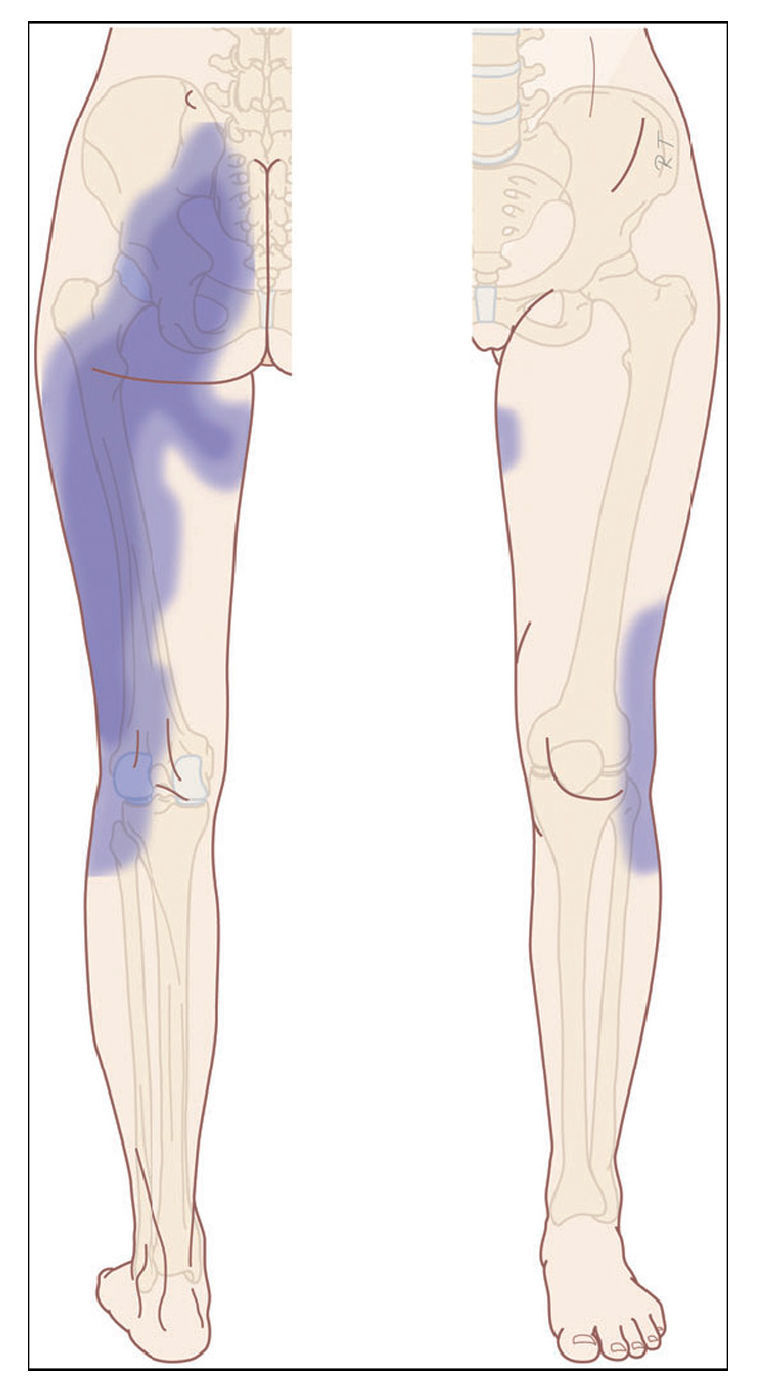
To compare the analgesic effects between the blockade and bipolar thermal radiofrequency in the treatment of sacroiliac joint pain.
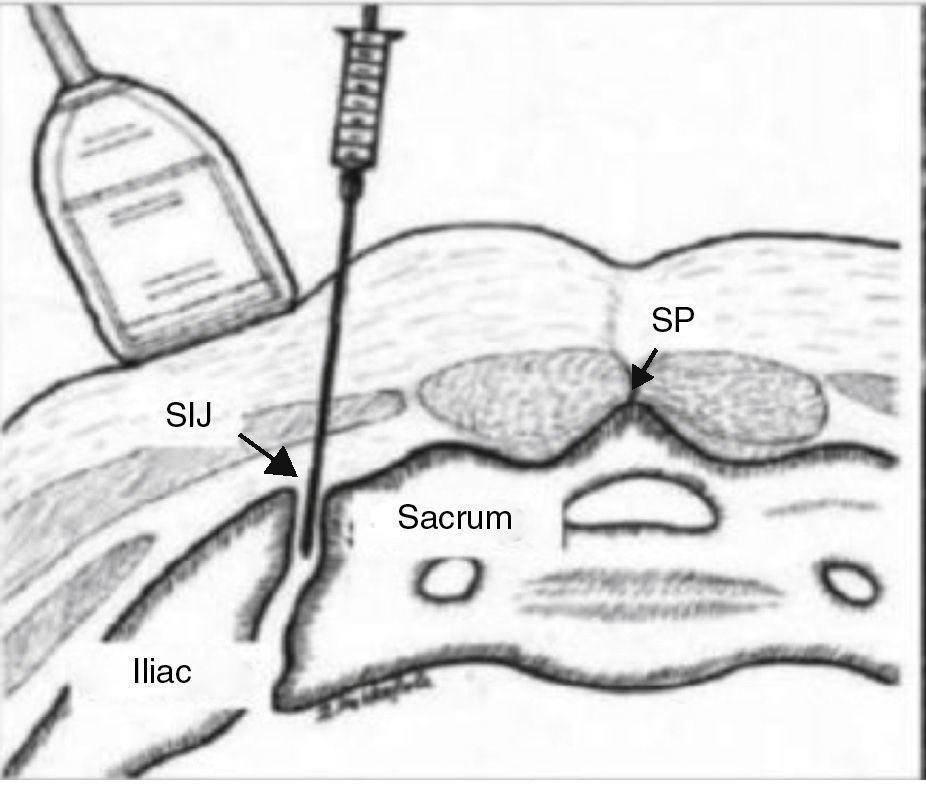
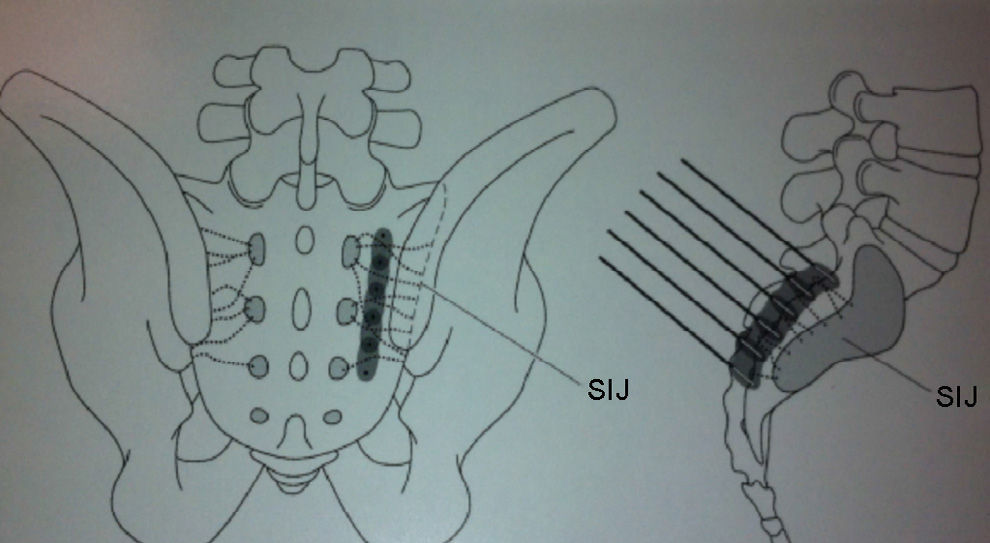
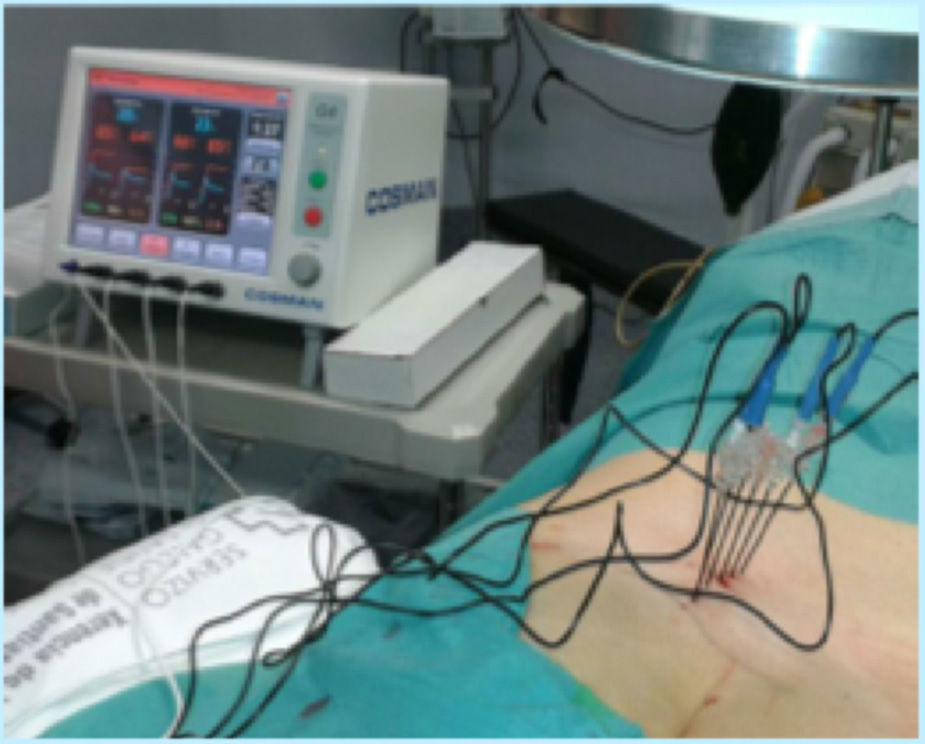
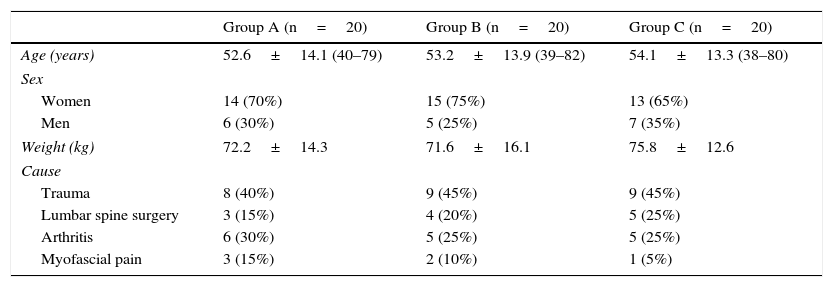
MethodProspective, randomised and experimental study conducted on 60 patients selected in the two hospitals over a period of nine months, who had intense sacroiliac joint pain (Visual Analogue Scale [VAS]>6) that lasted more than 3months. Patients were randomised into three groups (n=20): Group A (two intra-articular sacroiliac injections of local anaesthetic/corticosteroid guided by ultrasound in 7days). Group B: conventional bipolar radiofrequency “palisade”. Target points were the lateral branch nerves of S1, S2, and S3, distance needles 1cm. Group C: modified bipolar radiofrequency “palisade” (needle distance >1cm). Patients were evaluated at one month, three months, and one year. Demographic data, VAS reduction, and side effects of the techniques were assessed.
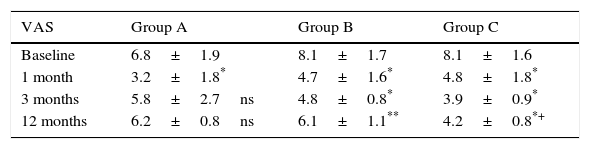
ResultsOne month after the treatment, pain reduction was >50% in the three groups p<.001. Three and 12months after the technique, the patients of the Group A did not have a significant reduction in pain. At 3 months, almost 50% patients of the Group B referred to improvement of the pain (p=.03), and <25% at 12months, and those results were statistically significant (p=.01) compared to the baseline. Group C showed an improvement of 50% at 3 and 12months (p<.001). All patients completed the study.
ConclusionsBipolar radiofrequency “palisade”, especially when the distance between the needles was increased, was more effective and lasted longer, compared to join block and steroids, in relieving pain sacroiliac joint.
Comparar el bloqueo con la radiofrecuencia térmica bipolar para el dolor de la articulación sacroilíaca.
MétodoEstudio prospectivo, aleatorizado y experimental en 60 pacientes, seleccionados en 9 meses en 2 centros, con dolor intenso (escala visual analógica [EVA]>6) de >3meses de duración. Fueron divididos en 3 grupos (n=20). GrupoA: pacientes a los que se les realizaron 2 bloqueos intraarticulares, con control ecográfico en 7 días. GrupoB: radiofrecuencia bipolar «palisade» utilizando 6 agujas perpendiculares a la zona dorsal del sacro, a una distancia de 1cm, para producir lesiones contiguas entre los forámenes S1-S2-S3 y la línea articular. Grupo C: radiofrecuencia bipolar «palisade» modificada (distancia entre agujas >1cm). Los pacientes fueron evaluados al mes, a los 3 y a los 12 meses del tratamiento. Se valoraron los datos demográficos (en la visita basal), la eficacia analgésica y los efectos secundarios (en el resto).
ResultadosAl mes, la reducción del dolor en los 3 grupos fue >50% (p≤0,001). A los 3 y 12meses el grupo A no refirió disminución significativa del dolor. El grupoB, a los 3meses, alivio cercano al 50% (p=0,03), y <25% (23,8) a los 12meses (p=0,01). En el grupo C, alivio próximo al 50% a los 3 y 12 meses (p<0,001) respecto al basal. Todos los pacientes finalizaron el estudio.
ConclusionesLa radiofrecuencia bipolar «palisade», especialmente aumentando la distancia entre las agujas, ha sido eficaz, a más largo plazo, que el bloqueo con anestésicos y corticoides en el alivio del dolor de la articulación sacroilíaca.