The proposal and implementation of a computational framework for the quantification of structural renal damage from 99mTc-dimercaptosuccinic acid (DMSA) scans.
The aim of this work is to propose, implement, and validate a computational framework for the quantification of structural renal damage from DMSA scans and in an observer-independent manner.
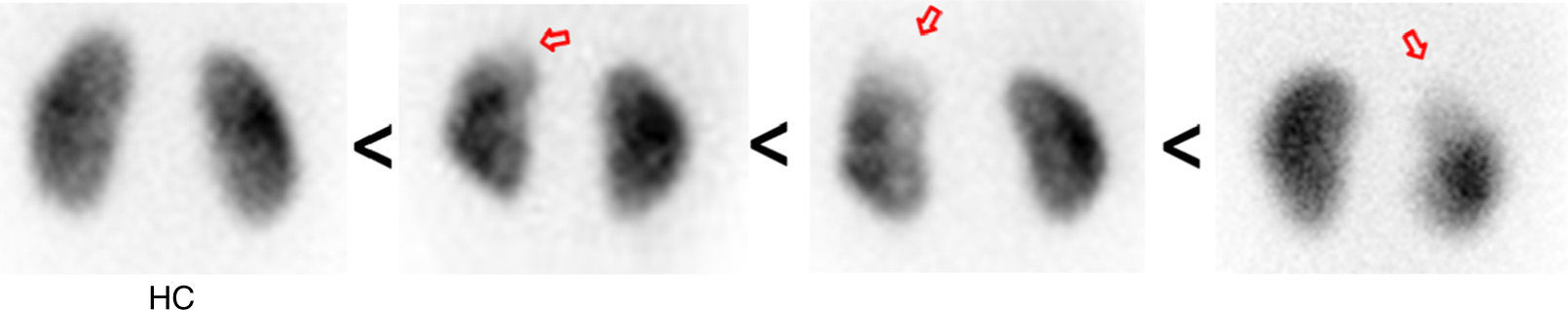
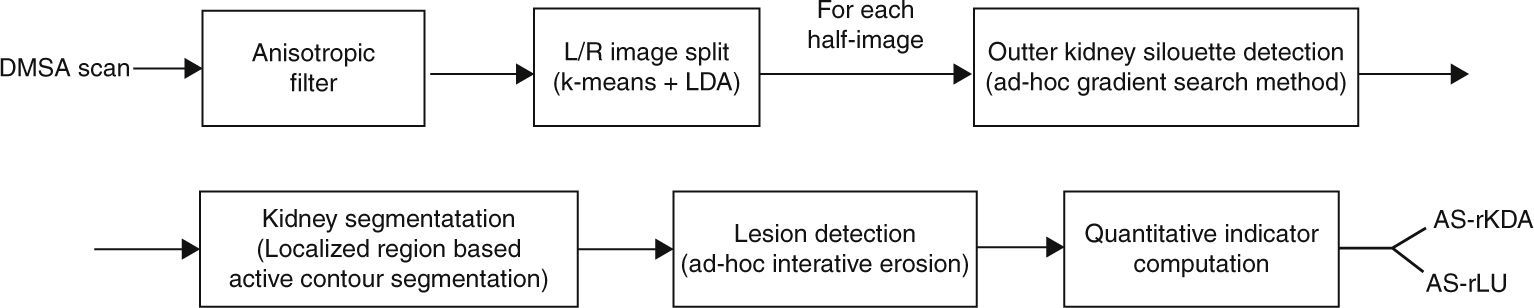
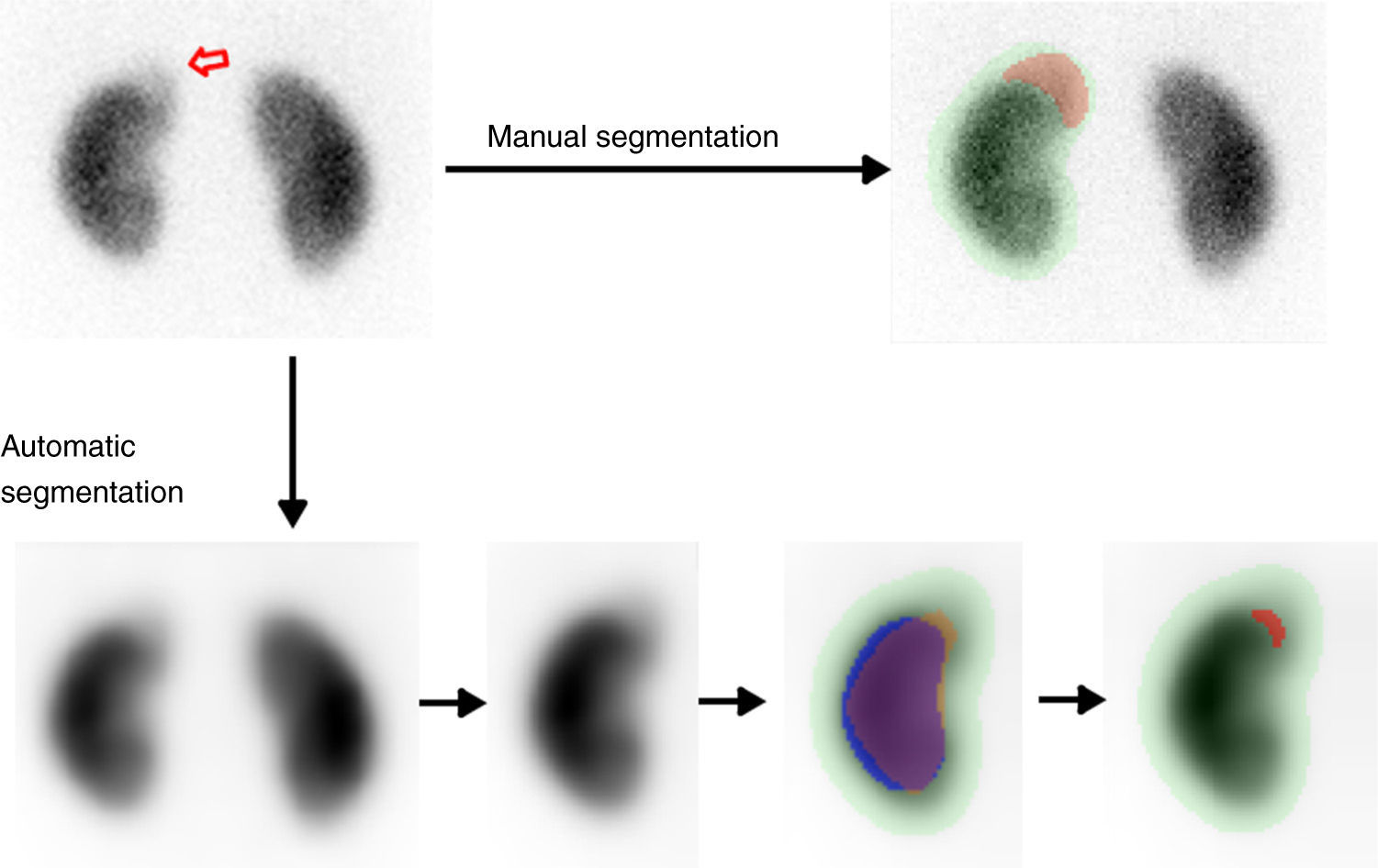
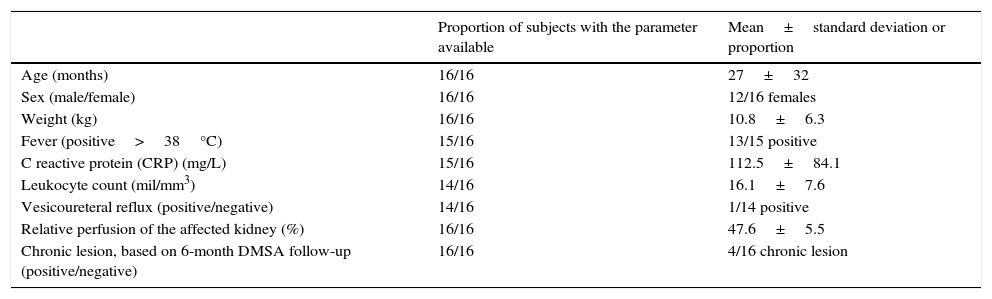
Materials and methodsFrom a set of 16 pediatric DMSA-positive scans and 16 matched controls and using both expert-guided and automatic approaches, a set of image-derived quantitative indicators was computed based on the relative size, intensity and histogram distribution of the lesion. A correlation analysis was conducted in order to investigate the association of these indicators with other clinical data of interest in this scenario, including C-reactive protein (CRP), white cell count, vesicoureteral reflux, fever, relative perfusion, and the presence of renal sequelae in a 6-month follow-up DMSA scan.
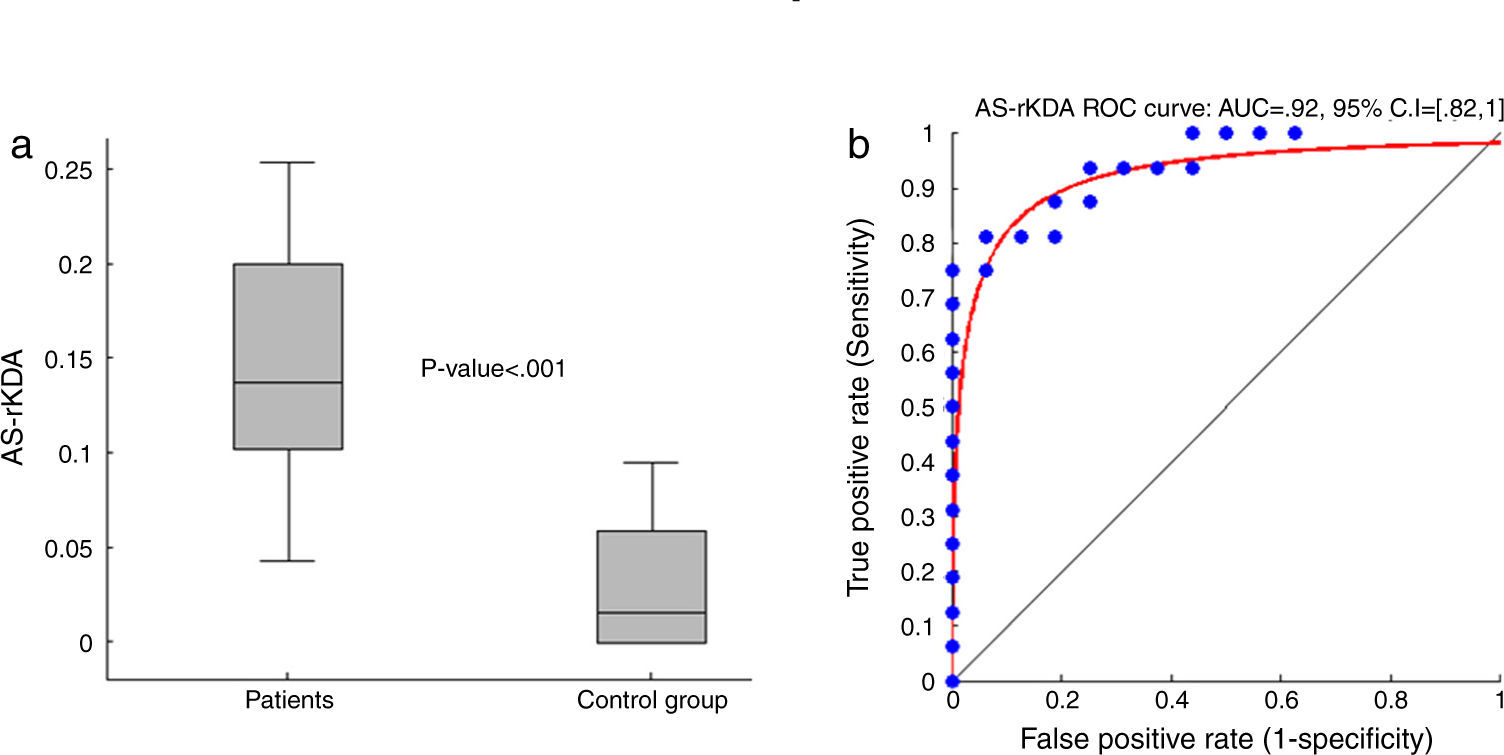
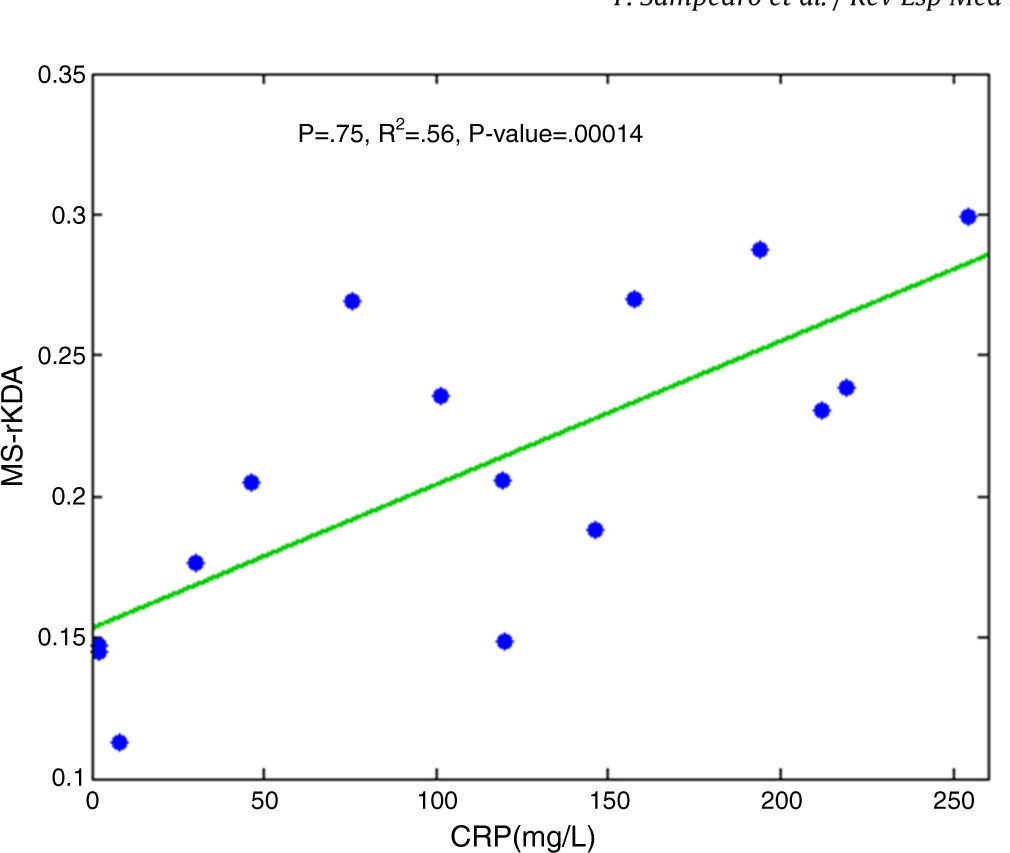
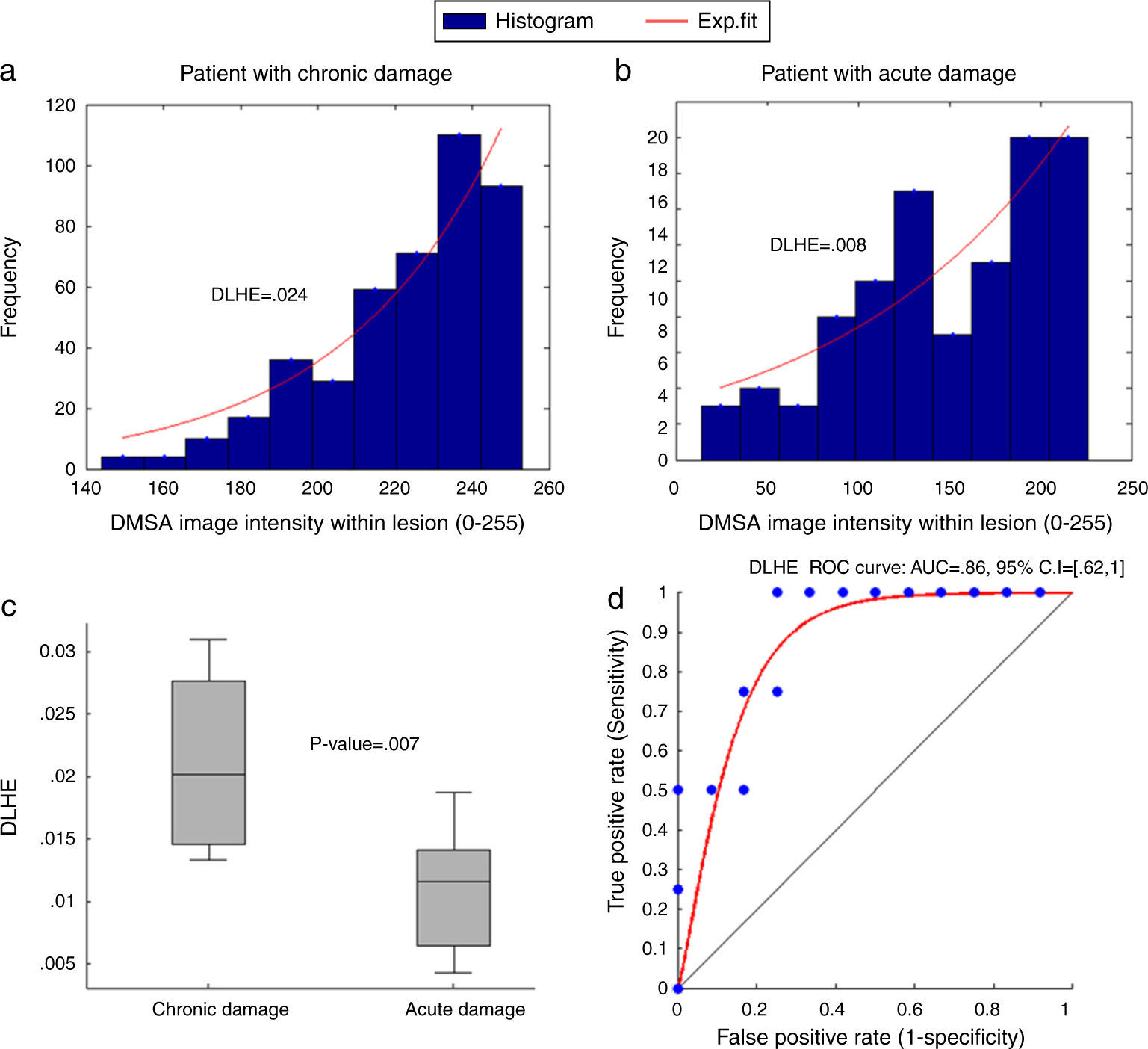
ResultsA fully automatic lesion detection and segmentation system was able to successfully classify DMSA-positive from negative scans (AUC=0.92, sensitivity=81% and specificity=94%). The image-computed relative size of the lesion correlated with the presence of fever and CRP levels (p<0.05), and a measurement derived from the distribution histogram of the lesion obtained significant performance results in the detection of permanent renal damage (AUC=0.86, sensitivity=100% and specificity=75%).
ConclusionsThe proposal and implementation of a computational framework for the quantification of structural renal damage from DMSA scans showed a promising potential to complement visual diagnosis and non-imaging indicators.
En el presente trabajo se propone, implementa y valida un entorno computacional de cuantificación de imágenes con 99mTc-ácido dimercaptosuccínico (DMSA) con el objetivo de obtener indicadores cuantitativos del daño renal subyacente. Estos indicadores se validan en un contexto de imágenes DMSA pediátricas, dada su relevancia en el diagnóstico de pielonefritis aguda y cicatrices renales.
Materiales y métodosPartiendo de un conjunto de 16 imágenes DMSA positivas para daño renal y 16 controles apareados por edad y sexo, se proponen y calculan una serie de indicadores cuantitativos basados en el área relativa lesionada y la distribución de su histograma. Se implementan aproximaciones manuales y automáticas para dicho cómputo. Los indicadores obtenidos se correlacionan con otras variables clínicas de interés en este contexto, como la proteína C reactiva, la cuenta leucocitaria, el reflujo vesicouretral, la fiebre, la perfusión relativa, y la presencia de secuelas renales en la imagen DMSA a los 6 meses de seguimiento.
ResultadosEl sistema implementado de detección y cuantificación de lesiones renales obtuvo un rendimiento significativo discriminando las imágenes DMSA positivas de las negativas (AUC=0,92, sensibilidad=81% y especificidad=94%). El indicador de área relativa de la lesión correlacionó con los niveles de proteína C reactiva y la presencia de fiebre (p<0,05). Finalmente, un indicador derivado de las propiedades del histograma de la lesión obtuvo un rendimiento significativo en la detección de la presencia de secuelas renales (AUC=0,86, sensibilidad=100% y especificidad=75%).
ConclusionesLa propuesta e implementación de un entorno computacional para la obtención de indicadores cuantitativos a partir de imágenes DMSA muestra un potencial prometedor para complementar el diagnóstico visual.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)