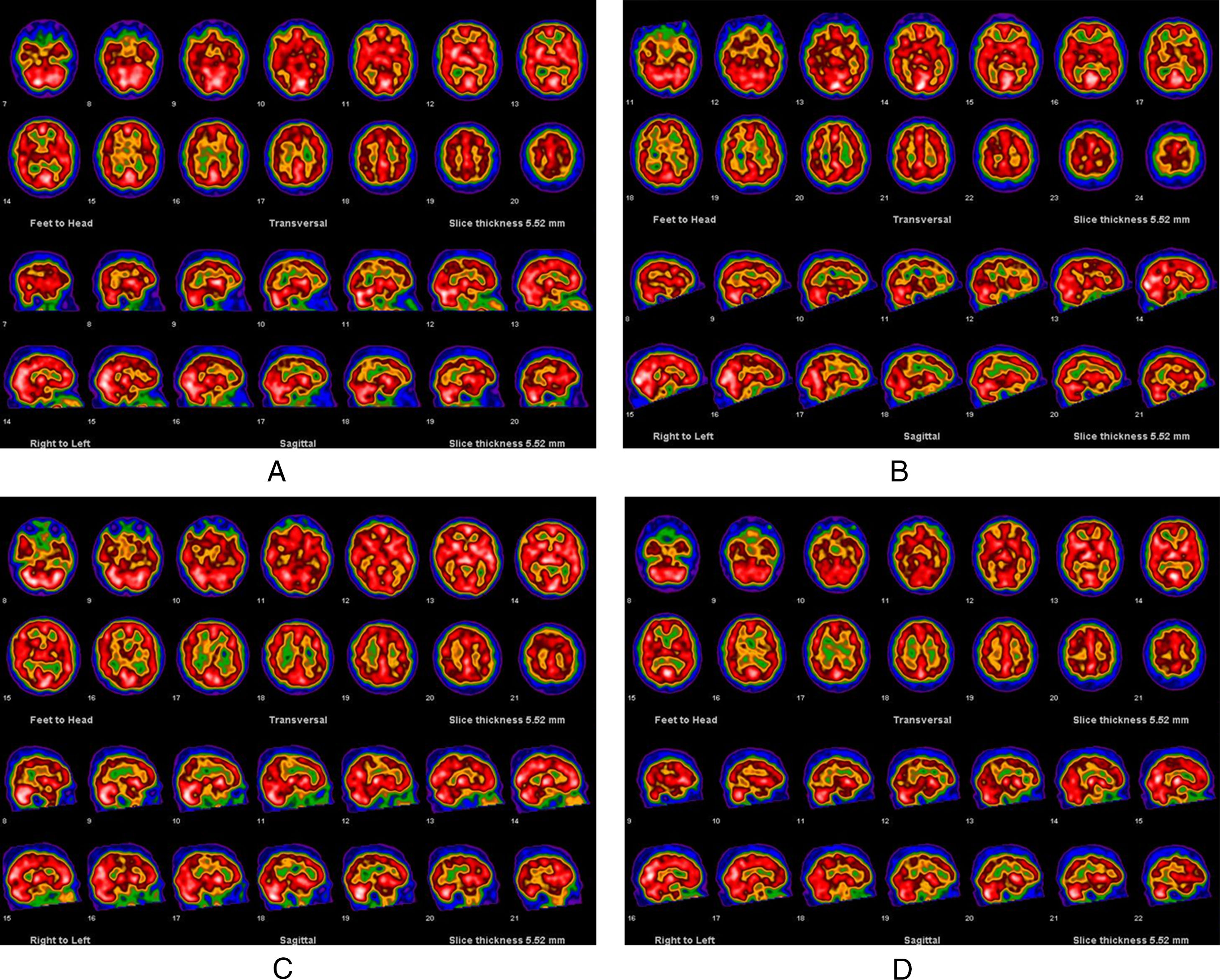
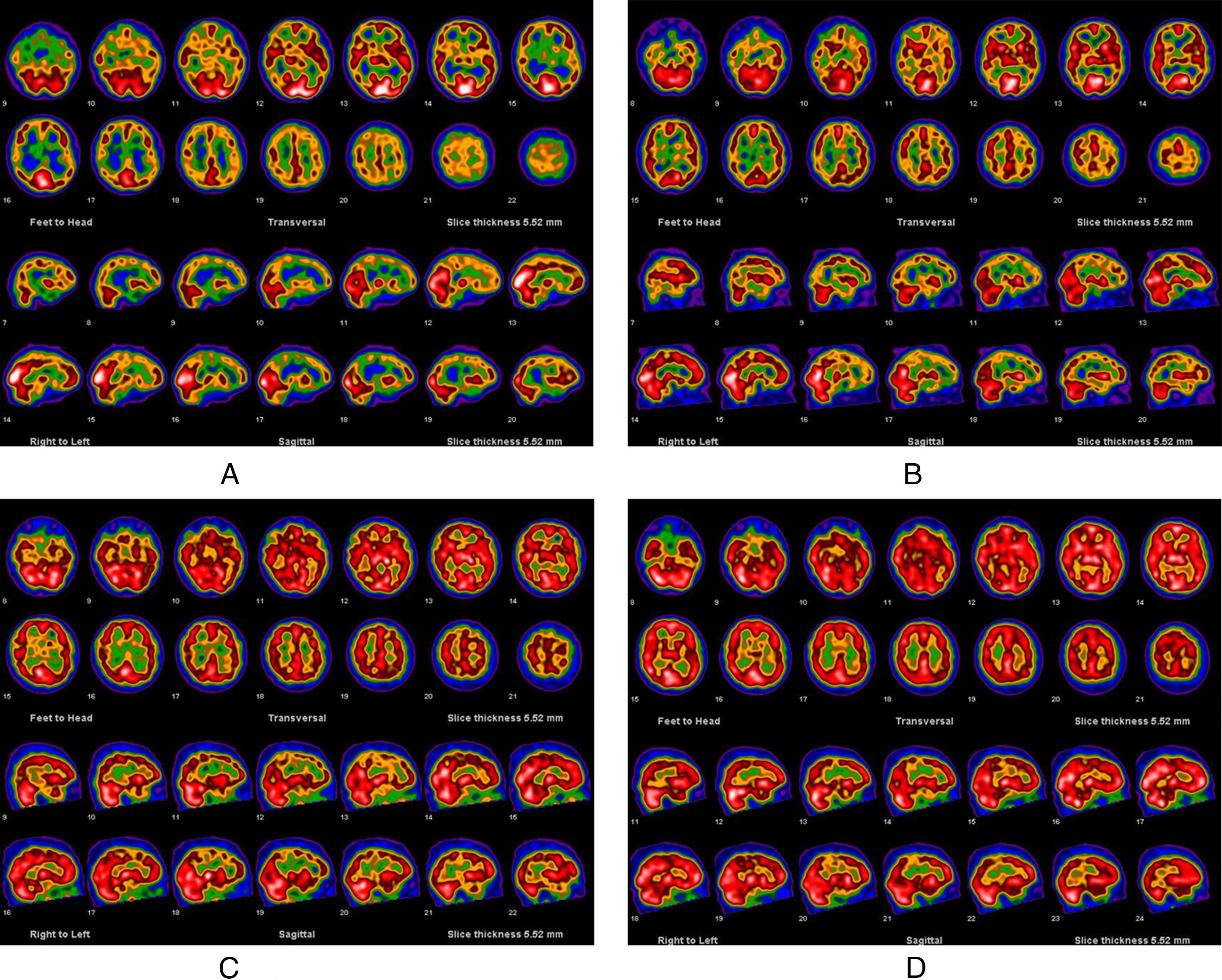
The central nervous system (CNS) may be involved in a variety of inflammatory diseases of the blood vessels, generally known as vasculitis. The clinical diagnosis of such involvement in early stages is difficult, since a mild cognitive impairment can be the only symptom. It was hypothesized that brain-perfusion SPECT would be able to reveal CNS involvement and to monitor the course of the disease. The purpose of this study was assess if and when an improvement of cerebral perfusion can be registered by SPECT during the follow-up of these diseases.
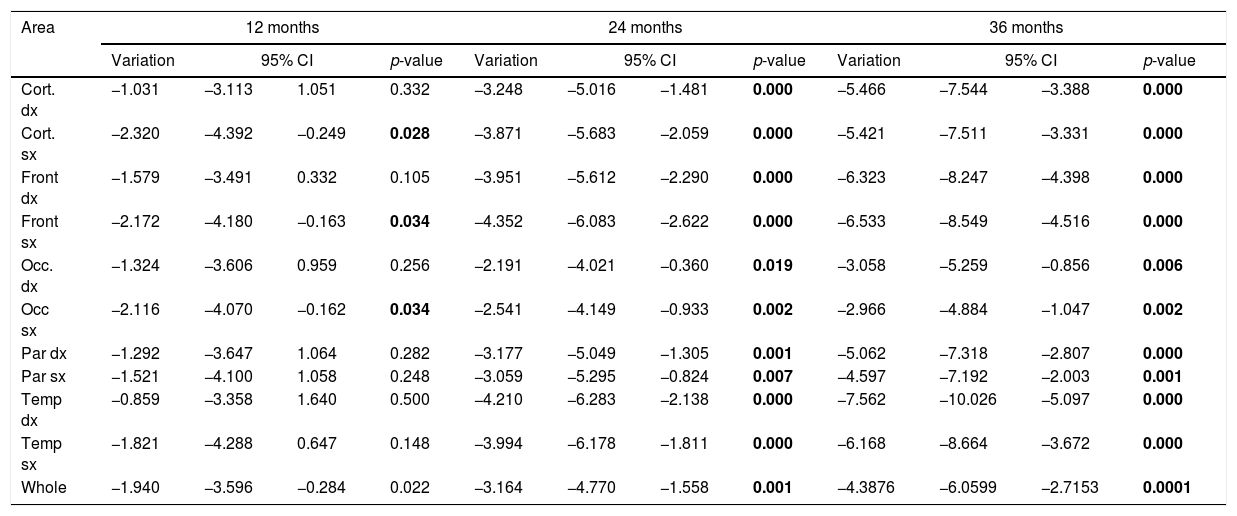
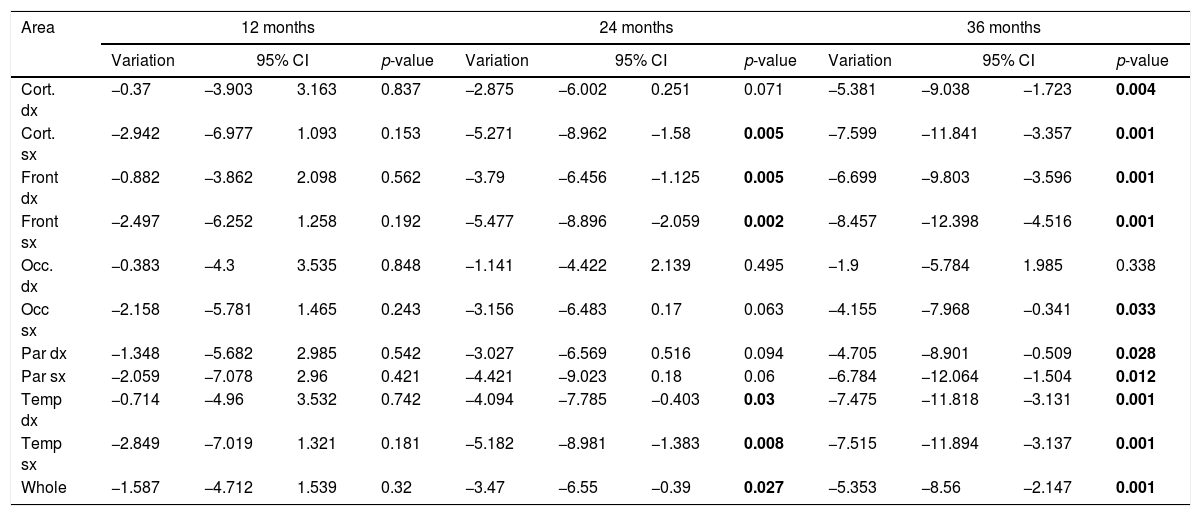
Material and methodsEighteen patients affected by Systemic Lupus Erythematosus (SLE), 22 by undifferentiated vasculitis (UV), 5 by Behcet's disease (BD) and 5 by primary Sjogren's Syndrome (pSS) were enrolled in this prospective study. A 99mTc-HMPAO brain perfusion SPECT was performed before the treatment and was repeated during the follow-up at different time intervals. Image analysis was performed on 10 cerebral areas using a specific software.
ResultsIn the SLE patients, no significant improvement of brain perfusion was found. On the contrary, in the UV the cerebral uptake of the tracer significantly improved from the twenty-fourth month (18/22 patients). Patients with BD showed an improvement of scintigraphic findings (5/5 patients), while a similar result was obtained only in 2 of the patients with pSS.
ConclusionsIn conclusion, brain SPECT seems to be able to monitor the disease in UV, indicating the moment when an improvement of the cerebral perfusion is achieved. In SLE patients this scintigraphic technique did not show a significant improvement in CNS perfusion.
El sistema nervioso central (SNC) puede estar afectado en una variedad de enfermedades inflamatorias de los vasos sanguíneos, generalmente conocidas como vasculitis. El diagnóstico clínico de dicha afectación en etapas tempranas es difícil, ya que un leve deterioro cognitivo puede ser el único síntoma. Se planteó la hipótesis de que la SPECT de perfusion cerebral podría mostrar la afectación del SNC y podría servir para controlar el curso de la enfermedad. El propósito de este estudio fue evaluar si y cuándo una mejora de la perfusión cerebral puede ser registrada por SPECT durante el seguimiento de estas enfermedades.
Material y métodosDieciocho pacientes afectados por Lupus eritematoso sistémico (LES), 22 por vasculitis indiferenciada (UV), 5 por la enfermedad de Behcet (BD) y 5 por el síndrome de Sjogren Primario (pSS) se incluyeron en este estudio prospectivo. Se realizó una SPECT de perfusión cerebral con 99mTc-HMPAO antes del tratamiento, y se repitió durante el seguimiento a diferentes intervalos de tiempo. El análisis de imagen se realizó en 10 áreas cerebrales utilizando un software específico.
ResultadosEn los pacientes con LES no se encontró una mejora significativa de la perfusión cerebral. Por el contrario, en la UV la captación cerebral del trazador comenzó a mejorar significativamente desde el vigésimo cuarto mes (18/22 pacientes). Los pacientes con BD mostraron una mejora de los hallazgos gammagráficos (5/5 pacientes), mientras que sólo se obtuvo un resultado similar en dos de los pacientes con pSS.
ConclusionesEn conclusión, el SPECT cerebral parece ser capaz de monitorizar la enfermedad en UV, evaluando cuándo se puede registrar una mejoría de la perfusión cerebral. En los pacientes con LES, esta técnica gammagráfica no ha encontrado una mejoría significativa en la perfusión del SNC.
Article
If you experience access problems, you can contact the SEMNIM Technical Secretariat by email at secretaria.tecnica@semnim.es or by phone at +34 619 594 780.

Revista Española de Medicina Nuclear e Imagen Molecular (English Edition)