To study the relationship between the values of SvcO2 and SrcO2 in lung resection with one lung ventilation (OLV) and changes in these variables and mean arterial pressure (MAP) and arterial oxygen saturation (SpO2) during the perioperative period.
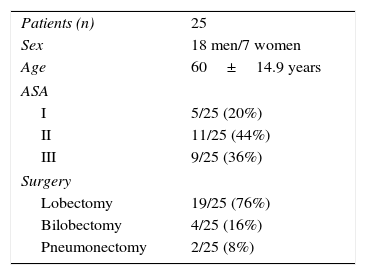
Material and methodsProspective, observational study of 25 patients in whom pulmonary resection was performed with OLV. The values of MAP, SpO2, SvO2, and SrcO2 were recorded at 6 different times: (1) baseline; (2) double-lung ventilation before the OLV (VBP1); (3) during OLV; (4) after double-lung ventilation (VBP2); (5) 30min after surgery, and (6) 6h after surgery.
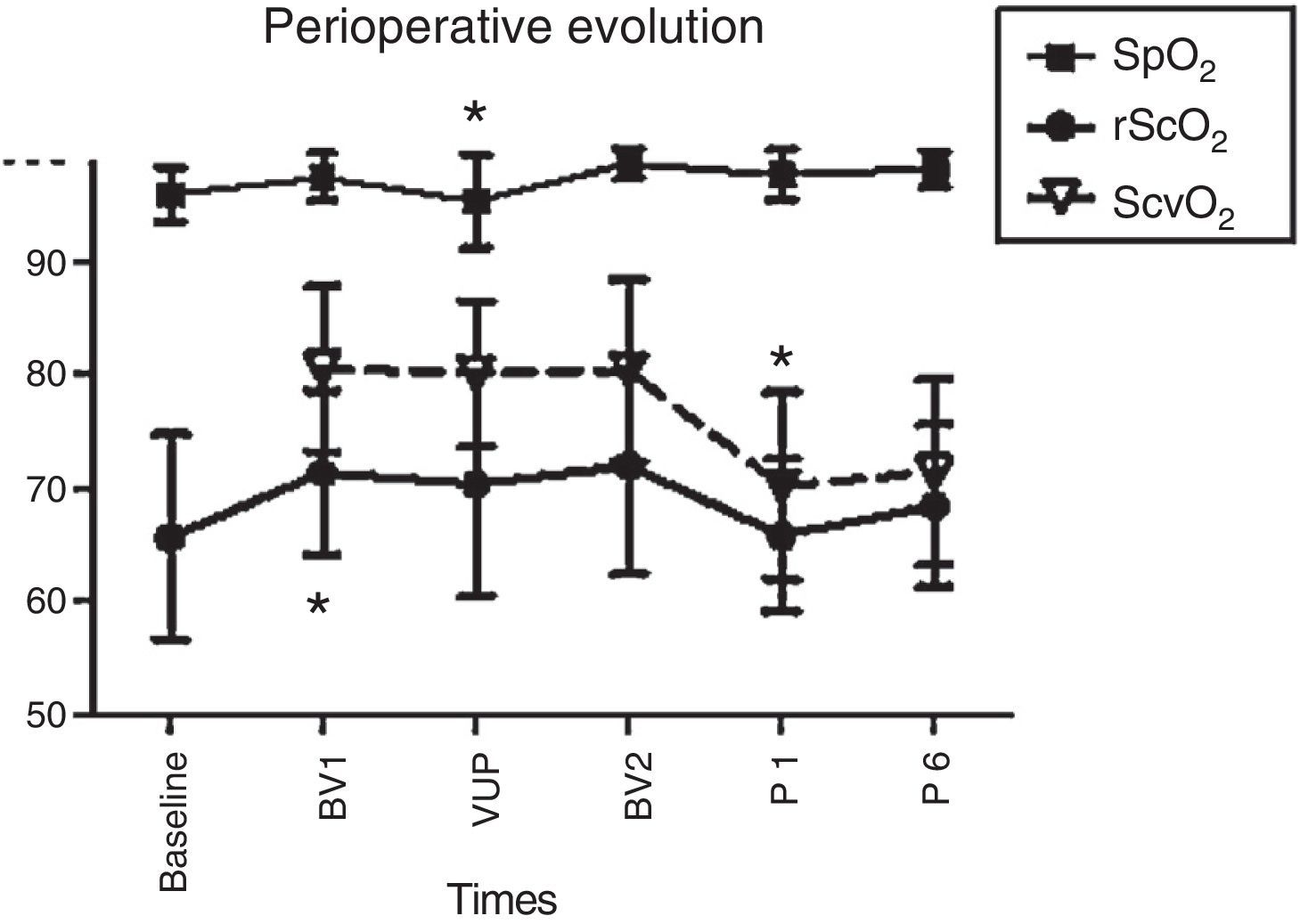
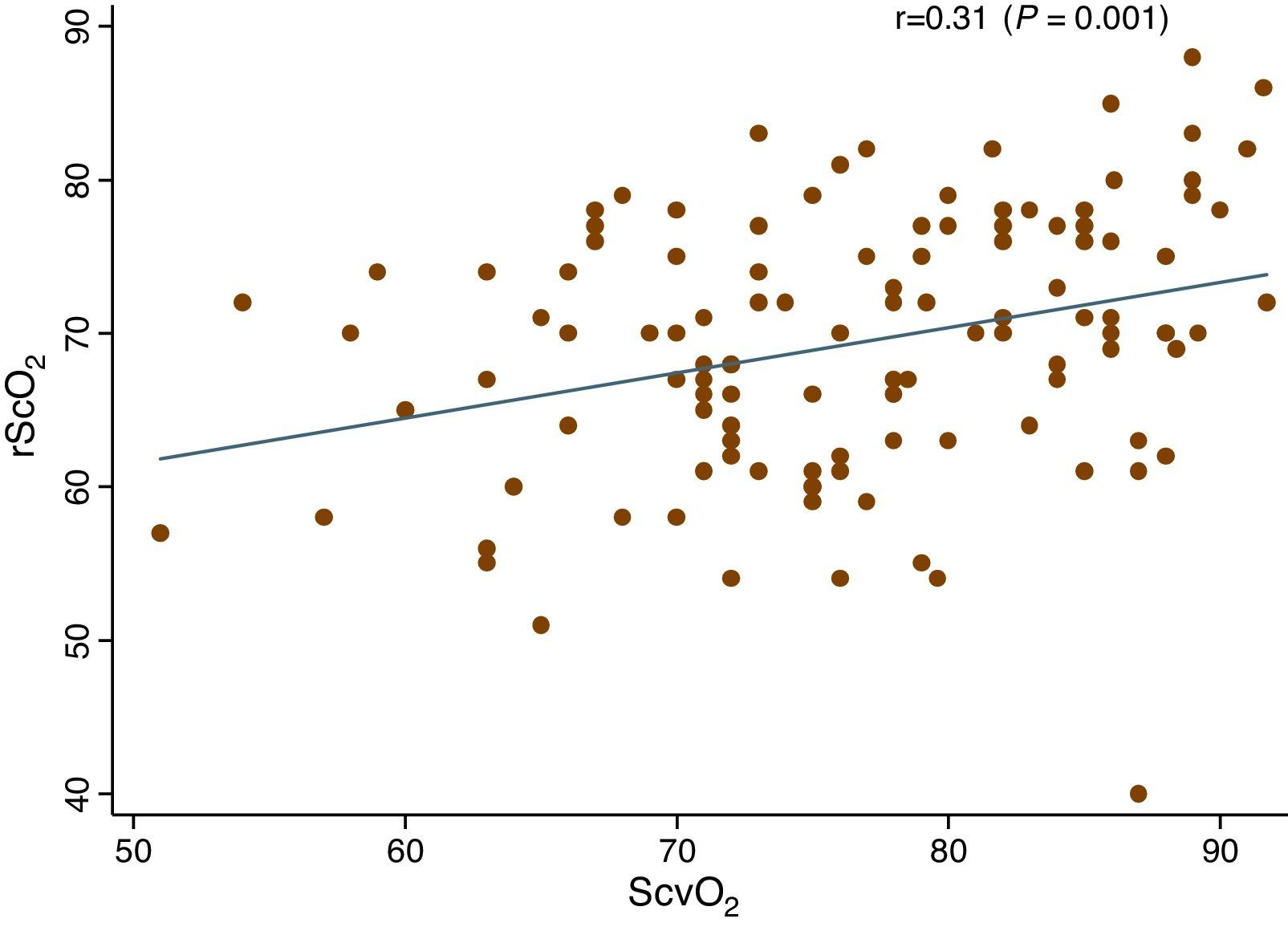
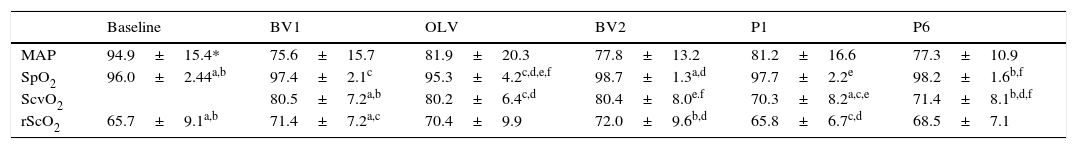
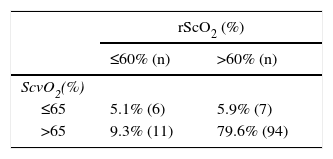
ResultsThe SrcO2 showed a significant increase from baseline to starting ventilation (65.72±9.05% vs 70.44±7.24%; p<.01). There were no significant changes in their values at the different intraoperative times. Post-operatively, as in the case of the SvcO2, a significant decrease (p<.001) of its value compared with the previous value was observed.
ConclusionsSrcO2 showed a significant increase after induction of anaesthesia and initiation of mechanical ventilation compared to baseline, and a significant decrease at the end of surgery after extubation in the immediate postoperative period. Being a tissue monitoring, non-invasive technique and with continuous values it can alert the clinician of changes in the ratio of oxygen consumption (VO2) to oxygen delivery (DO2) at times of greatest risk, such as OLV, extubation, and the early postoperative period.
Estudiar la relación existente entre los valores de SvcO2 y de SrcO2 en la resección pulmonar con ventilación unipulmonar (VUP) y los cambios de dichas variables y de la presión arterial media (PAM) y la saturación arterial de oxígeno (SpO2) durante el periodo perioperatorio.
Material y métodosEstudio prospectivo observacional en 25 pacientes en quienes se realizó una resección pulmonar con VUP. Los valores de PAM, SpO2, SvcO2 y SrcO2 se registraron en 6 momentos diferentes: 1) basal; 2) en ventilación bipulmonar antes de la VUP (VBP1); 3) durante la VUP; 4) en ventilación bipulmonar después de la VUP (VBP2); 5) en los primeros 30min del postoperatorio, y 6) a las 6h de postoperatorio.
ResultadosLa SrcO2 mostró un aumento significativo desde su valour basal al iniciar la ventilación (65,72±9,05% vs 70,44±7,24%; p<0,01). No hubo cambios significativos en sus valores en los diferentes momentos intraoperatorios. En el postoperatorio, al igual que en el caso de la SvcO2, se observó una disminución significativa (p<0,001) de su valour en comparación con el valour previo.
ConclusionesLa SrcO2 experimenta un aumento significativo tras la inducción de la anestesia e inicio de la ventilación mecánica respecto al valour basal y un descenso significativo al final de la cirugía, tras la extubación en el postoperatorio inmediato. Al tratarse de una monitorización tisular, no invasiva y continua, advierte al clínico de cambios en la relación DO2/VO2 en momentos de mayor riesgo como la VUP, la extubación y el periodo postoperatorio inmediato.