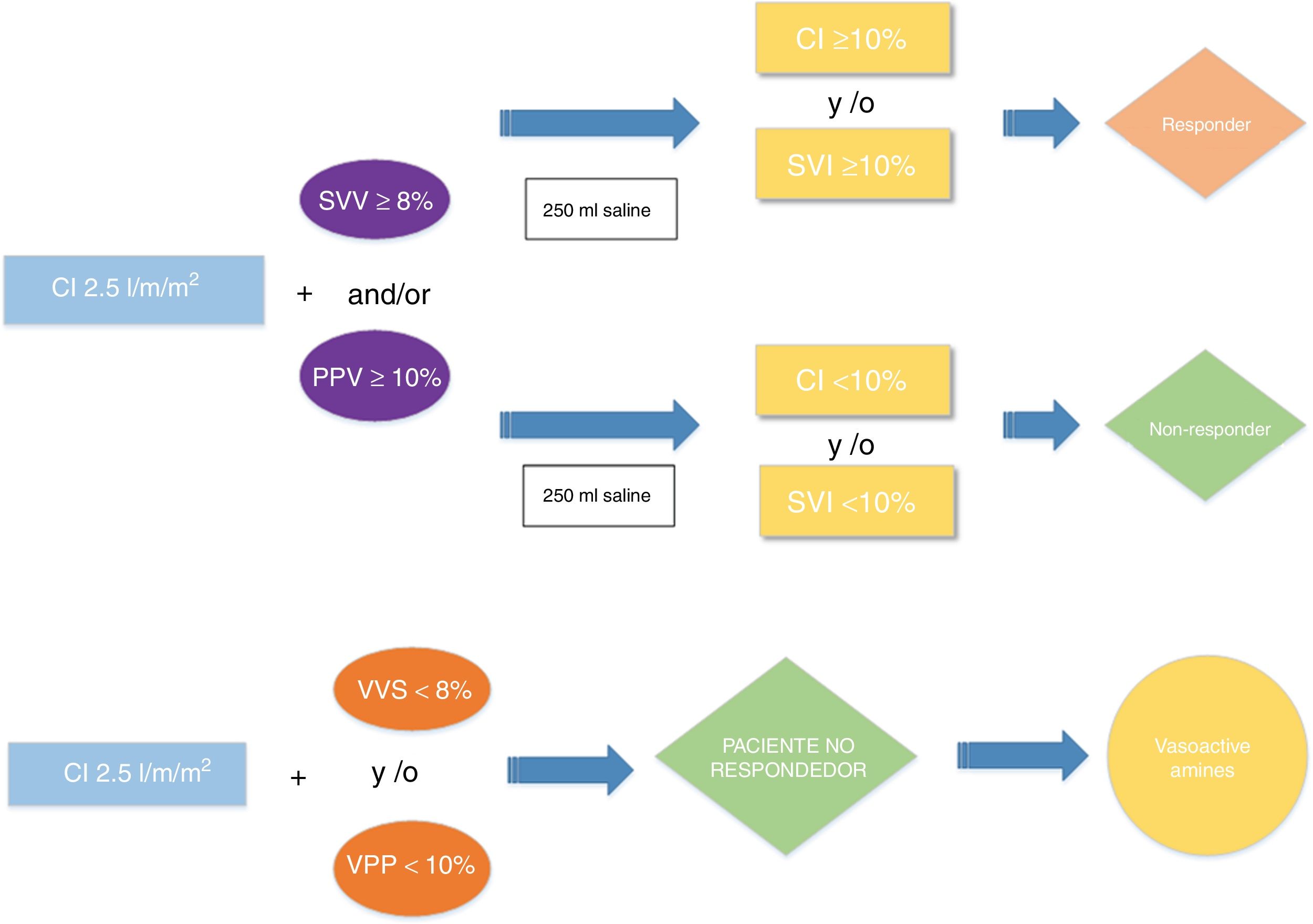
In lung resection surgery, restrictive fluid therapy is recommended due to the risk of acute lung injury. In contrast, this recommendation increases the risk of hypoperfusion. Guided fluid therapy allows individualization of fluid intake. The use of dynamic volume response parameters is not validated during one-lung ventilation. The main objective is the validation of dynamic parameters, stroke volume variation (SVV) and pulse pressure variation (PPV), during lung resection surgery as fluid response predictors, after the administration of 250 ml crystalloid volume loads, if IC < 2.5 ml/min/m2 and if SVV ≥ 8% and/or PPV ≥ 10%.
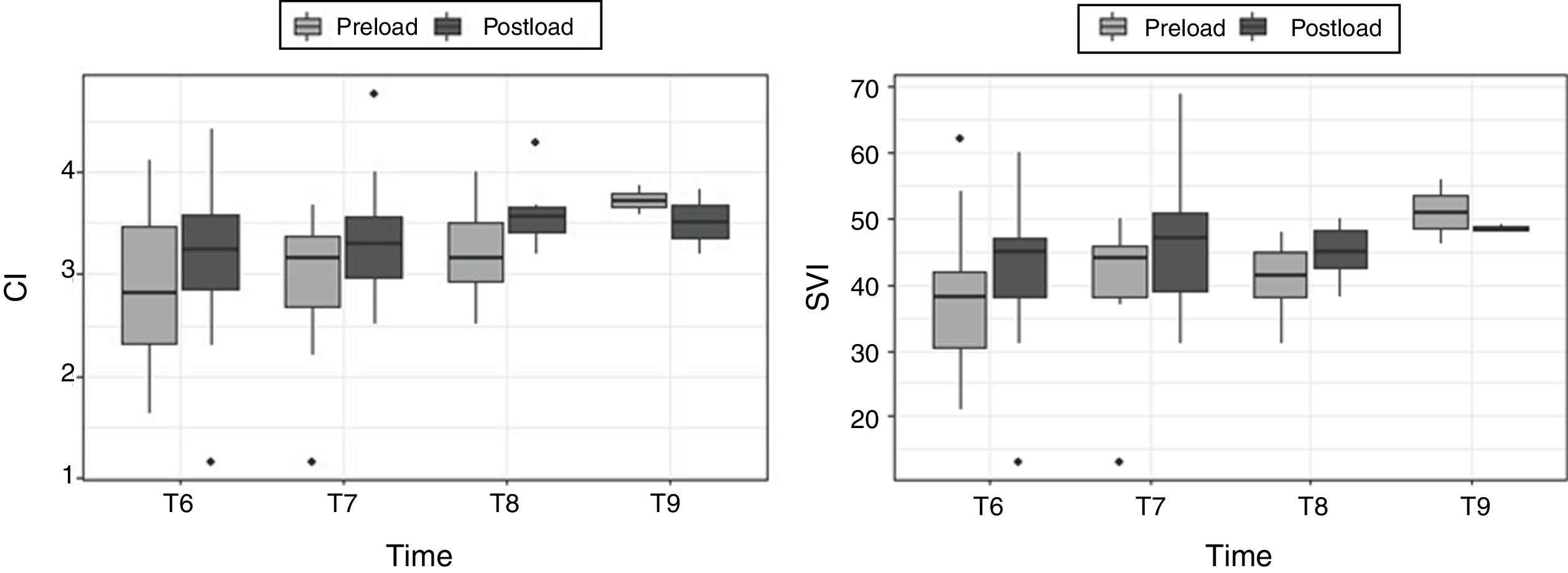
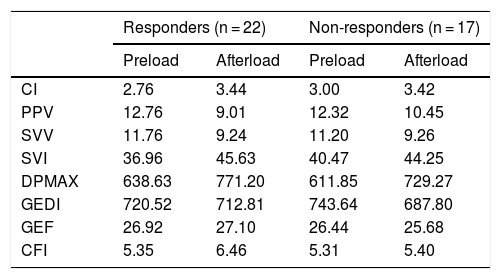
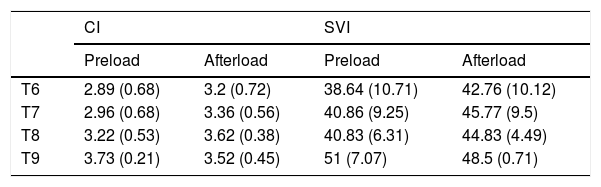
Material and methodsPilot, prospective, observational and single centre study. Twenty-five patients monitored with the PiCCO system were included during open lung resection surgery with the patient in a lateral position, one lung ventilation with tidal volume (TV): 6 ml/kg and open chest. Hemodynamic variables were collected before and after volume loading. The results were classified into two groups: volume responders (increase IC ≥ 10% and/or VSI ≥ 10% after volume loading) and non-responders (no increase or increase IC < 10% and/or VSI < 10% after volume loading). We assess the diagnostic efficacy of SVV and PPV by analyzing the AUC (area under curve) in the ROC curves.
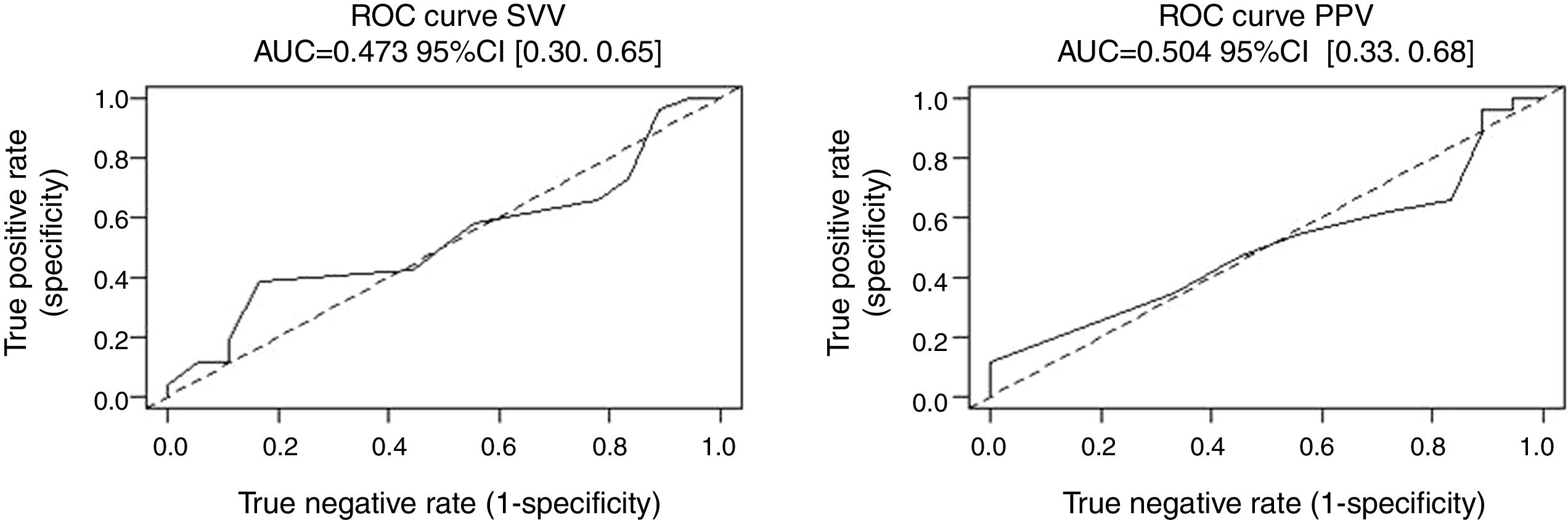
ResultsIn the analysis of ROC curves, SVV and PPV did not reach a discriminative value (AUC SVV: 0.47; AUC PPV: 0.50), despite the decrease in the threshold value of SVV and PPV to initiate an overload of volume during one-lung ventilation, in lateral position and open chest.
ConclusionsThe results obtained show that the values of the dynamic parameters of volume response (SVV ≥ 8% and PPV ≥ 10%) do not discriminate against responders patients and nonresponders during open lung resection surgery.
En cirugía de resección pulmonar, se recomienda la fluidoterapia restrictiva debido al riesgo de lesión pulmonar aguda. Por contra, esta recomendación aumenta el riesgo de hipoperfusión. La terapia guiada por objetivos permite individualizar el aporte de fluidos. El uso de parámetros dinámicos de respuesta a volumen no está validado durante la ventilación unipulmonar. El objetivo principal es la validación de los parámetros dinámicos, variación de volumen sistólico (VVS) y presión de pulso (VPP), durante cirugía de resección pulmonar como predictores de respuesta a fluidos, tras la administración de cargas de volumen de 250 ml de cristaloides, si IC < 2.5 ml/min/m2 y si VVS ≥ 8% y/o VPP ≥ 10%.
Material y MétodosEstudio piloto, prospectivo, observacional y unicéntrico. Se incluyeron 25 pacientes monitorizados con el sistema PiCCO durante la cirugía abierta de resección pulmonar con el paciente en posición de decúbito lateral, ventilación unipulmonar con VC: 6 ml/kg y tórax abierto. Se recogieron variables hemodinámicas antes y después de la carga de volumen. Los resultados se clasificaron en dos grupos: respondedores a volumen (aumento de IC ≥ 10% y/o VSI ≥ 10% tras la carga de volumen) y los no respondedores (no aumento o aumento del IC < 10% y/o VSI < 10% tras la carga de volumen). Evaluamos la eficacia diagnóstica de VVS y VPP mediante el estudio del AUC (área bajo a curva) de las curvas ROC.
ResultadosEn el análisis de curvas ROC, VVS y VPP no alcanzaron un valor discriminativo (AUC VVS: 0,47; AUC VPP: 0,50), a pesar de la disminución del valor umbral de VVS y VPP para iniciar una sobrecarga de volumen durante la ventilación unipulmonar, en decúbito lateral y con el tórax abierto.
ConclusionesLos resultados obtenidos muestran que los valores de los parámetros dinámicos de respuesta a volumen (VVS ≥ 8% y VPP ≥ 10%) no discriminan a los pacientes respondedores y los no respondedores durante la cirugía de resección pulmonar abierta.