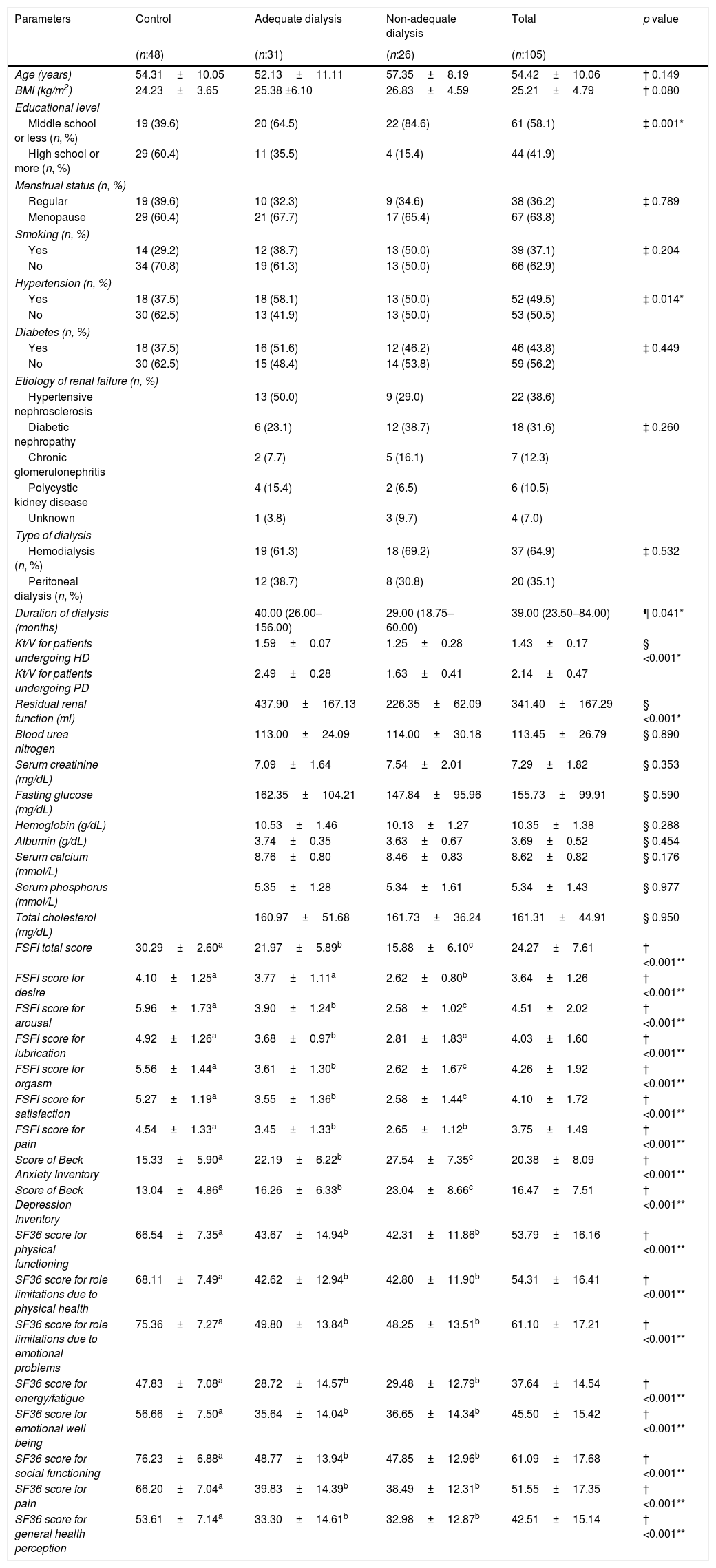
MethodsSeventy men and 57 women undergoing haemodialysis (HD) or peritoneal dialysis (PD) and 65 healthy male volunteers and 48 healthy female volunteers, age-matched, were included in the study. The International Index of Erectile Function, Female Sexual Function Index, Beck Depression Inventory, Beck Anxiety Inventory and The Short Form-36 Health Survey were applied to all participants. The cut off value of Kt/V was determined as 1.3 for HD and 1.7 for PD to assess dialysis adequacy. Per gender, all the participants were divided into three groups as control, adequate dialysis and non-adequate dialysis.
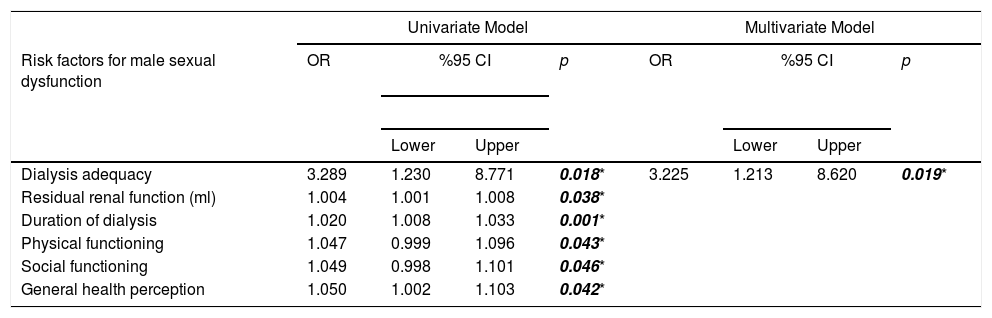
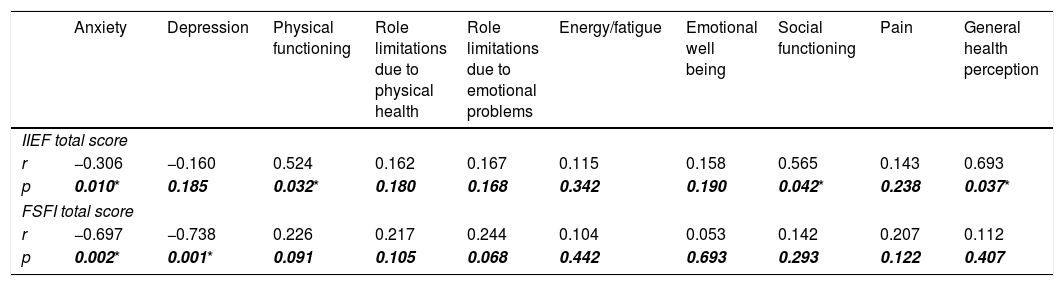
ResultsDialysis adequacy [OR: 3.225, 95%CI (1.213–8.620), p=.019] was found as a more decisive factor for male SD, while dialysis adequacy [OR: 3.015, 95%CI (.991–7.250), p=.041] and depression [OR: 4.280, 95%CI (1.705–10.747), p=.002] were more significant for female SD. In addition, a strong relationship was found between male SD and physical functioning (r: .524, p=.032), social functioning (r: .565, p=.042), general health (r: .693, p=.037) perception, while female SD was found to be strongly associated with anxiety (r: −.697, p=.002) and depression (r: −.738, p=.001).
DiscussionDialysis adequacy was found to be the most important factor in reducing SD. Non-adequate dialysis resulted in worse sexual function, higher levels of depression and anxiety. Its negative effect on health-related quality of life was only seen in men.
El desarrollo de la disfunción sexual (DS) en pacientes en diálisis es multifactorial. El objetivo fue evaluar si la diálisis adecuada tuvo un efecto sobre el desarrollo de la DS en los pacientes masculinos y femeninos sometidos a diálisis debido a enfermedad renal en etapa terminal. La ansiedad, la depresión, la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud y los otros factores de riesgo relacionados con la diálisis también se evaluaron en términos de DS.
MétodosSetenta varones y 57 mujeres sometidos a hemodiálisis (HD) o diálisis peritoneal (PD) y 65 voluntarios varones sanos y 48 voluntarias sanas se incluyeron para estudiar. Se aplicaron a todos los participantes el índice internacional de la función eréctil, el índice de la función sexual femenina, el inventario de depresión de Beck, el inventario de ansiedad de Beck y el formulario breve-36 encuesta de salud. El valor de corte de Kt/V se determinó como 1,3 para HD y 1,7 para PD para evaluar la adecuación de la diálisis. Para cada género, todos los participantes se dividieron en 3 grupos como control, diálisis adecuada y diálisis no adecuada.
ResultadosAdecuación de la diálisis (OR: 3,225; IC 95%: 1,213-8,620; p=0,019) se encontró un factor más decisivo para la DS masculina, mientras que la adecuación de la diálisis (OR: 3,015; IC 95%: 0,991-7,250; p=0,041) y depresión (OR: 4,280; IC 95%: 1,705-10,747; p=0,002) fueron más significativas para las mujeres con DS. Además, se encontró una fuerte relación entre la DS de los varones y el funcionamiento físico (r: 0,524; p=0,032), el funcionamiento social (r: 0,565; p=0,042), la percepción general de salud (r: 0,693; p=0,037), mientras que se descubrió que la DS femenina estaba fuertemente asociada con la ansiedad (r: −0,697; p=0,002) y la depresión (r: −0,738; p=0,001).
DiscusiónLa adecuación de la diálisis se encontró como el factor más importante para reducir la DS. La diálisis no adecuada resultó en una función sexual peor, niveles más altos de depresión y de ansiedad. Su efecto negativo en la calidad de vida relacionada con la salud solo se observó en los hombres.