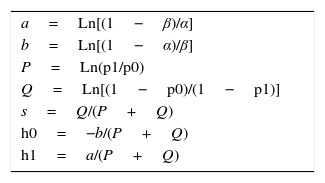Although ultrasound is a basic competence for anaesthesia residents (AR) there is few data available on the learning process. This prospective observational study aims to assess the learning process of ultrasound-guided continuous femoral nerve block and to determine the number of procedures that a resident would need to perform in order to reach proficiency using the cumulative sum (CUSUM) method.
MethodsWe recruited 19 AR without previous experience. Learning curves were constructed using the CUSUM method for ultrasound-guided continuous femoral nerve block considering 2 success criteria: a decrease of pain score>2 in a [0–10] scale after 15min, and time required to perform it.
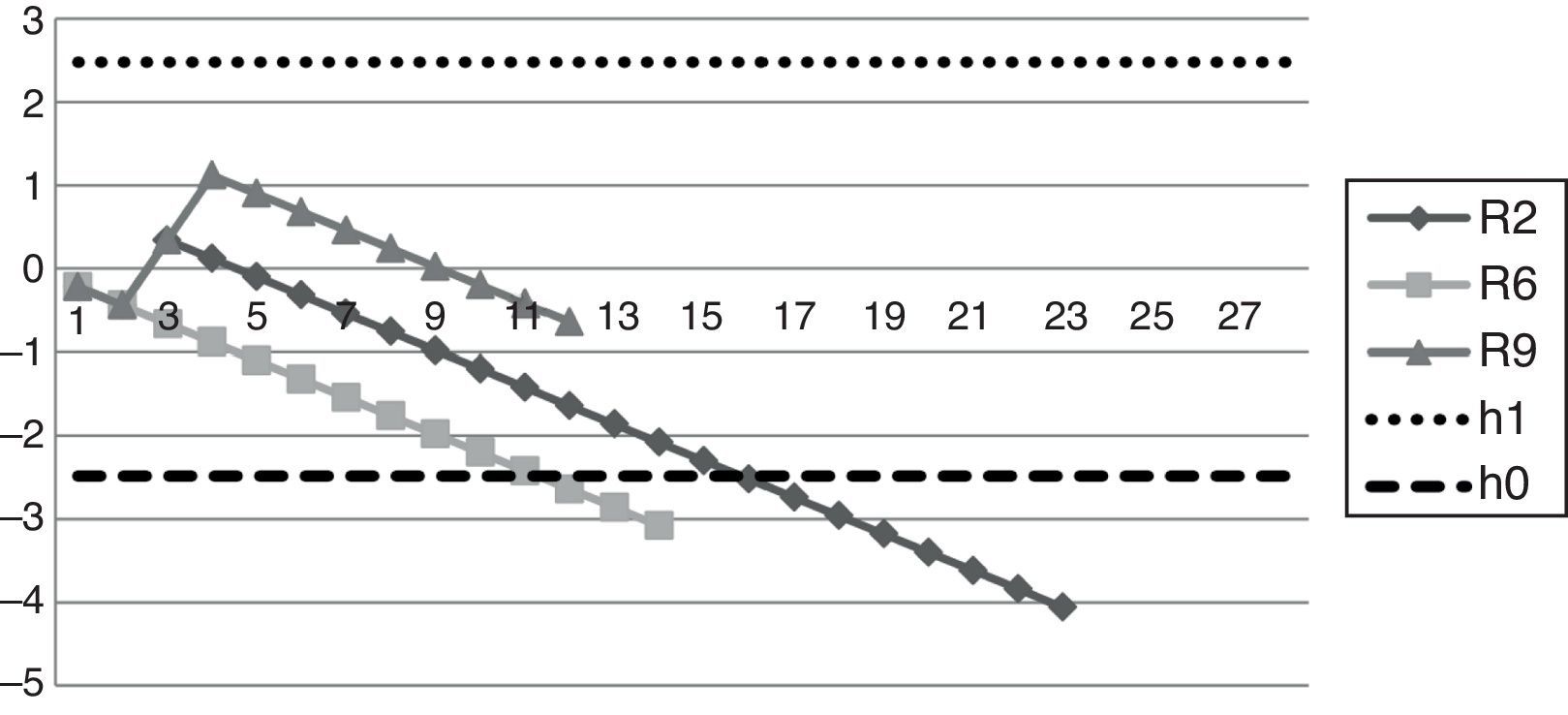
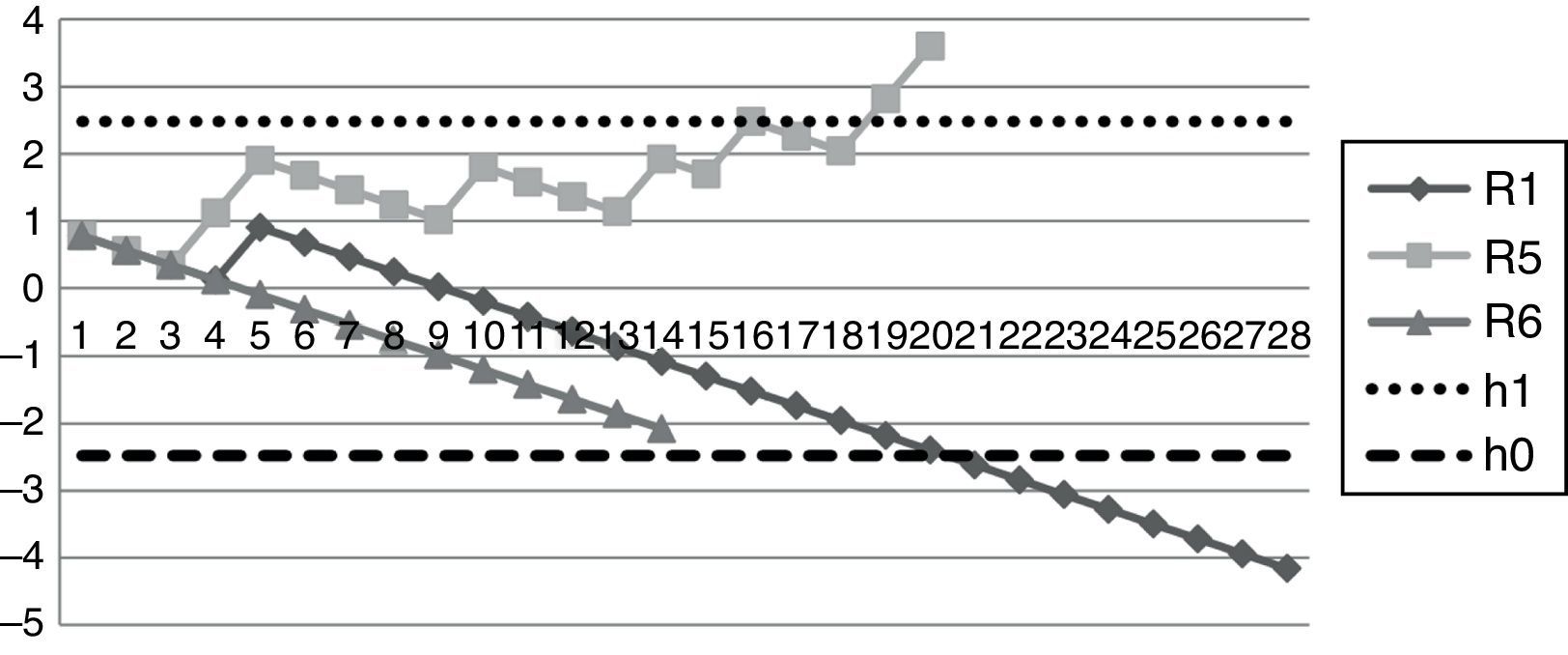
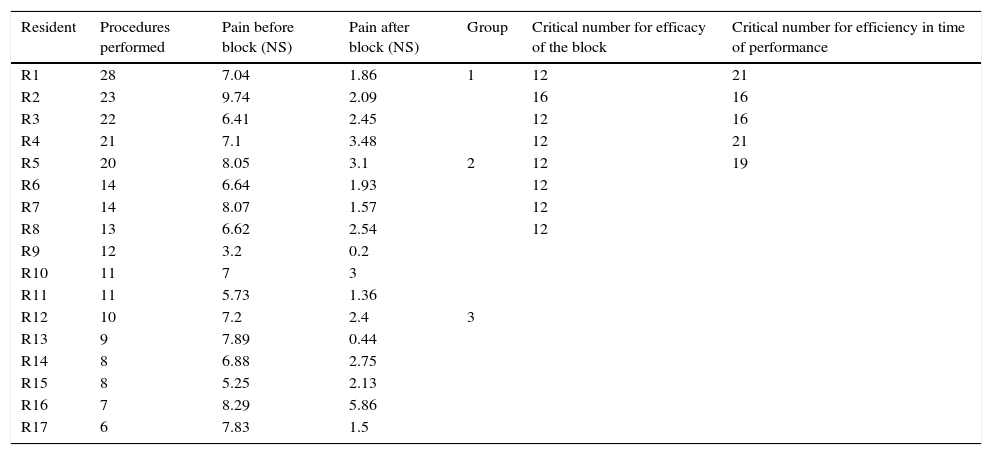
ResultsWe analyze data from 17 AR for a total of 237 ultrasound-guided continuous femoral nerve blocks. 8/17 AR became proficient for pain relief, however all the AR who did more than 12 blocks (8/8) became proficient. As for time of performance 5/17 of AR achieved the objective of 12min, however all the AR who did more than 20 blocks (4/4) achieved it.
ConclusionsThe number of procedures needed to achieve proficiency seems to be 12, however it takes more procedures to reduce performance time. The CUSUM methodology could be useful in training programmes to allow early interventions in case of repeated failures, and develop competence-based curriculum.
Aunque la ecografía es una competencia básica de los residentes de anestesia (RA) hay pocos datos disponibles sobre su proceso de aprendizaje. Este estudio prospectivo observacional tiene como objetivo evaluar el proceso de aprendizaje del bloqueo del nervio femoral continuo guiado por ecografía y determinar el número de procedimientos necesarios que un RA debe realizar para ser exitoso, utilizando el método de suma acumulada (CUSUM).
MétodoReclutamos 19 RA sin experiencia previa. Construimos las curvas de aprendizaje utilizando la metodología CUSUM para el bloqueo del nervio femoral continuo guiado por ecografía considerando 2 criterios de éxito: disminución del dolor>2 puntos en una escala numérica [0-10] tras 15min y el tiempo necesario para realizar la técnica.
ResultadosAnalizamos los datos de 17 RA, que realizaron un total de 237 bloqueos del nervio femoral continuo guiados por ecografía. Ocho de 17 RA tuvieron éxito en cuanto a la disminución del dolor, y asimismo aquellos RA que realizaron>12 bloqueos (8/8) lo consiguieron. En cuanto al tiempo de realización, 5/17 RA alcanzaron el objetivo en 12min; y todos los RA que realizaron>20 procedimientos (4/4) lo alcanzaron.
ConclusionesEl número de procedimientos necesarios para alcanzar el éxito parece ser 12, sin embargo es necesario realizar un número mayor para reducir el tiempo de realización del mismo. La metodología CUSUM podría ser útil en programas de formación, permitiendo intervenciones precoces en casos de fallos repetidos, y realizar un currículo basado principalmente en las competencias.